Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →CData Sync - Change Tracking in Dynamics 365 Entities for CDC Replication
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a powerful suite of business applications that unifies CRM and ERP capabilities to help organizations streamline operations, improve customer engagement, and drive growth. When replicating data from Dynamics 365 to databases like SQL Server, especially for Change Data Capture (CDC) scenarios, enabling the Change Tracking feature on entities is essential to ensure only incremental changes are synced.
However, manually enabling Change Tracking across multiple entities can be tedious and error-prone. This is where CData Sync comes in. It simplifies the process by automatically enabling Change Tracking on Dynamics 365 entities during replication, eliminating the need for manual configuration and significantly reducing setup time and complexity.
In this article, we'll explore how CData Sync streamlines CDC replication from Dynamics 365 by intelligently handling Change Tracking behind the scenes with the assistance of stored procedures.
Creating entities in Dynamics 365
Entities in Dynamics 365 represent core business data such as contacts, accounts, or custom objects. They are created by defining the schema in the Power Apps Maker portal. This involves setting up primary fields, establishing relationships, and configuring basic settings.
In this section, we will create a custom entity without manually enabling the Change Tracking option so that CData Sync can automatically activate it during the CDC replication process. Follow the steps below to create an entity in Power Apps:
- Log in to your Microsoft Dynamics 365 account.
- Navigate to Settings in the Dynamics 365 Power Platform Environment Settings and select Advanced Settings.
- Go to Customizations from the left panel and select Customize the system.
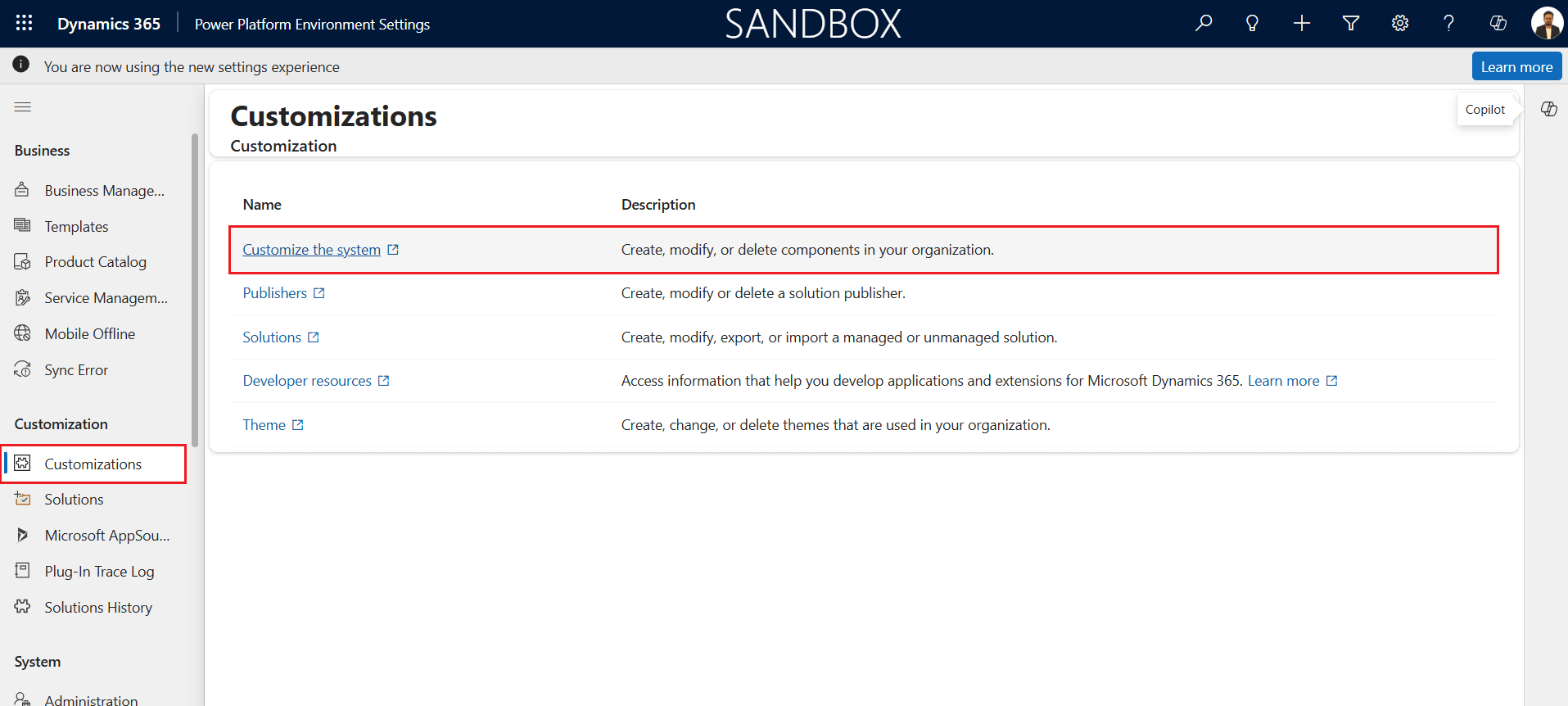
- Under Components, select Entities and click New.
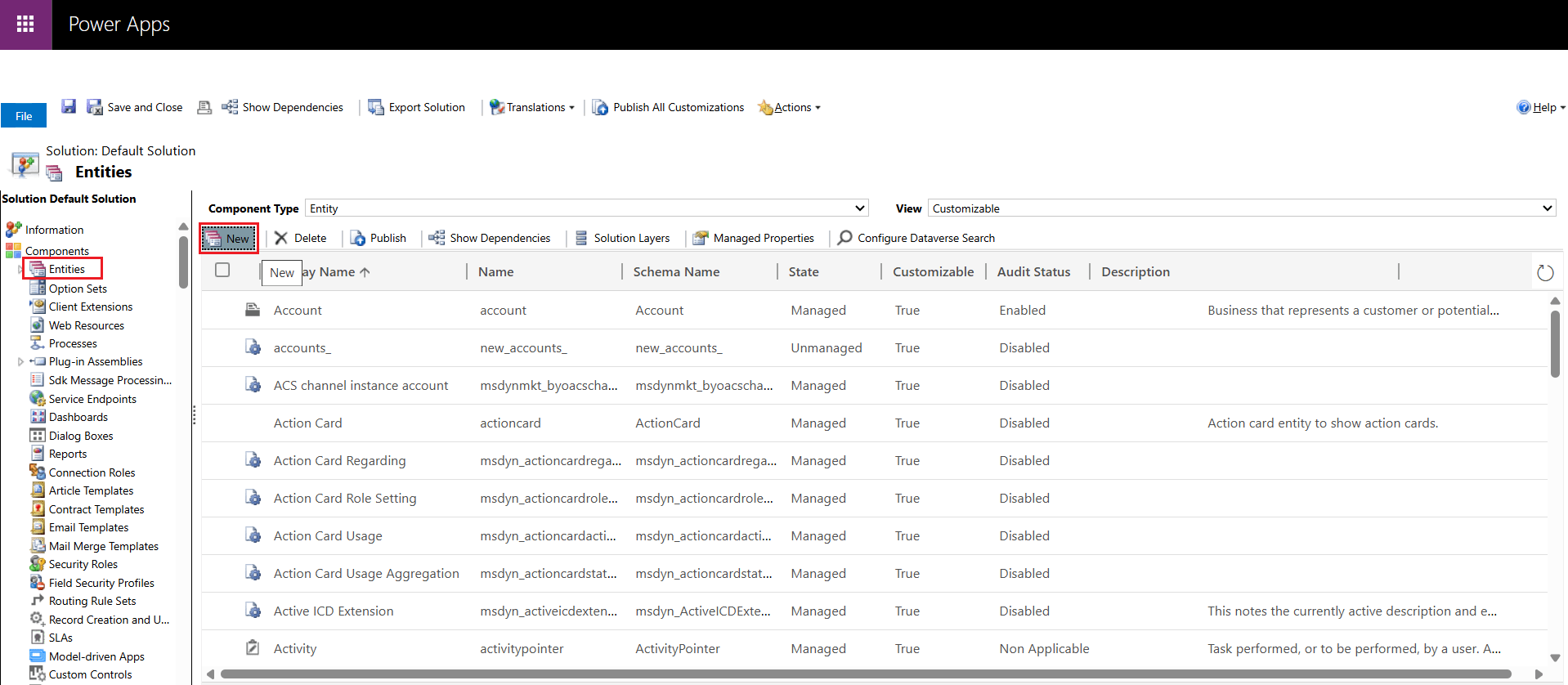
- In the General tab, fill out the necessary information under Entity Definition, including Display Name, Plural Name, Name, and Ownership. Note that while defining the Name, the "new_" prefix cannot be changed, so your table name will be prefixed accordingly (e.g., 'new_changetrackingtest').
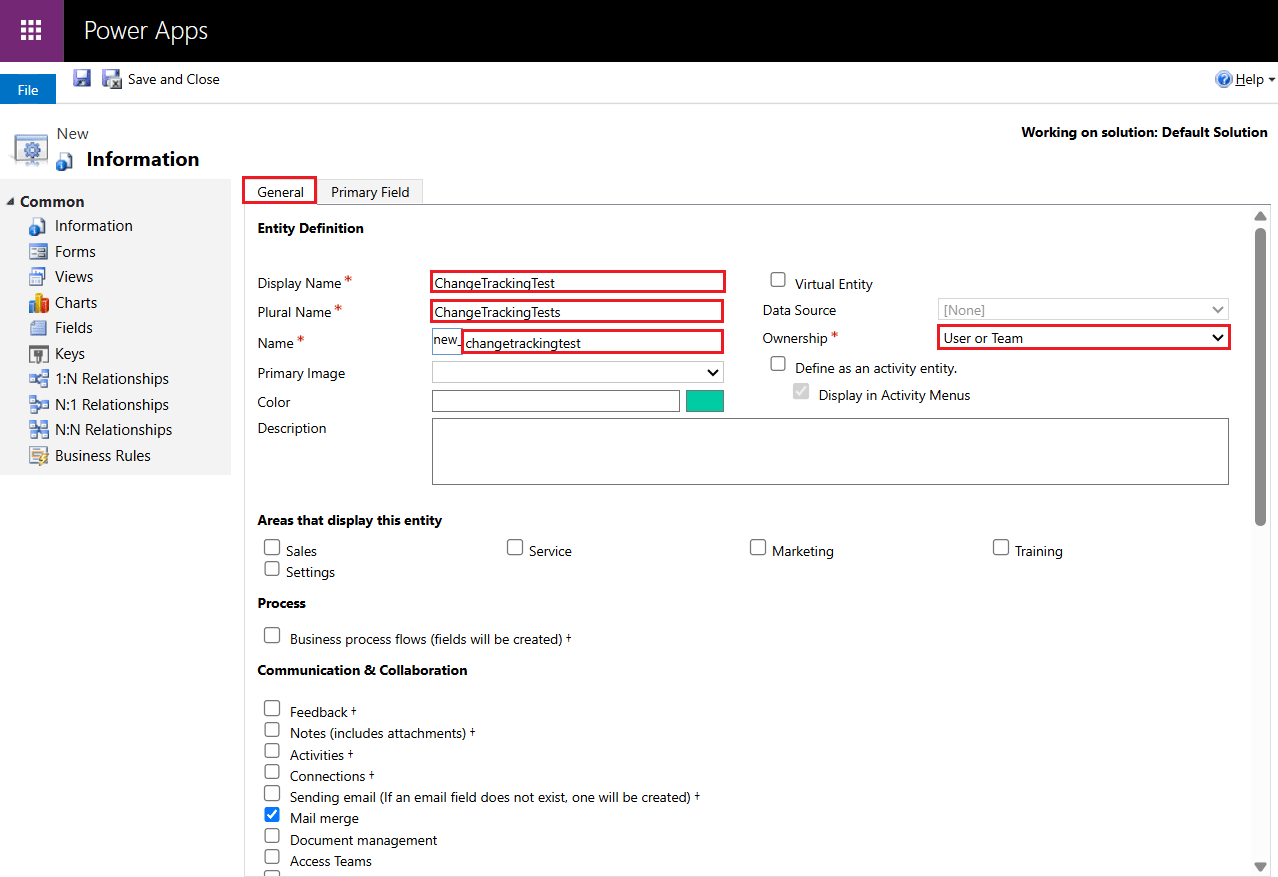
- Make sure to not enable the Change Tracking option under Data Services in the General tab. This will allow CData Sync to demonstrate its automatic enablement in a later section.
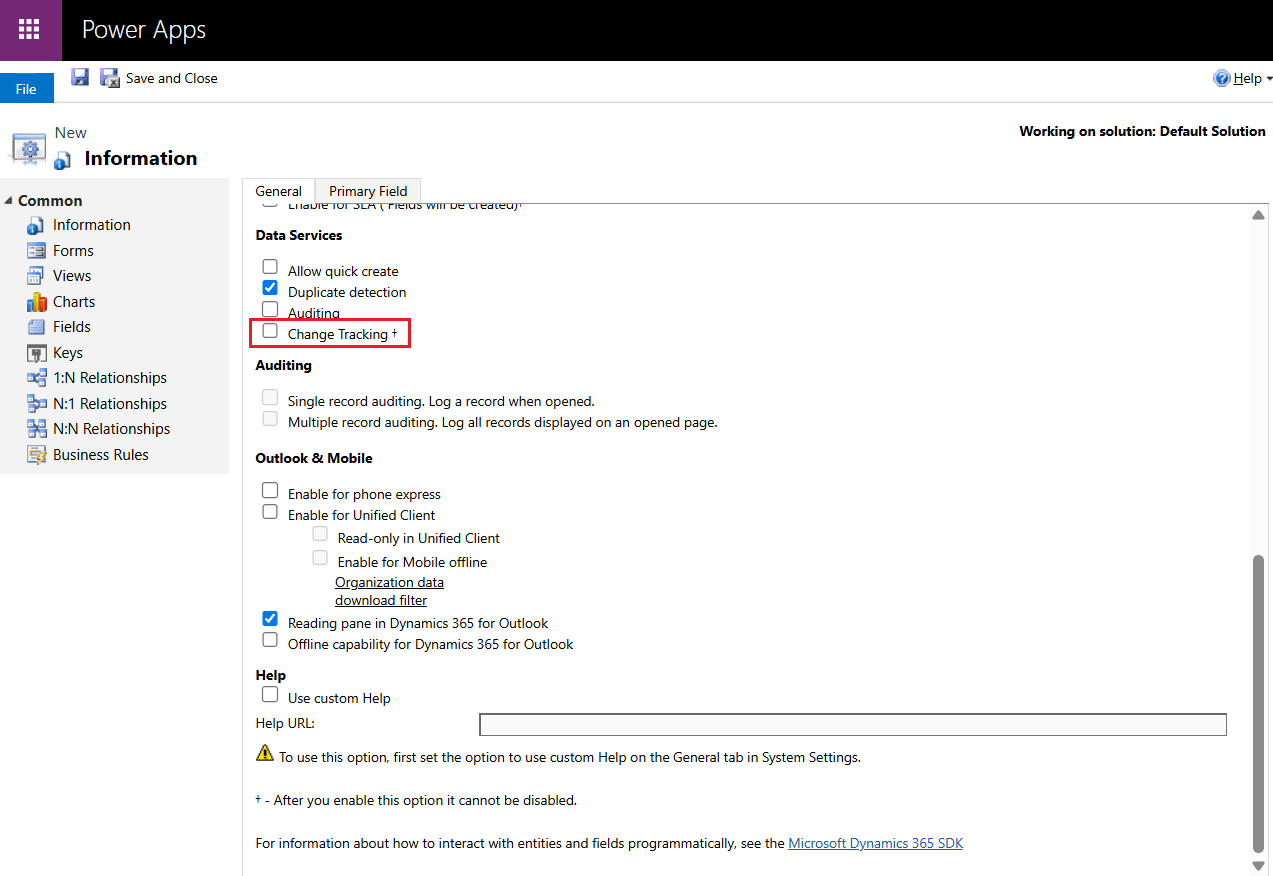
- In the Primary Field tab, define the schema (attributes and data types).
- Click Save & Close and then Publish All Customizations.
- The new entity is now created and will appear in the entity list.
Note: Change Tracking is available only through the API for the CRM editions of Microsoft Dynamics 365. This means the FinOpsOnline, FinOpsOnPremise, and HumanResources editions do not support Change Tracking.
Getting data into the Dynamics 365 entities
Once an entity or table is created in Dynamics 365, data can be added through several methods depending on the use case. Users can manually enter records through forms in the Dynamics interface, import bulk data using Excel or CSV files, or use automated data flows through Power Automate and third-party integrations. Developers can also push data programmatically using the Web API or SDK.
Alternatively, you can bypass these traditional methods and use the reverse ETL capability of CData Sync to push data directly from your source systems into Dynamics 365 entities. Reverse ETL is supported for source platforms like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and Snowflake.
It's important to note that reverse ETL is available only for source databases that support Delta Snapshot replication, which requires compatibility with the SQL EXCEPT statement.
Automatically enable change tracking for CDC replication with CData Sync
CData Sync simplifies the process of replicating data from Dynamics 365 by automatically enabling Change Tracking on selected entities, even if the setting is initially disabled. Below are the steps to set this up:
- Start CData Sync and log into the application.
- Configure the Microsoft Dynamics 365 connection (as the source) in CData Sync.
- Add a new job for the replication process. Select Dynamics 365 as the source, choose any supported destination database, data warehouse, or data lake from the 35+ options CData Sync currently supports (check here), and set the Type to Change Data Capture.
- Run the CDC incremental replication job.
- Once the job completes successfully, check the replicated entity or table in Dynamics 365. The Change Tracking option should now be enabled.
This process shows that you do not need to manually enable the Change Tracking feature in Dynamics 365 entities to perform CDC replication with CData Sync. The application automatically runs an EnableChangeTracking stored procedure in the background to activate the feature. This eliminates the need for a tedious and error-prone manual process and ensures that incremental replication works seamlessly without missing any changes.
Note: Once Change Tracking is enabled for an entity, it cannot be disabled later.
Perform CDC using CData Sync
Now that you have seen how to perform CDC using CData Sync, visit our CData Sync page to learn more about its powerful data replication capabilities and download a free 30-day trial. Start capturing and synchronizing your enterprise data with ease and reliability today.
As always, our world-class Support Team is here to help if you have any questions or need assistance getting started.


