Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Build a Dynamic React App with Live Data Using CData API Server
React is a fast, flexible, and widely adopted JavaScript library for building dynamic, interactive user interfaces. Combined with the CData API Server, which supports 270+ on-premises and cloud-based data sources, you can effortlessly create REST APIs that connect your app to live data — enabling real-time, responsive web applications.
This guide walks you through setting up the CData API Server to create a REST API for a SQLite database and building a lightweight React web app that fetches and displays live data from the API. The app dynamically generates an interactive, customizable table based on the database content. While key steps and code snippets are included, you can also download the complete React project and SQLite sample database below to dive into the full source code and explore the functionality yourself.
Let's begin!
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to run the React project.
Note: This guide assumes you're already familiar with React.js and have Node.js installed on your machine, and you're using a text editor or an IDE, such as VSCode.
- CData API Server. Get a free trial here.
- Sample React project with SQLite database to follow along with. Download it here.
Overview
Here's an overview of the steps we'll follow:
- Install and Connect: Set up the CData API Server and configure a connection to your data source.
- Build and Develop: Create the React app, fetch data from API endpoints, and render it dynamically.
- Run and Test: Run the app, test functionality, and interact with the data.
Step 1: Install, Connect, and Configure CData API Server
1.1. Install the CData API Server
- For Windows: Run the .exe installer and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup.
- For Other Platforms: Download and install the Cross-Platform (Java) version for Mac and Linux.
-
For Cloud Deployment:
- AWS: Deploy the pre-configured Amazon Machine Image (AMI) to set up your API server quickly.
- Azure: Deploy directly through the Microsoft Azure Marketplace for a streamlined setup.
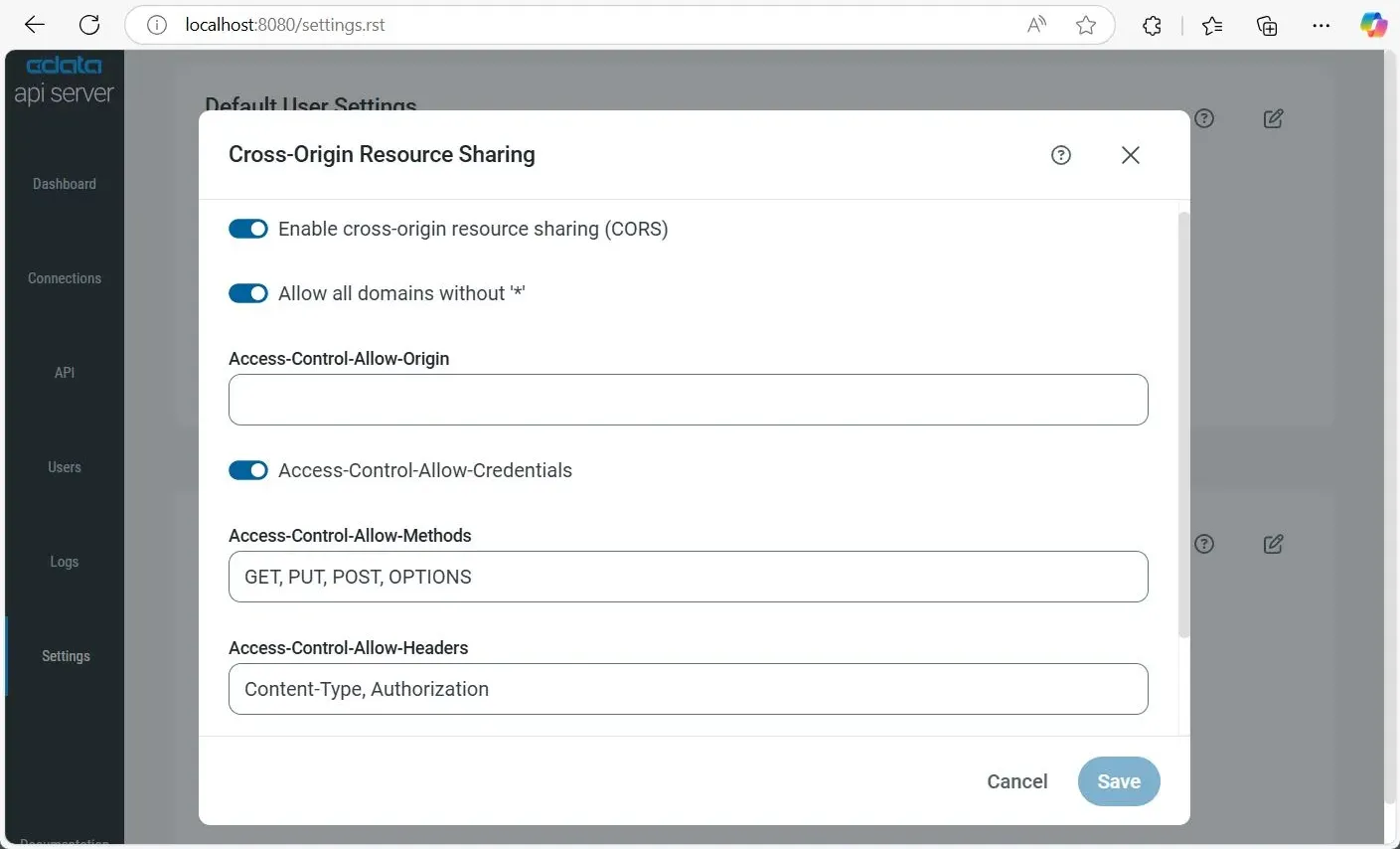
1.2. Enable CORS
When a React web app and API server operate on different domains, cross-domain requests are generated. To ensure these cross-domain requests are processed successfully, CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) should be enabled on the API Server. This can be configured in from the SETTINGS page.
- Go to Settings on the left and click the icon to edit CORS settings.
- Toggle on Enable Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS).
- Toggle on Allow all domains without '*' to allow any origin sent by the client.
- In Access-Control-Allow-Origin, enter your app's origin (e.g., https://localhost:3001) or enter * to allow all incoming requests for public APIs.
- Enable Access-Control-Allow-Credentials to allow client credentials (e.g., cookies, HTTP authentication).
- In Access-Control-Allow-Methods, enter GET, PUT, POST, OPTIONS to define allowed request methods.
- In Access-Control-Allow-Headers, enter Authorization, Content-Type to specify allowed headers.
- Set Access-Control-Max-Age in seconds (default: 3600 seconds) to cache preflight requests.
- Click Save.
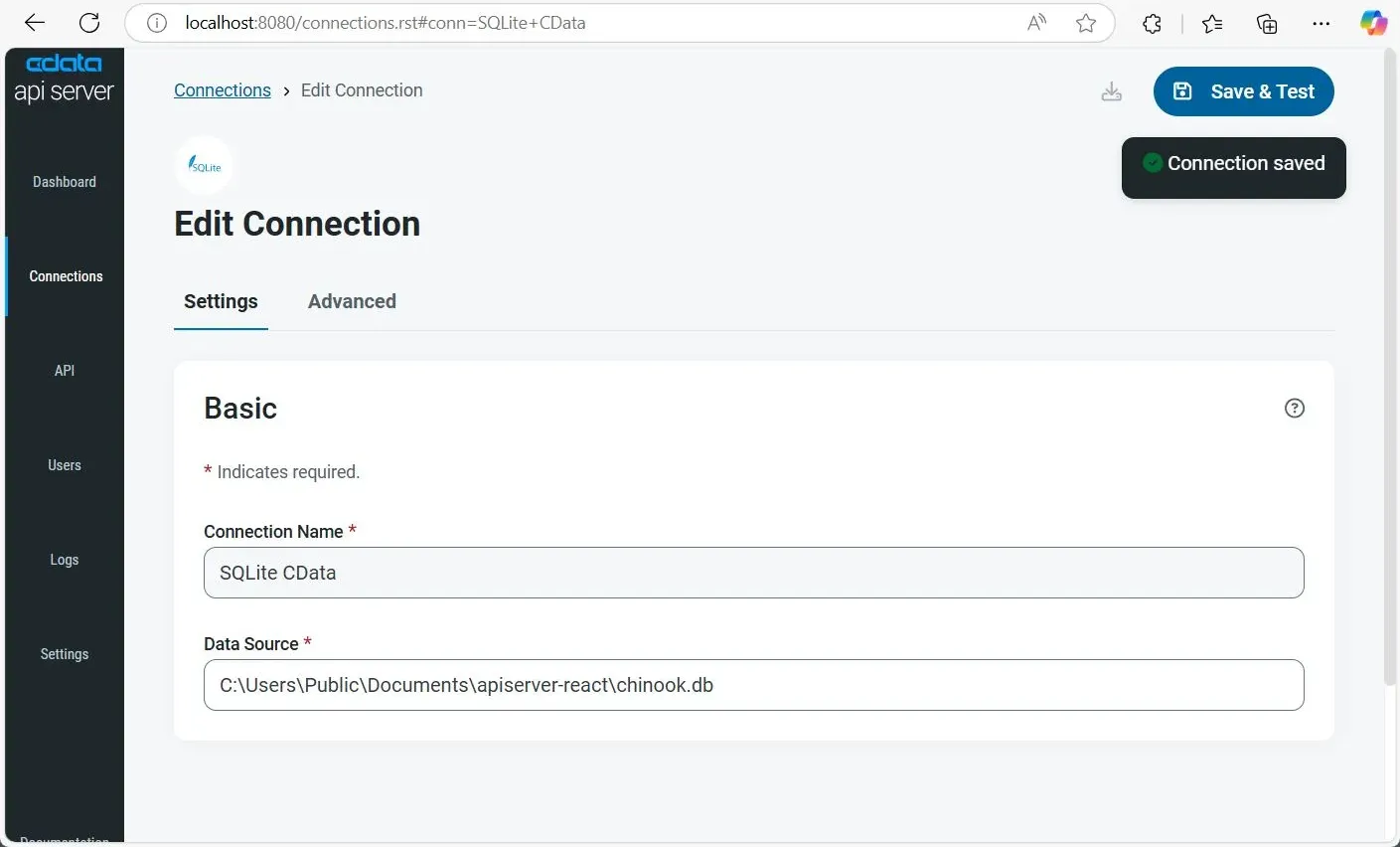
1.3. Add a Connection
- Go to Settings on the left and click on Add Connection in the top-right.
- Select a connector from the list. If your connector isn't installed, toggle off Only Installed to view all available connectors.
- Click the Install Connector icon () to download and install it automatically. For manual installation, select Manual Install and upload the provided ZIP file.
- After installation, click the connector again to open Configure Connection.
- Note: For this example, we'll use the SQLite connection, but this setup works for all the 270+ connectors that CData API Server supports.
- Select SQLite and configure the connection in the dialog box:
- Connection Name: Enter a descriptive name for your connection.
- Database Source: Enter the full path of the sample chinook.db SQLite database file included in the project ZIP. For example: C:\Users\Public\Downloads\apiserver-react\chinook.db
- Click Save & Test to validate the connection and complete the setup.
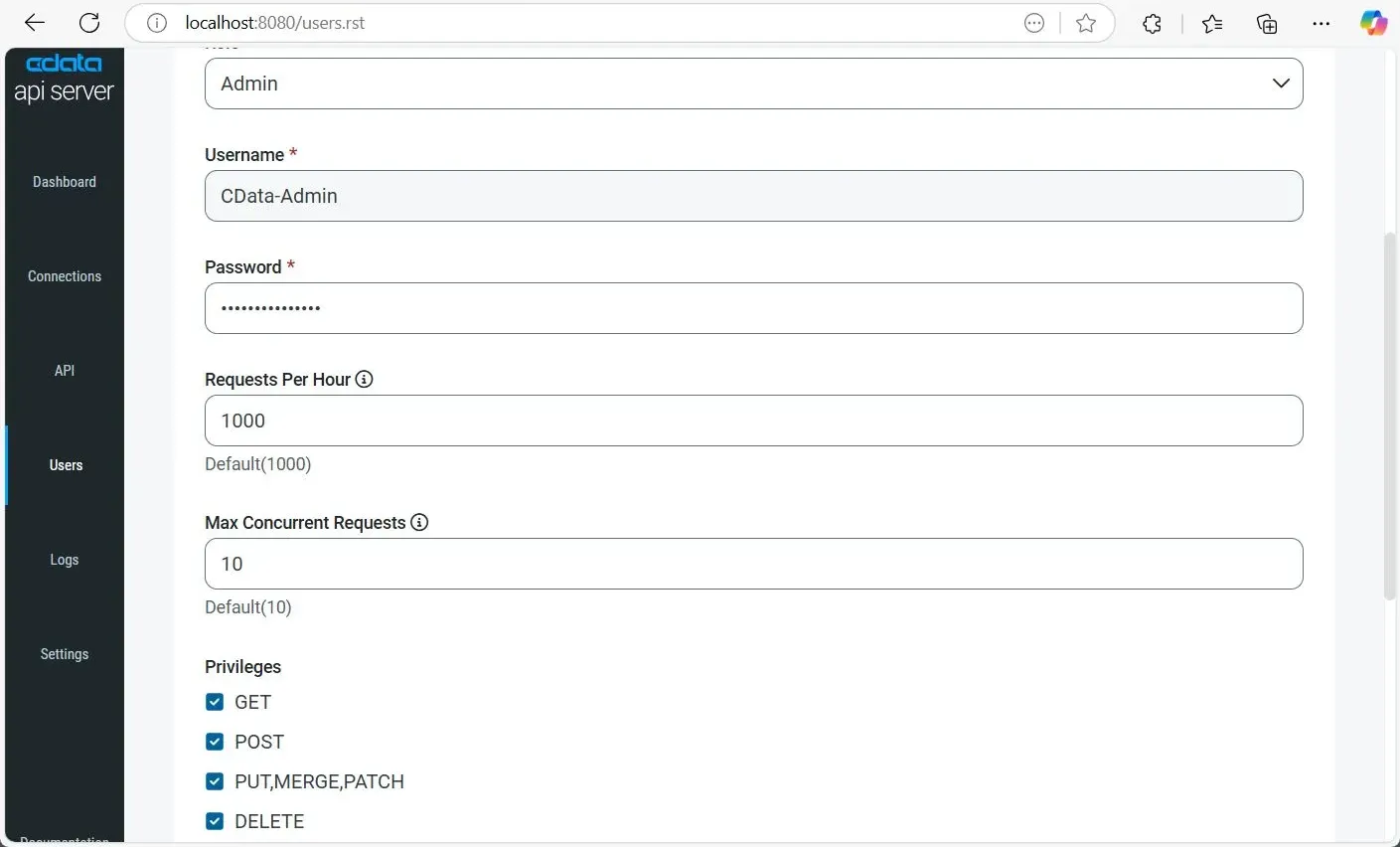
1.4. Add and Configure a User
Create a user to access API Server data:
- Go to Users on the left, then click + Add User in the top-right.
- Enter a Username and a secure Password for the user to login.
- Choose a Role:
- Admin: Full control.
- Query: Data access only.
- (Optional) Set limits:
- Requests Per Hour: Default 1000.
- Max Concurrent Requests: Default 10.
- Set Privileges:
- GET: Read data.
- POST: Create records.
- PUT, MERGE, PATCH: Update data.
- DELETE: Remove data.
- Click Add User to finish.
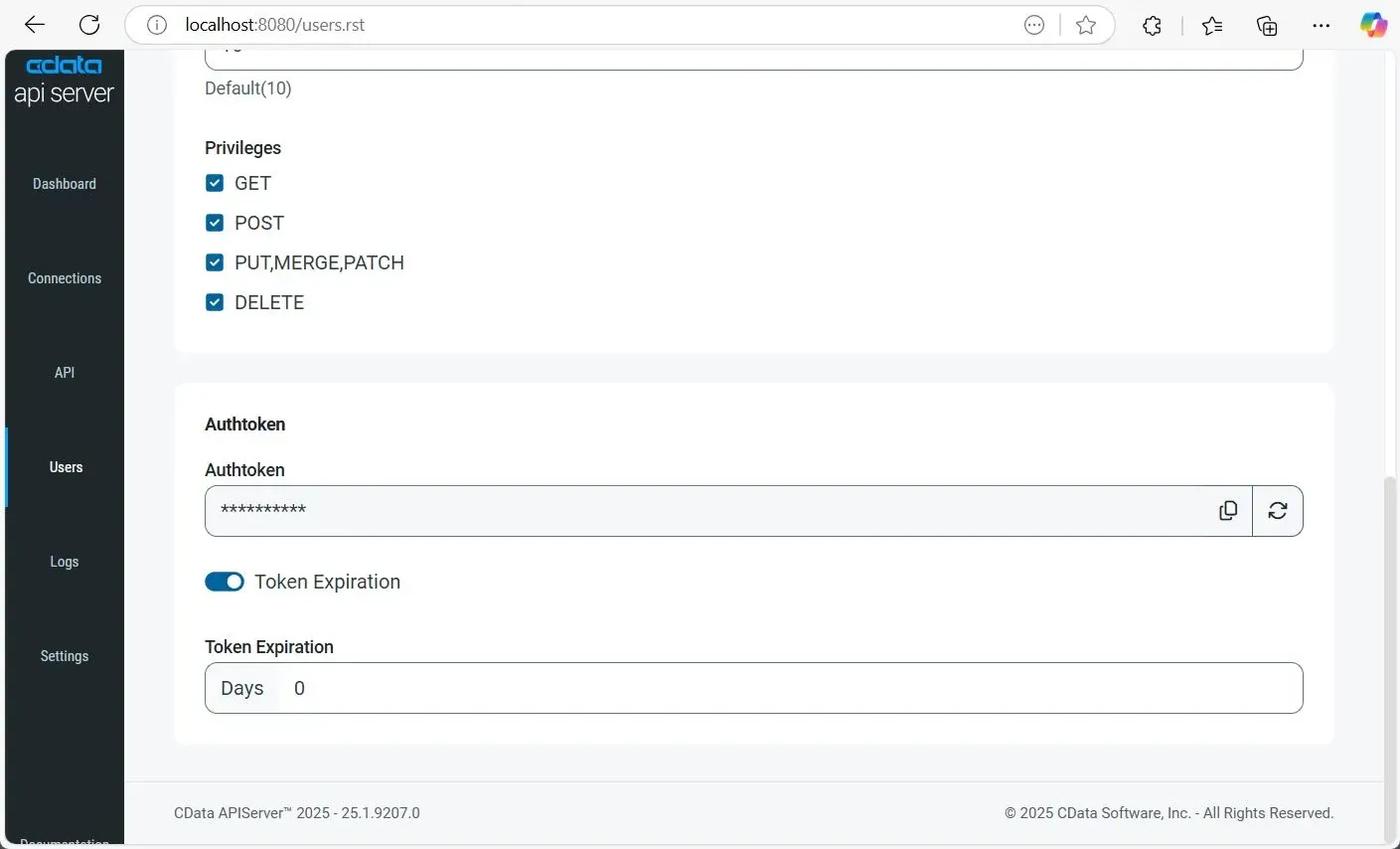
Once a user is added, an Authtoken is generated. You can log in using this Authtoken along with the Username if a password isn't applicable. You can also refresh the Authtoken and set it to expire after a specific number of days by toggling the Token Expiration option.
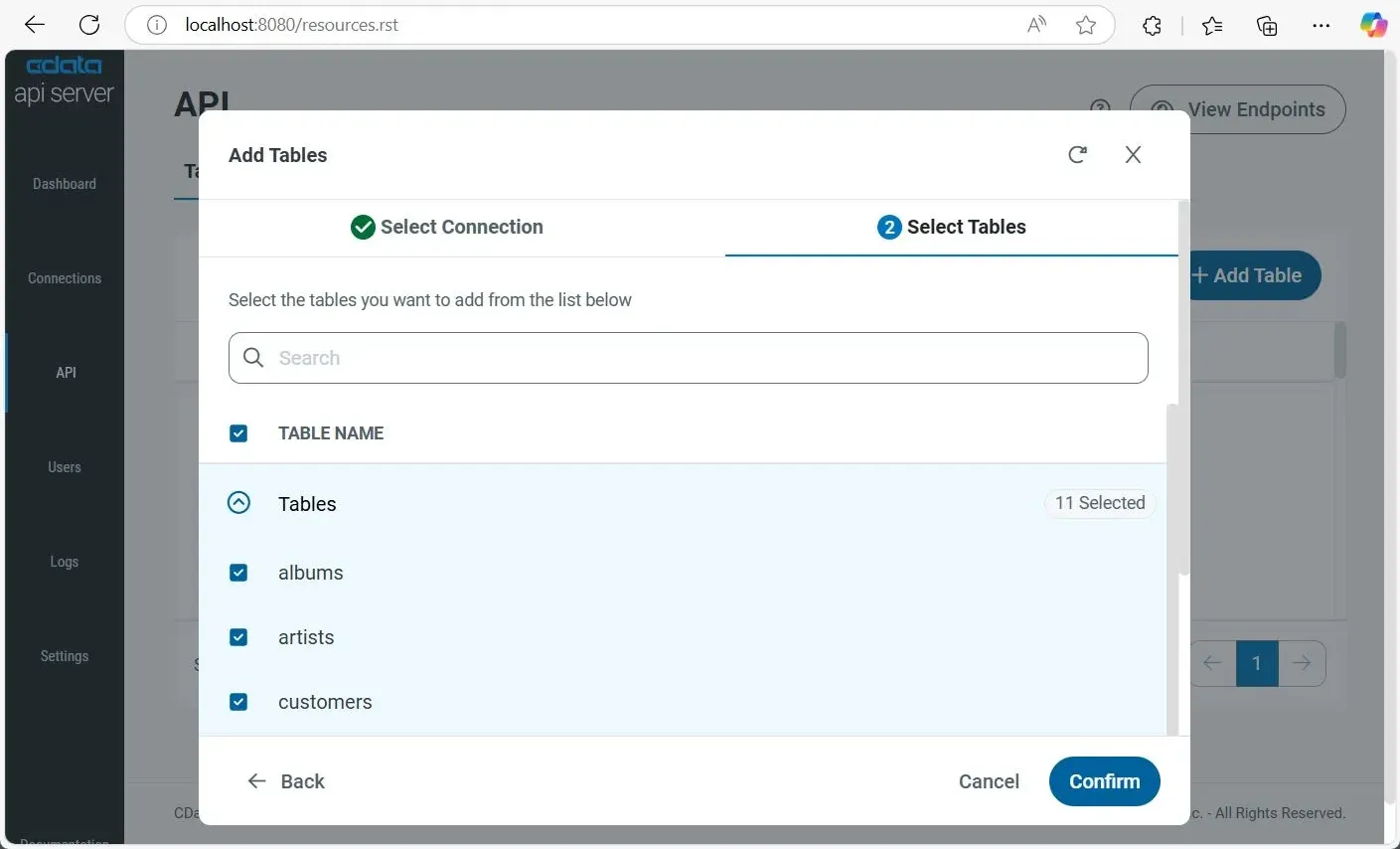
1.5. Add Tables for the Endpoint
To enable access to database tables through the API endpoints, add tables from your connection:
- Go to API on the left, then click the Add Table button on the top-right.
- Select your connection, then click Next.
- Select tables by toggling-down Tables, or click the top checkbox to select all, then click Confirm to add them.
1.6. Access Endpoints for the REST API
After setting everything up, you now have a fully accessible REST API (OData protocol). Use the endpoint URLs below:
| Table | URL | |
|---|---|---|
| Entity (table) List | http://address:port/api.rsc/ | |
| Metadata for table albums | http://address:port/api.rsc/albums/$metadata?@json | |
| Albums data | http://address:port/api.rsc/albums |
To limit returned fields, add $select, $filter, $orderby, $skip, and $top parameters.
Step 2: Build and Develop the React App
Now that the CData API Server is configured and serving live data endpoints, it's time to build the >React app. This app will let users interact with your data dynamically — allowing them to select available tables and view live data instantly. Here's how to do it:
2.1. Set Up the React App
Let's start by setting up the React app from scratch using a manual Webpack and Babel configuration. This gives you more control over the build process and keeps the project lightweight.
- Create a project folder and open a terminal inside it (e.g., ~/Downloads/CData-Python-CSV).
- Initialize a new project: npm init -y.
- Install core dependencies: npm install react react-dom axios.
- Install development tools: npm install --save-dev webpack webpack-cli webpack-dev-server @babel/core @babel/preset-env @babel/preset-react babel-loader html-webpack-plugin
2.2. Create the Core App Component
Now, let's build the main App.jsx component that powers the app. This component will fetch data from the API and display it in a table. Here's how to do it:
Create a folder named src in your project directory, then create a new file named App.jsx in that folder as src/App.jsx. Define the component as shown below:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import axios from "axios";
// Clean URL utility
const cleanUrl = (base, endpoint = "") => `${base.replace(/\/+$/, "")}/${endpoint.replace(/^\/+/, "")}`;
const App = ({ user, pass, baseUrl }) => {
const [tables, setTables] = useState([]);
const [columns, setColumns] = useState([]);
const [selectedTable, setSelectedTable] = useState("");
const [selectedColumns, setSelectedColumns] = useState([]);
const [tableData, setTableData] = useState([]);
// Set authentication header
axios.defaults.headers.authorization = "Basic " + btoa(`${user}:${pass}`);
// Fetch utility function
const fetchData = (url, callback) =>
axios.get(url).then((res) => callback(res.data)).catch((err) => alert(`Error: ${err.response?.status || "Network error"}`));
// Fetch tables on load
useEffect(() => {
fetchData(cleanUrl(baseUrl), (data) => {
setTables(data.value);
setSelectedTable(data.value[0]?.name || "");
});
}, [baseUrl]);
// Fetch columns when a table is selected
useEffect(() => {
if (selectedTable) {
fetchData(cleanUrl(baseUrl, `${selectedTable}/$metadata?@json`), (data) =>
setColumns(data.items[0]["odata:cname"] || [])
);
}
}, [selectedTable]);
// Fetch data based on selected columns
const handleFetchData = () => {
if (selectedColumns.length) {
fetchData(cleanUrl(baseUrl, `${selectedTable}/?$select=${selectedColumns.join(",")}`), (data) => setTableData(data.value));
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: "center", fontFamily: "Arial", padding: "20px" }}>
<h1>CData API Server React Demo</h1>
{/* Table Selector */}
<label>Select a Table:</label>
<select value={selectedTable} onChange={(e) => setSelectedTable(e.target.value)}>
{tables.map((table) => (
<option key={table.url} value={table.name}>
{table.name}
</option>
))}
</select>
{/* Column Selector */}
<div style={{ margin: "10px 0" }}>
<label>Select Columns:</label>
{columns.length ? (
columns.map((col) => (
<label key={col} style={{ display: "block" }}>
<input
type="checkbox"
value={col}
onChange={(e) =>
setSelectedColumns((prev) => (e.target.checked ? [...prev, col] : prev.filter((c) => c !== col)))
}
/>
{col}
</label>
))
) : (
<p>No columns found.</p>
)}
</div>
{/* Fetch Data Button */}
<button onClick={handleFetchData} disabled={!selectedColumns.length}>
Get Data
</button>
{/* Render Data Table */}
{tableData.length > 0 && (
<table border="1" style={{ marginTop: "10px", width: "100%", borderCollapse: "collapse" }}>
<thead>
<tr>{selectedColumns.map((col) => <th key={col}>{col}</th>)}</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{tableData.map((row, index) => (
<tr key={index}>
{selectedColumns.map((col) => (
<td key={col}>{row[col] ?? "N/A"}</td>
))}
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
)}
</div>
);
};
export default App;
2.3. Configure App Entry
Create a new file main.js inside the src folder as src/main.js. This file will serve as the app's entry point and will initialize the app. Use the foll owing code and replace your_username and your_password with your CData API Server credentials.
// src/main.js
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import App from "./App.jsx";
// Set API credentials and base URL
const user = "your_username";
const pass = "your_password";
const baseUrl = "http://localhost:8080/api.rsc/";
// Render the app
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
root.render(<App baseUrl={baseUrl} user={user} pass={pass} />);
This script defines the entry point for the app. It imports React, grabs the root HTML element, and renders the App.jsx component while passing user credentials and API details as props.
2.4. Set Up Webpack Configuration
Create a webpack.config.js file in the project root folder. This file configures Webpack to build the app. Use the following code:
// webpack.config.js
const path = require("path");
module.exports = {
entry: "./src/main.js", // Entry point for the app
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "public"),
filename: "index.js", // Output bundle file
},
devServer: {
static: path.resolve(__dirname, "public"),
port: 3001, // Port updated to avoid conflict with CData API Server
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.jsx?$/, // Handle both .js and .jsx files
loader: "babel-loader",
exclude: /node_modules/,
options: {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react"],
},
},
],
},
};
This configuration specifies the entry point for the app, the output bundle file, and the port for the development server. It also sets up Babel to transpile JSX (JavaScript XML) to JavaScript.
2.5. Create a Basic HTML Page
Create a public folder inside your project folder and create a new file index.html inside it as public/index.html. Use the following code:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>CData React App</title> </head> <body> <div id="root"></div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
This file sets up a basic HTML structure. The <div id="root"> acts as a container where the React app renders dynamically. The index.js file — generated by Webpack — ensures the app loads and runs as soon as the page loads in the browser.
Step 3: Run and Test the App
Now that the app is set up and built, it's time to run it locally and test it. Follow these steps:
3.1. Run the Built App
- Open your terminal and navigate to the project folder.
- Run npm start.
- Open http://localhost:3001 in your browser.
- Select a table and see live data from the CData API Server rendered instantly.
Note: The port number for the app is updated to 3001 to avoid conflicts with the CData API Server, which uses port 8080 by default. You can change this port in the webpack.config.js file if needed.
3.2. Run the Sample App
The sample app has better structure and is already configured to work with the CData API Server. To run it, follow these steps:
- Download and extract the sample app from here.
- Open a terminal and navigate to the extracted folder.
- Run npm install to install dependencies.
- Replace the API credentials in src/main.js with your own CData API Server credentials.
- Run npm start to start the app.
- Open http://localhost:3001 in your browser and test the app.
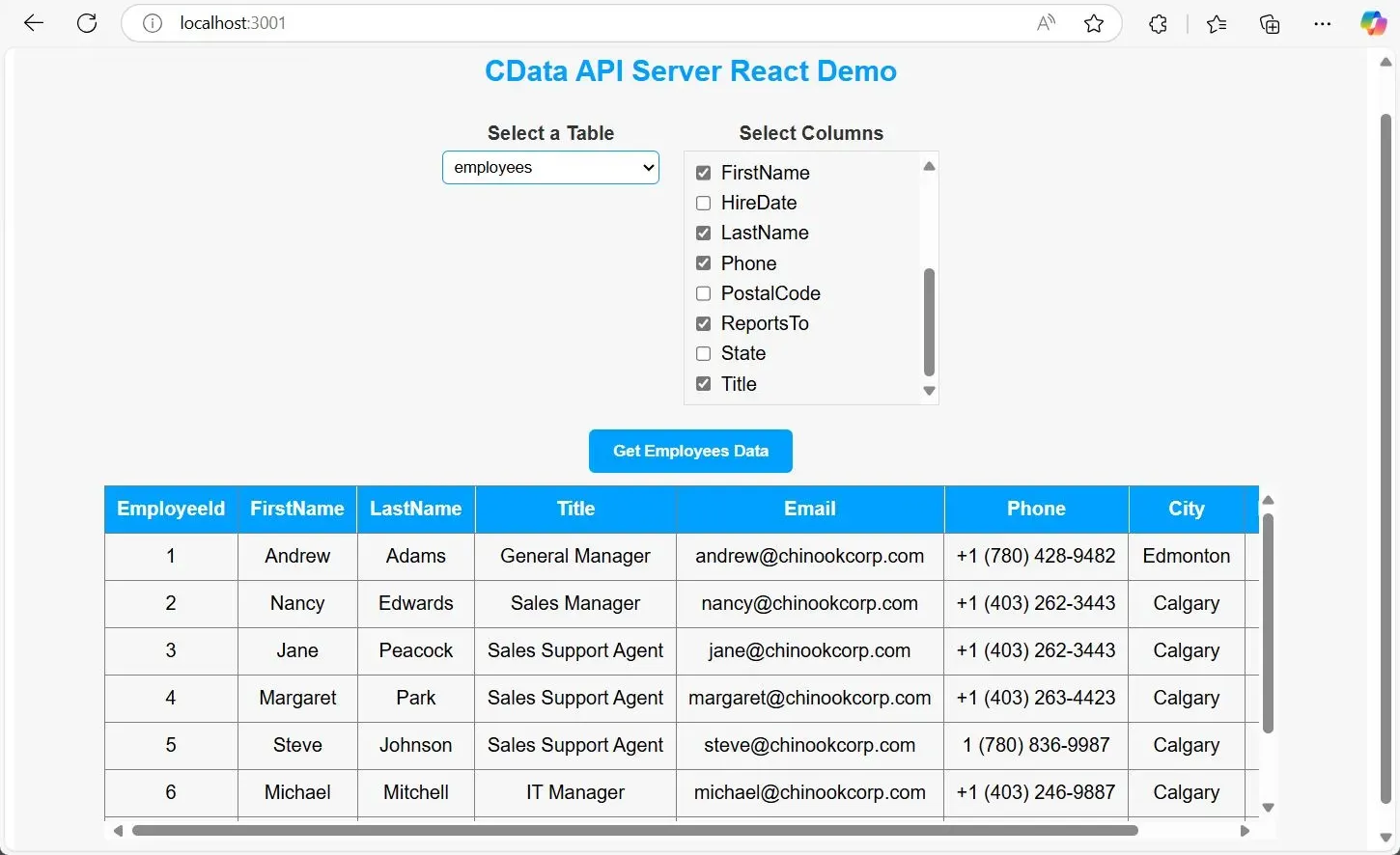
3.3. Test the App Functionality
Open your running app in the browser. Ensure the tables load from the API Server, select a table, and verify that data renders correctly. The app should now be fully functional and ready for further customization if needed.
Conclusion: Go Beyond the Basics
You've built a complete React app that connects to live data via CData API Server, pulls tables, and displays data dynamically. This setup can easily scale to handle more data sources, larger datasets, and additional UI features like sorting or pagination.
To deploy, build the production version with npm run build and host it on platforms like Netlify, Vercel, or your own server. Ensure your API Server instance is accessible and update the API base URL in src/main.js to point to your server's public URL.
A CData API Server license, configured for your deployment machine, is required for production. You can check for available licenses and get a quote here.
Ready to explore more? Start a free trial of CData API Server and unlock endless possibilities to expand your app's capabilities — whether you're integrating databases, SaaS data, or custom APIs.


