Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →How to Access Google Calendar Information with a Service Account
Google Calendar is a free, web-based and mobile application developed by Google for time management and scheduling. When paired with CData's connectivity platform, users get live access to read and write Calendars, Events, Attendees, and more.
This article shows how to access Google Calendar using a service account, which typically represents an application or service, not an individual user. For the purposes of this article, we are exploring programmatic access through authorized API calls (how CData solutions interact with Google Calendar).
Prerequisites
- A Google Calendar account
- The CData JDBC Driver for Google Calendar (download here)
- A query tool compatible with JDBC (this article uses DBVizualizer, download here)
Steps Overview
- Enabling the Google Calendar API
- Creating a service account
- Working with live calendar data (via JDBC)
Step 1: Enabling the Google Calendar API
- Navigate to the Google Cloud Console.
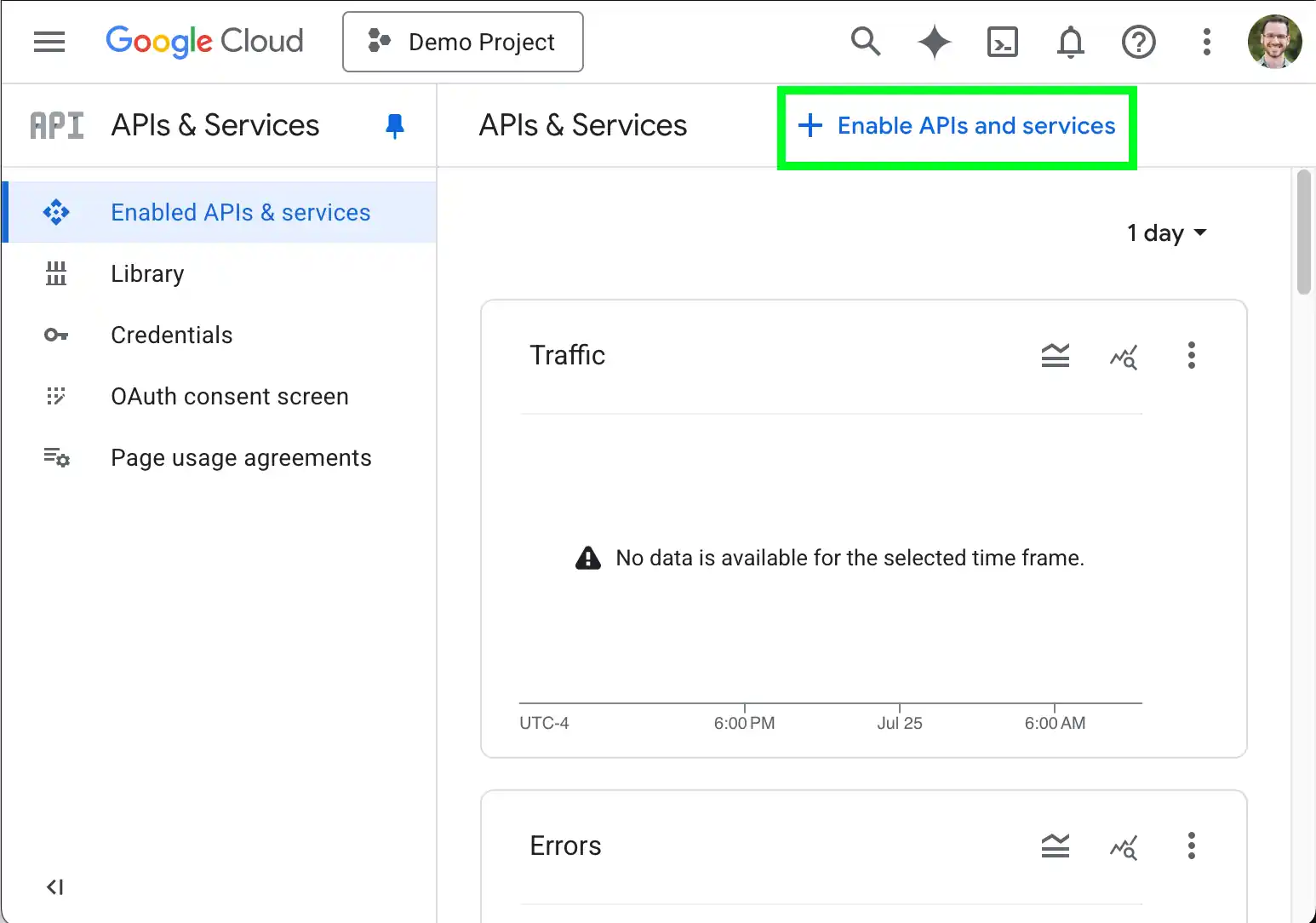
- Click Enable APIs and services.
- In the search field, enter "Google Calendar API" and select Google Calendar API from the search results.
- On the Google Calendar API page, click ENABLE.

Step 2: Creating a service account
Service accounts can be used in an OAuth flow to access Google APIs on behalf of users in a domain. A domain administrator can delegate domain-wide access to the service account.
To create a new service account:
- Navigate to the Google Cloud Console.
- Create a new project or select an existing project.
- At the left-hand navigation menu, select Credentials.
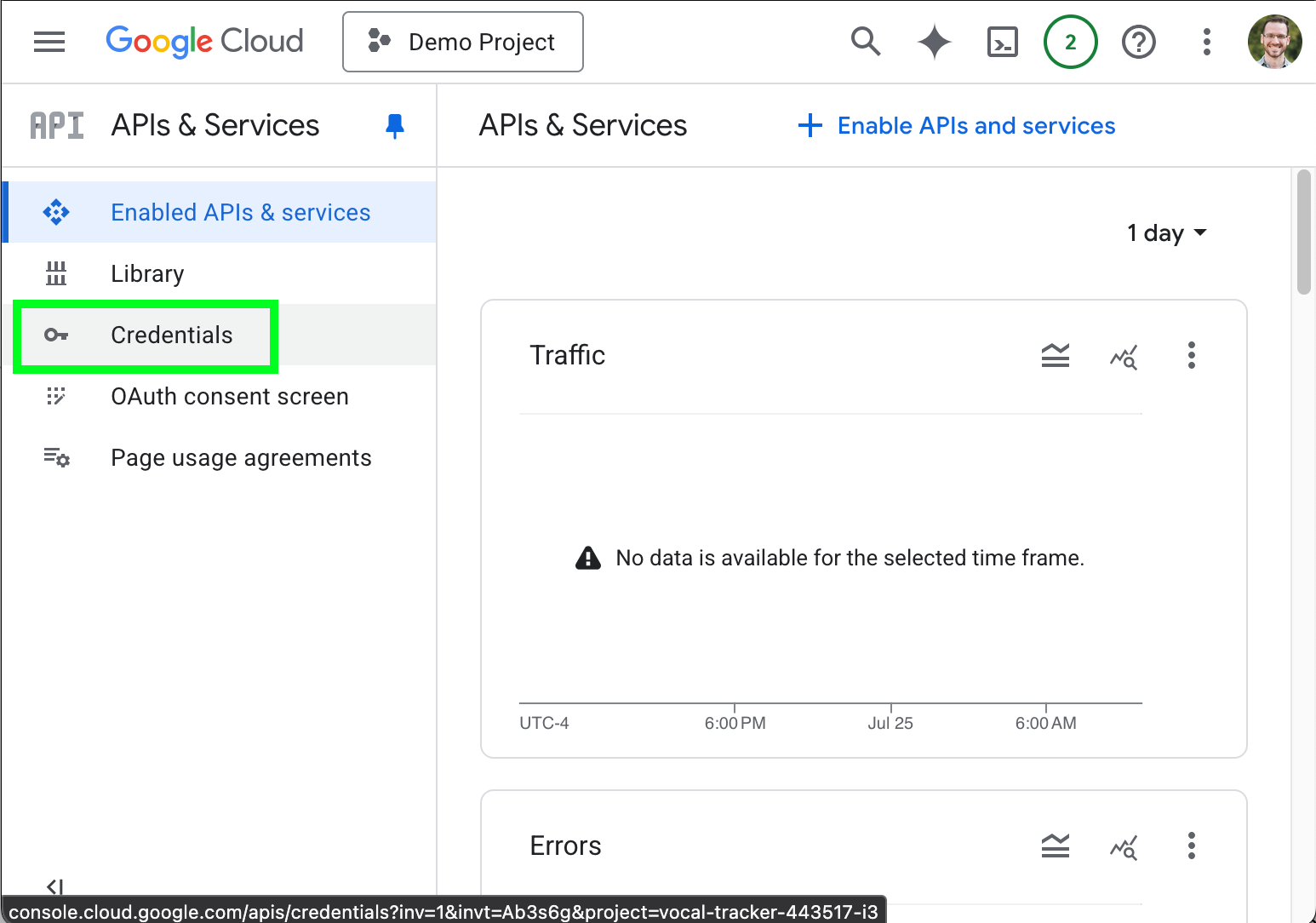
- Open the options menu ( ) and select Create Credentials.
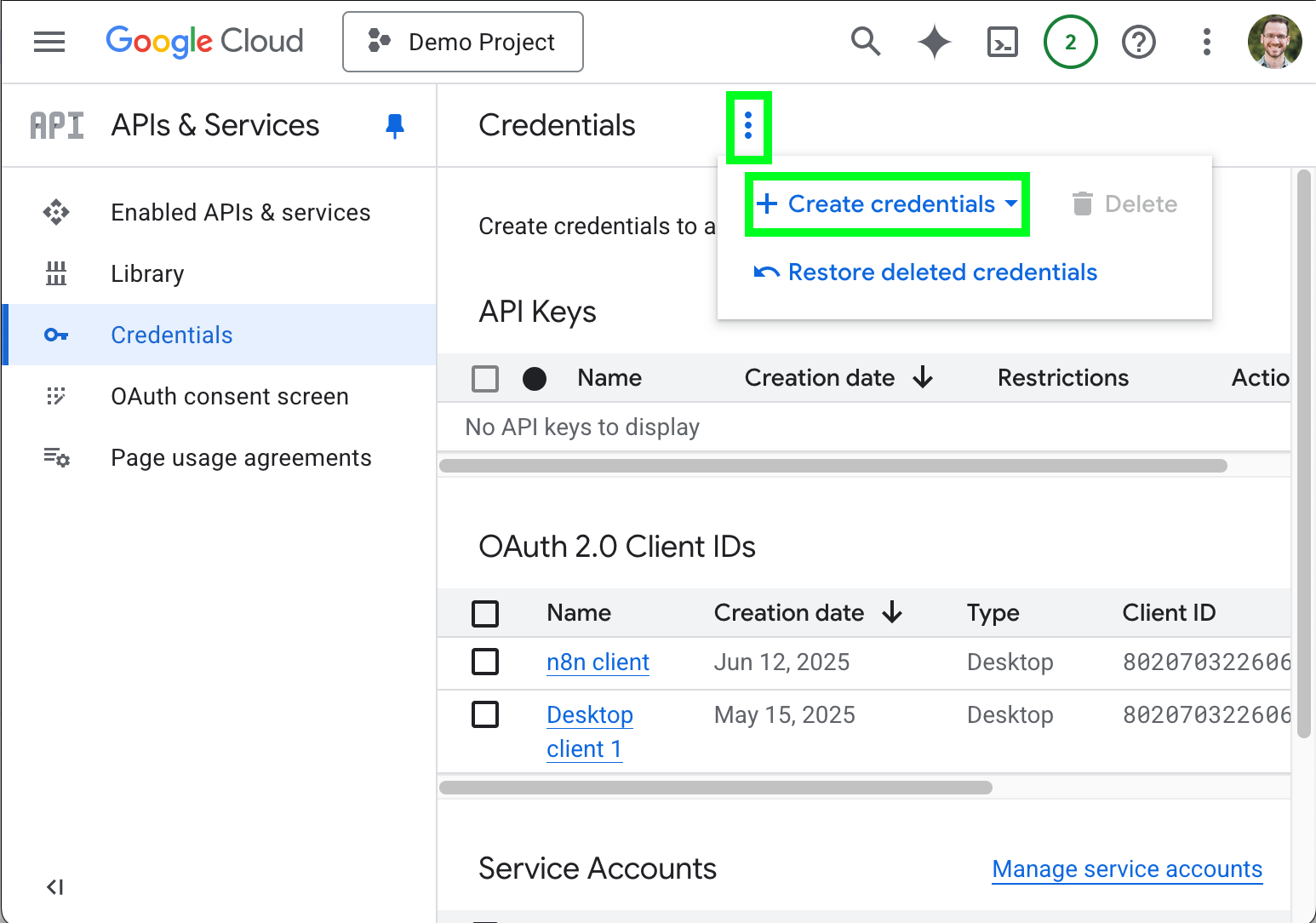
- Click Service account.
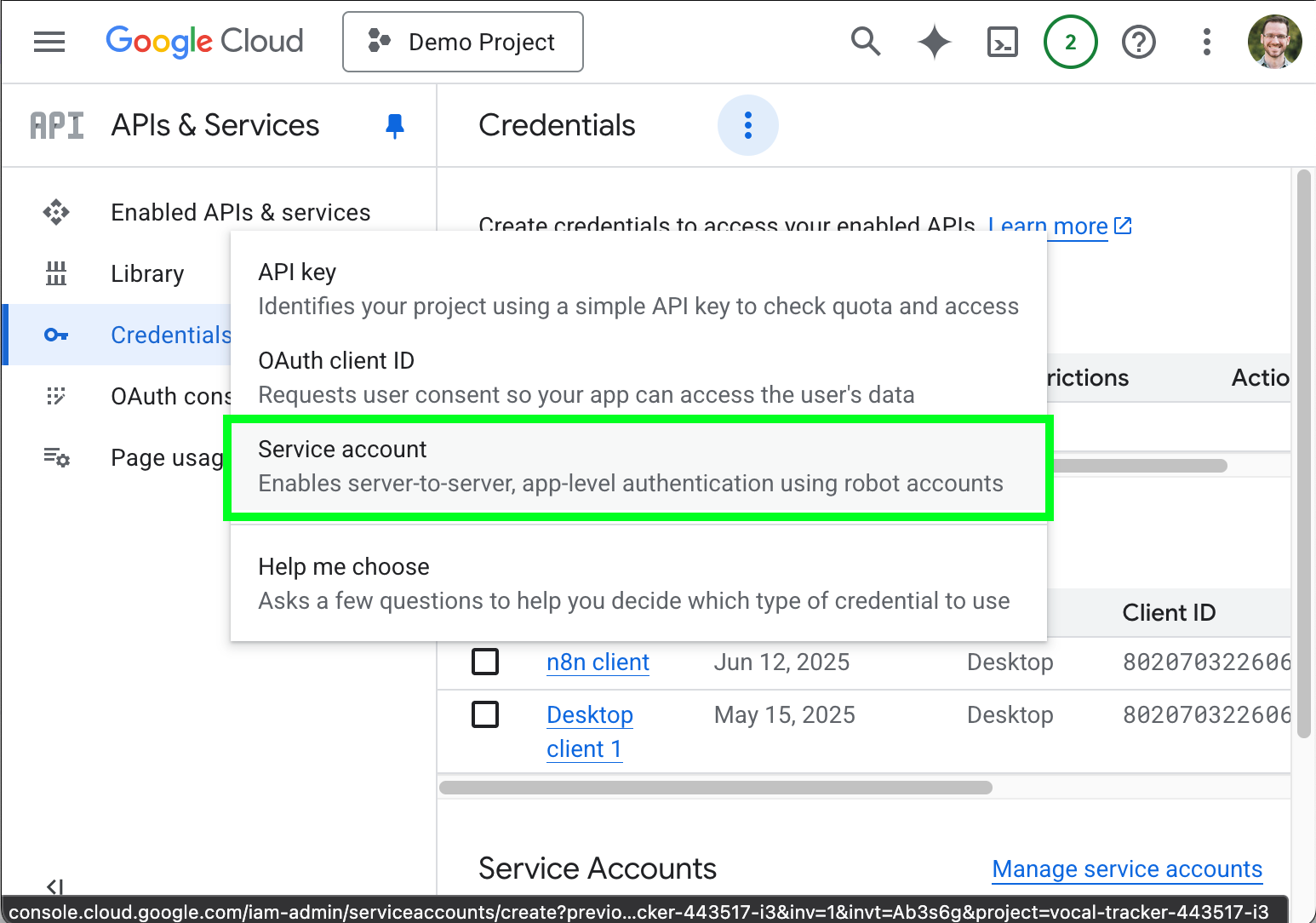
- On the Create service account page, enter the Service account name, the Service account ID, and,
optionally, a description.
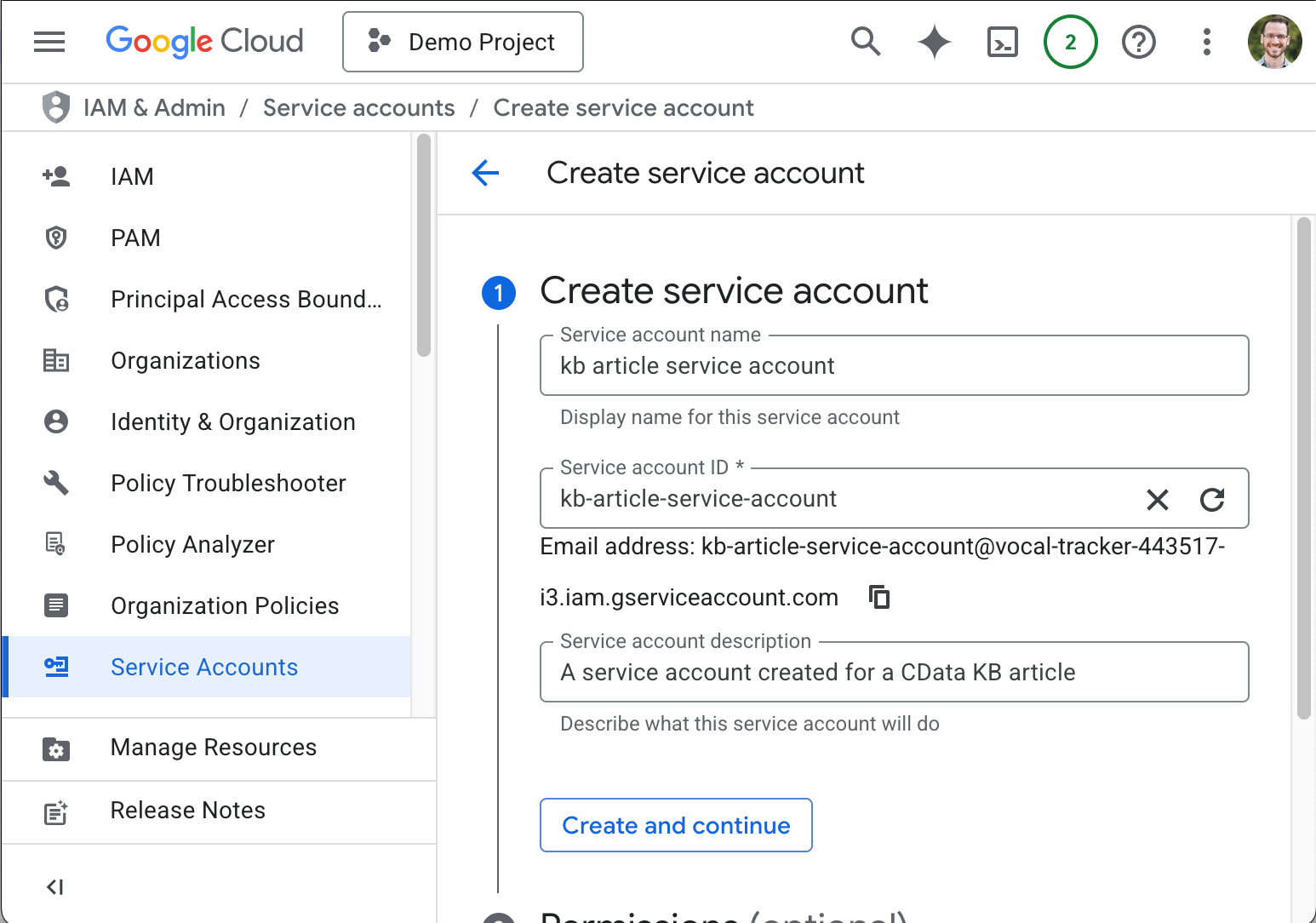
Make note of the service account email address (we use it later), likely in the format: my-service-account-id@service-account-agent.iam.gserviceaccount.com
- Optionally configure permissions and principals with access and click Done.
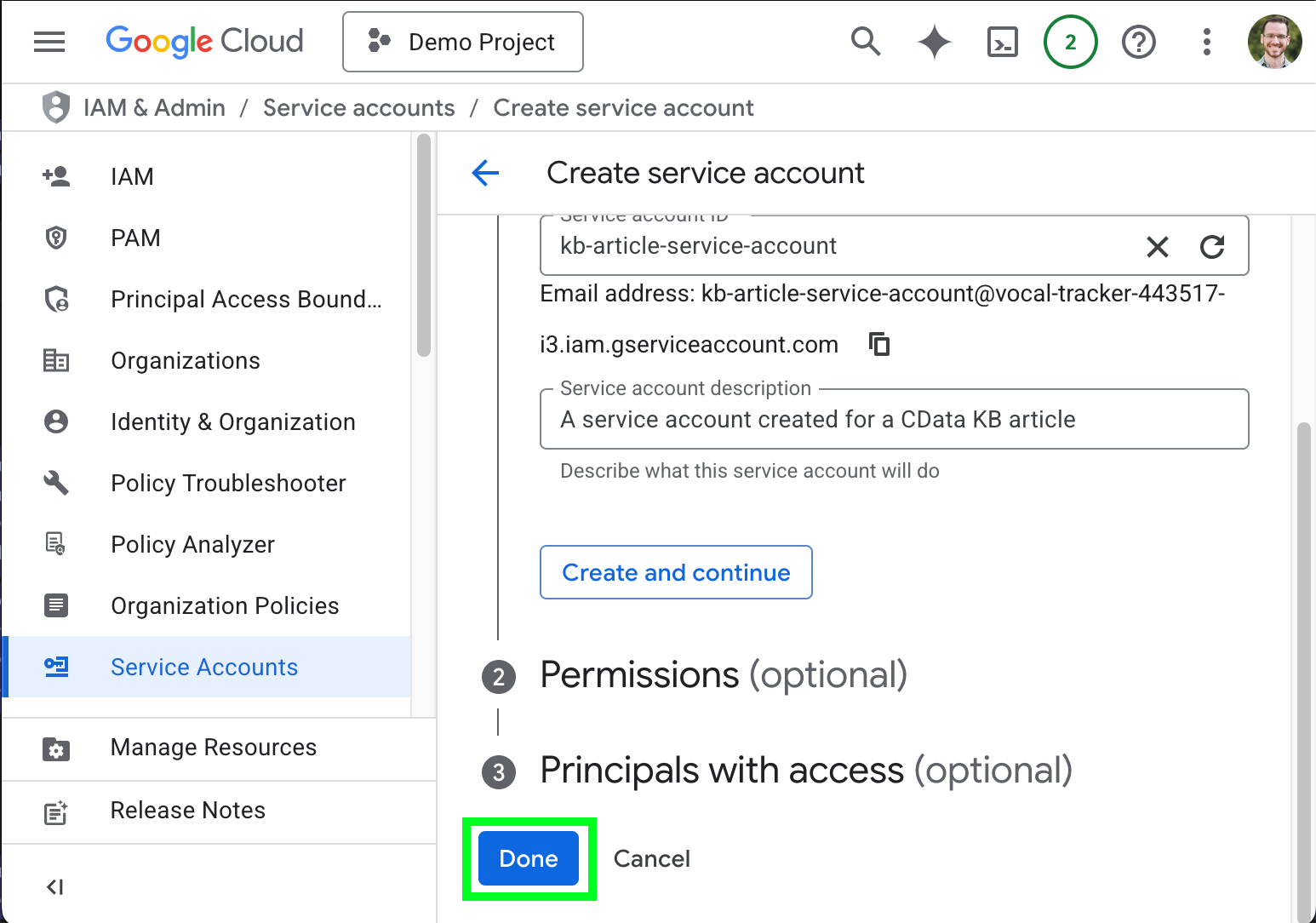
- Back on the the Cloud Console Credentials page, scroll to the Service Accounts section and select the service account you just created.
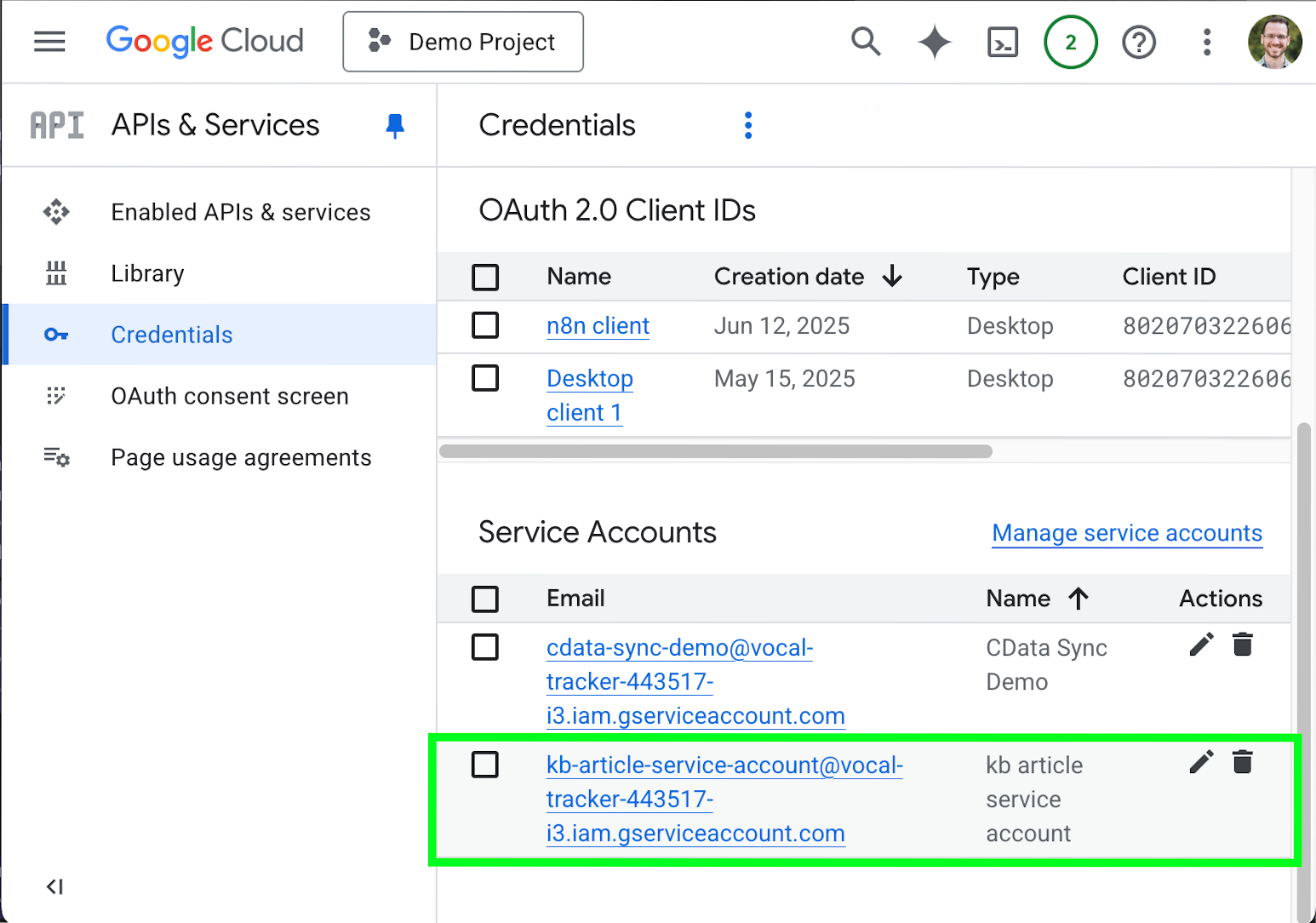
- Click the Keys tab.
- Click Add key > Create new key.
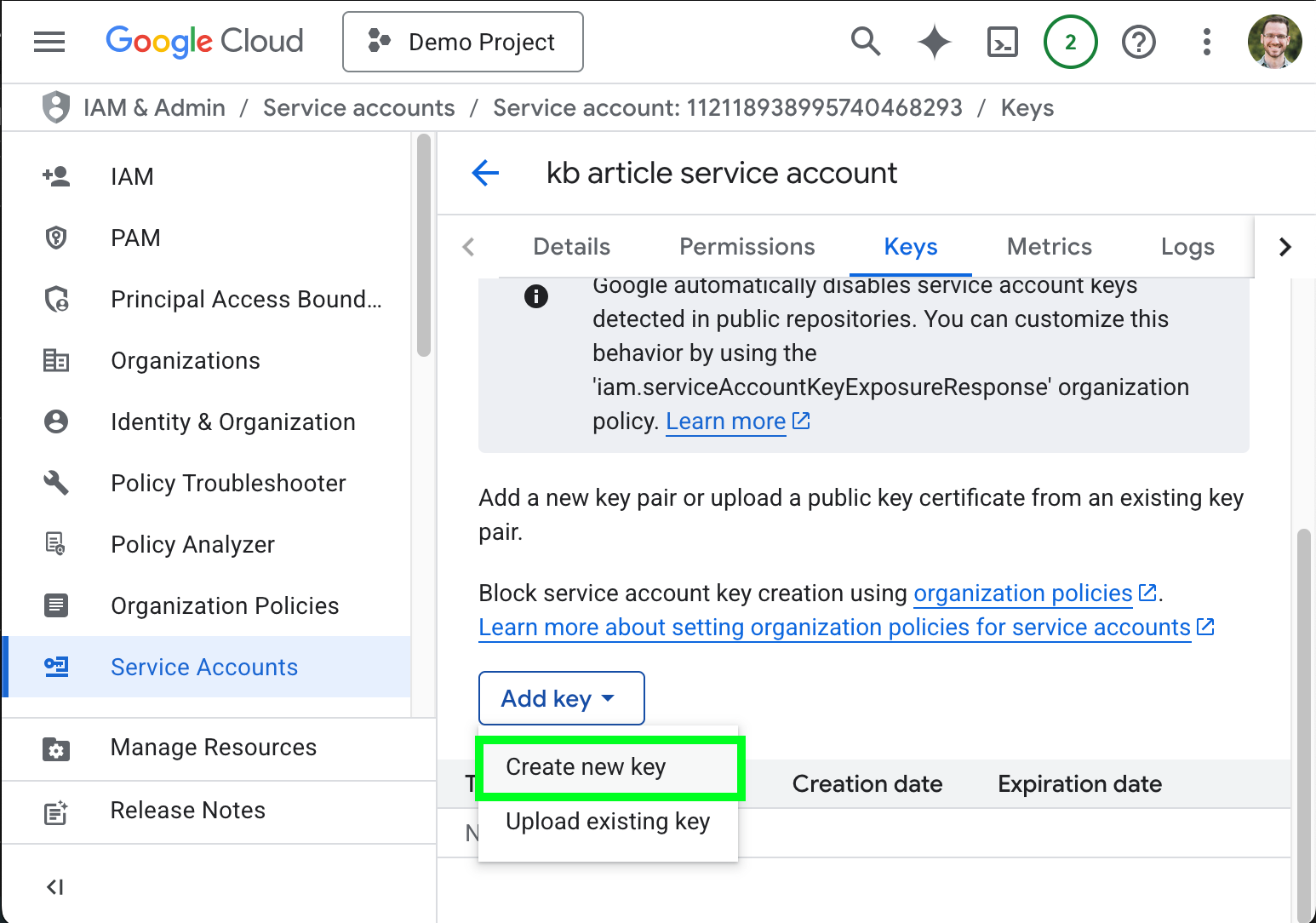
- Select any supported Key typ (we use JSON for this article) and click Create.
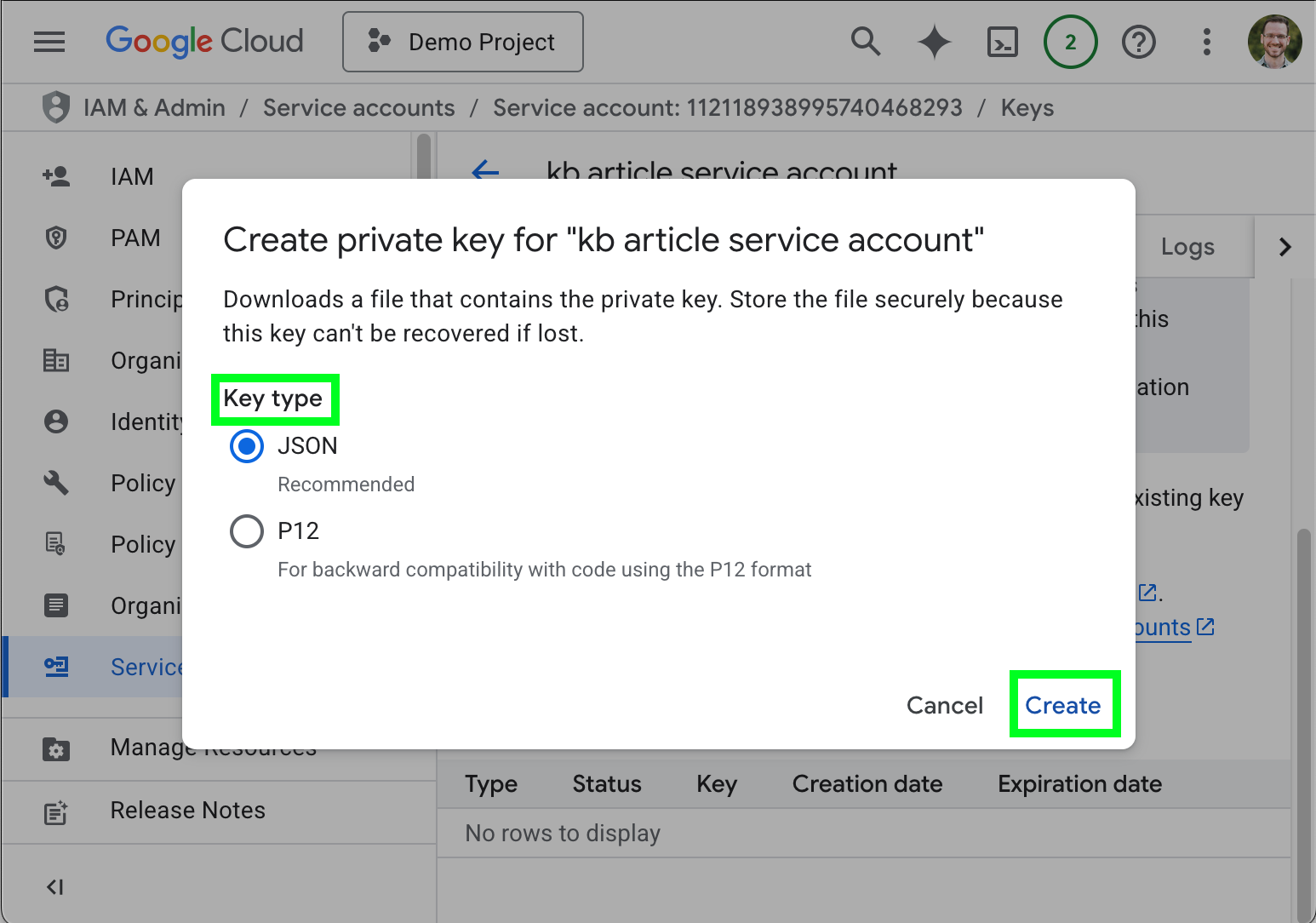
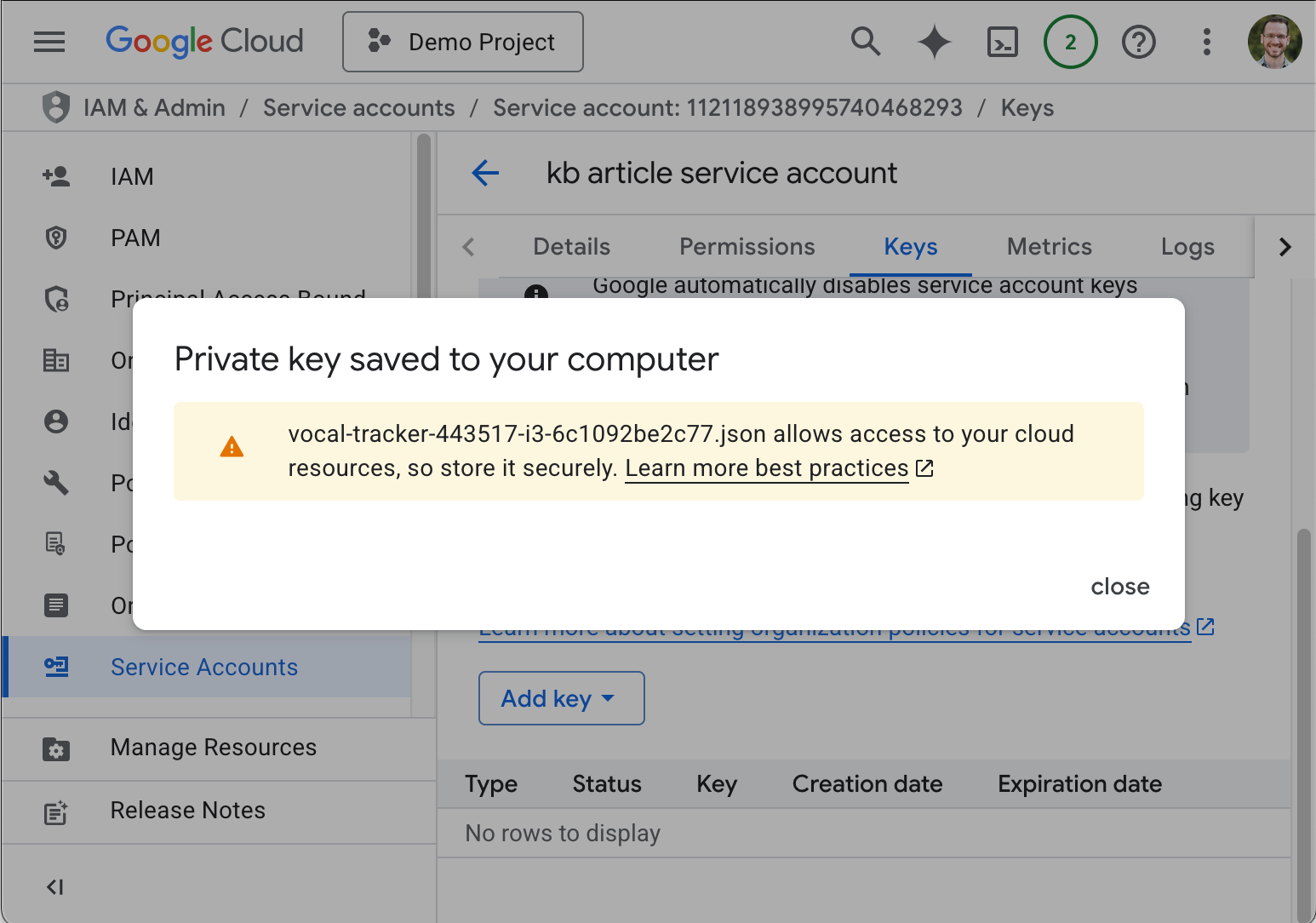
The key is automatically downloaded to your device, and any additional information specific to the key is displayed.
- Record the additional information for future use.
Step 3: Sharing calendar(s) with the service account
To access Google Calendars with service account, the individual Calendars must be shared with the service account. Calendar additions can only be accepted by service accounts through the API, which can be tedious. With CData's connectors, calendars can be accepted via basic SQL. For this article, we use DBVisualizer, but you can use any SQL tool with JDBC connectivity (or even custom Java applicaitons).
Step 3.1: Adding the calendar in the Google Console
- Open Google Calendar.
- Expand the Calendar menu (if the list of calendars is not visible).
- Open the options menu ( ) for a calendar and select Settings and sharing.
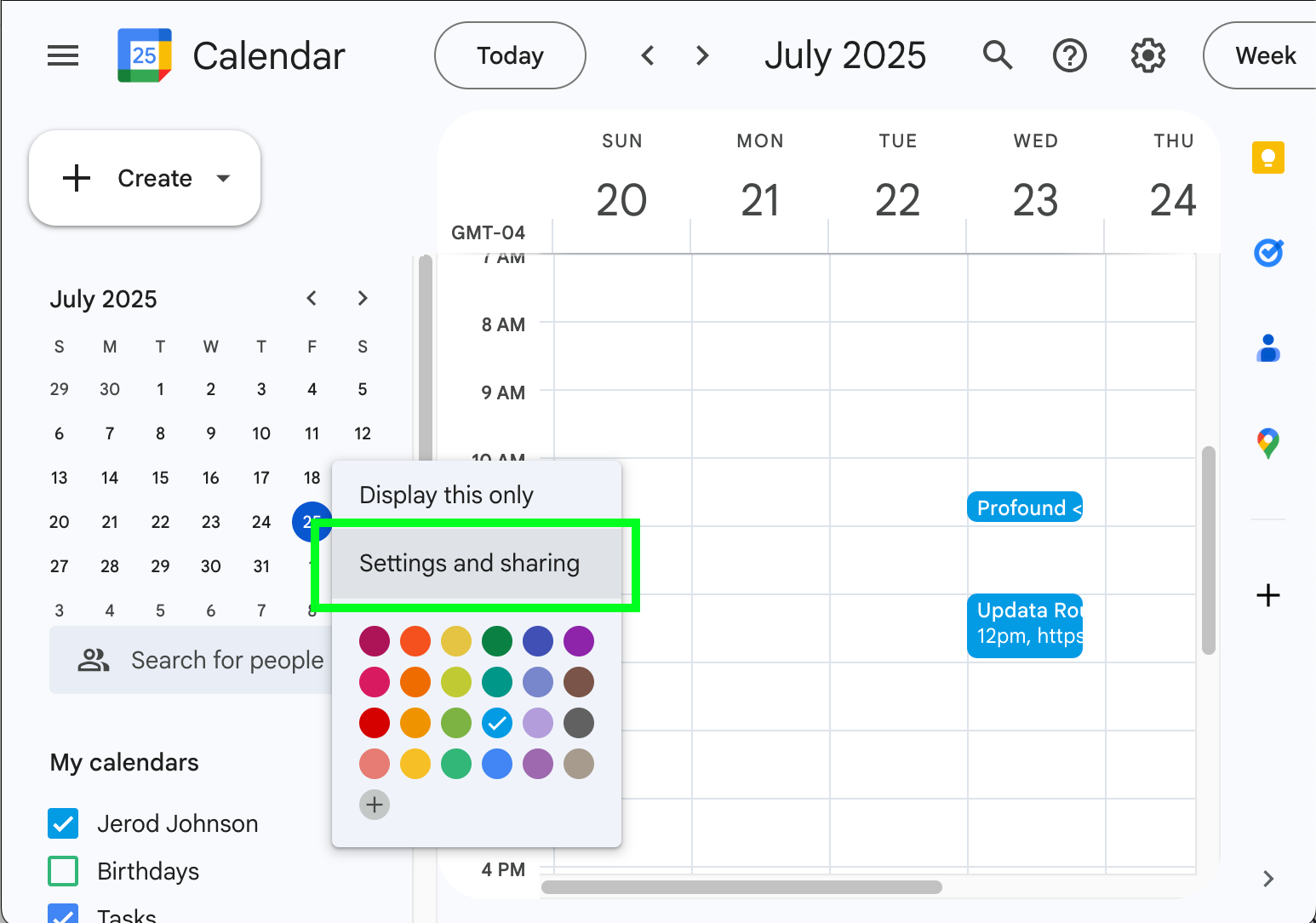
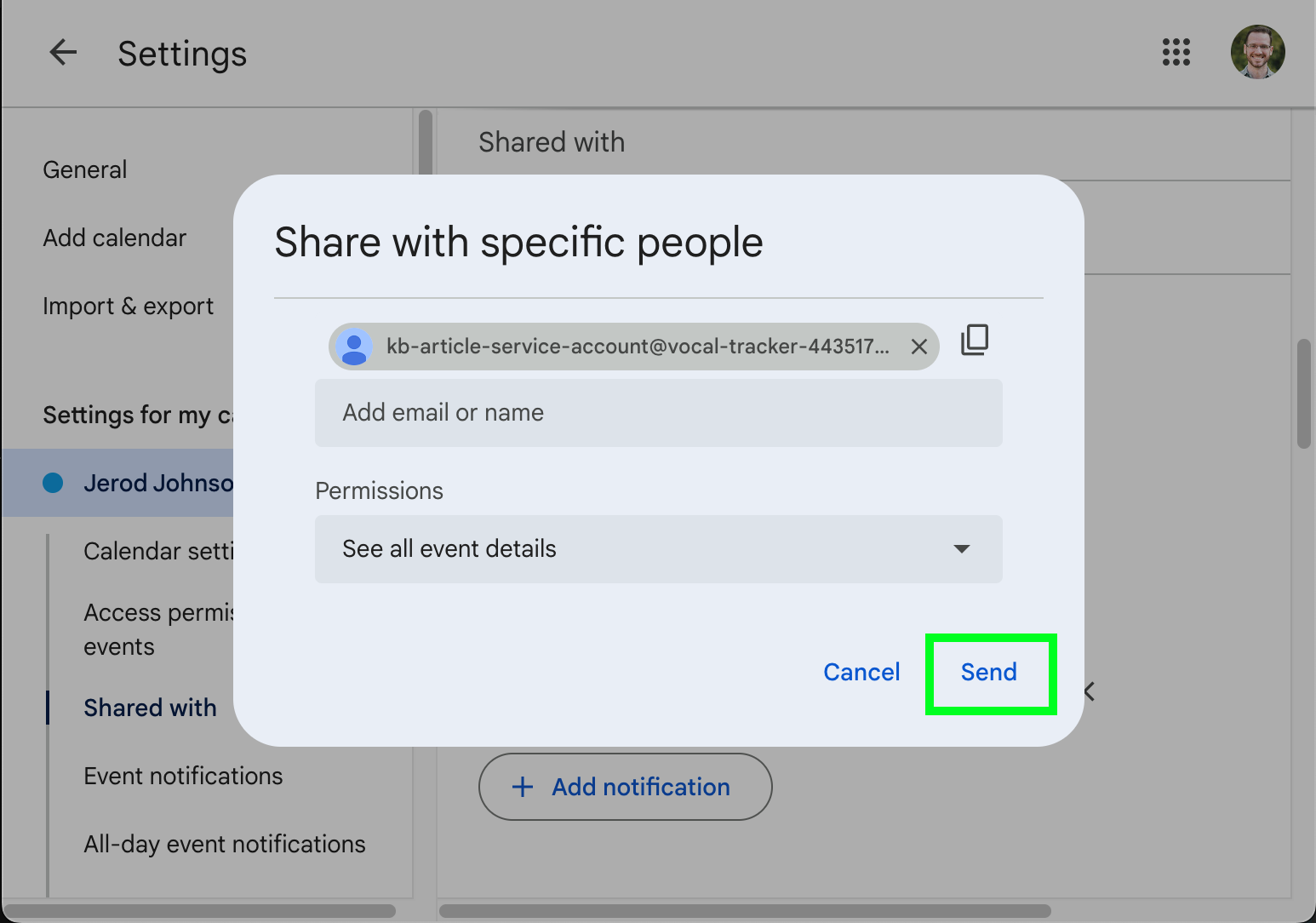
- Click or scroll to Shared with
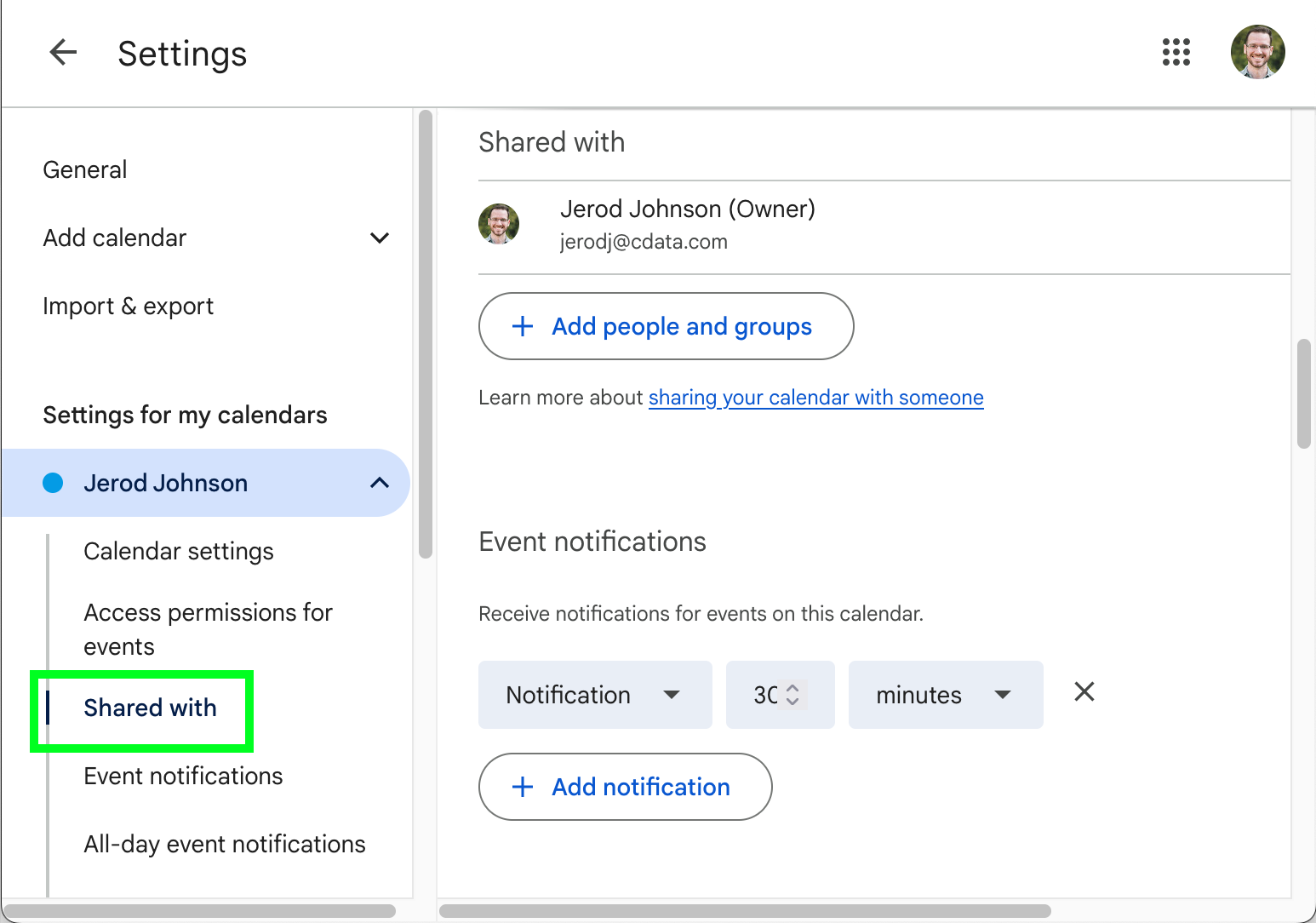
- Click Add people or groups.
- Enter the email for your service account (likely in the format my-service-account-id@service-account-agent.iam.gserviceaccount.com), assign permissions, and click Send.
Step 3.2: Connecting to Google Calendar with the service account
- Open the connection string wizard for the JDBC driver. From a terminal execute the following:
java -jar /PATH/TO/CData JDBC Driver for Google Calendar/lib/cdata.jdbc.googlecalendar.jar
- Configure the connection to build the connection string:
- Set AuthScheme to "OAuthJWT"
- Set InitiateOAuth to "GETANDREFRESH"
- Set OAuth JWT Cert Type to "GOOGLEJSON"
- Set OAuth JWT Cert to the path to the key you downloaded earlier.
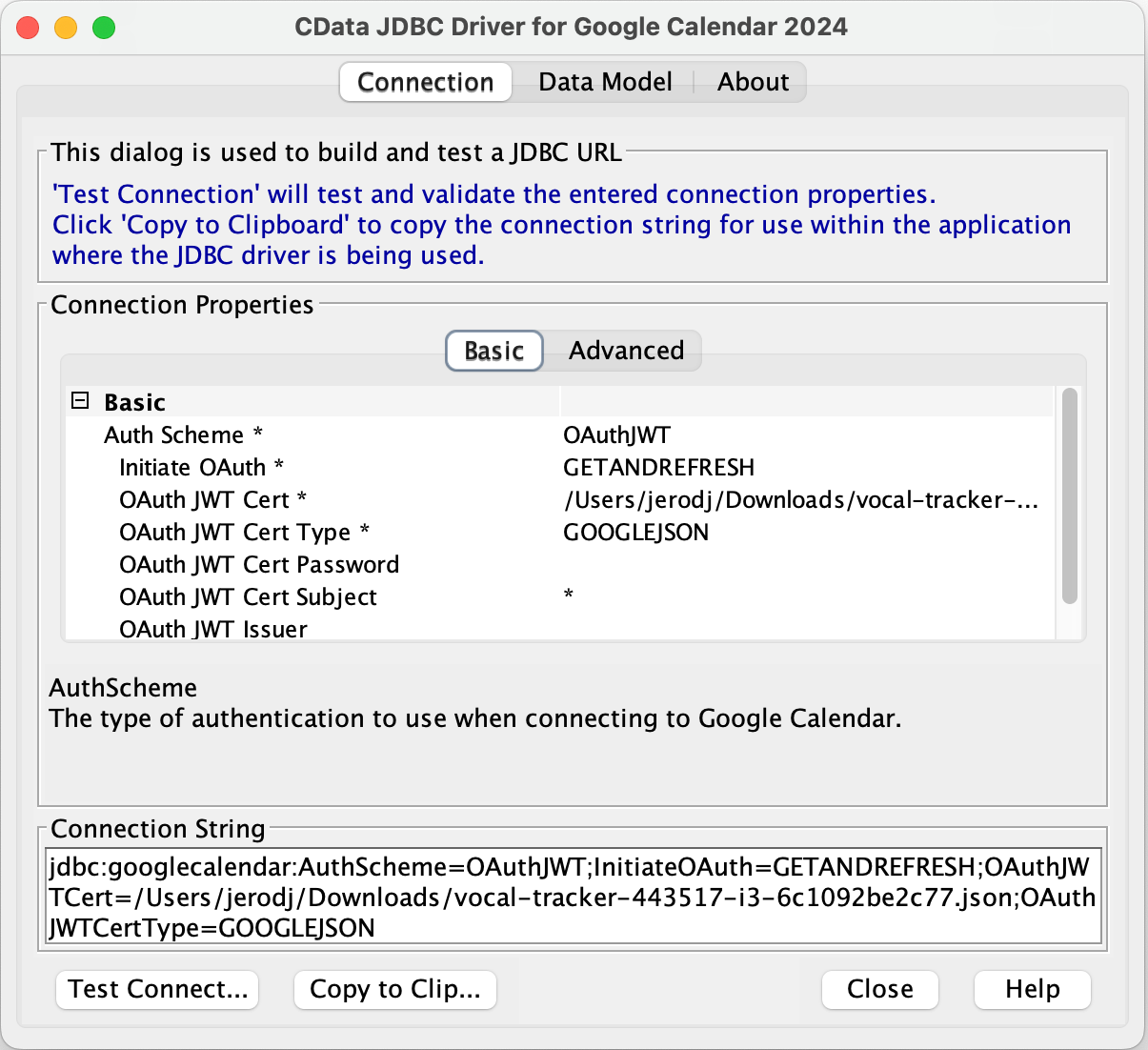
- Click "Test Connection" to confirm the configuration.
- Copy the connection string for use in your SQL tool. It should look similar to the following:
jdbc:googlecalendar:AuthScheme=OAuthJWT;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH;OAuthJWTCert=/Users/jerodj/Downloads/vocal-tracker-443517-i3-6c1092be2c77.json;OAuthJWTCertType=GOOGLEJSON;
Step 3.3: Finalizing the Calendar add and working with live calendar data
- Open your JDBC tool and connect using the connection string you saved above (for a detailed walkthrough of using DBVisaulizer with the CData JDBC Driver for Google Cal, refer to our Knowledge Base article.)
- Use a SQL INSERT to accept the calendar invitation by the calendar ID (typically the email address of the calendar owner):
INSERT INTO "CData"."GoogleCalendar"."Calendars" (id) VALUES ("[email protected]") - The calendar is now available via the JDBC Connection:
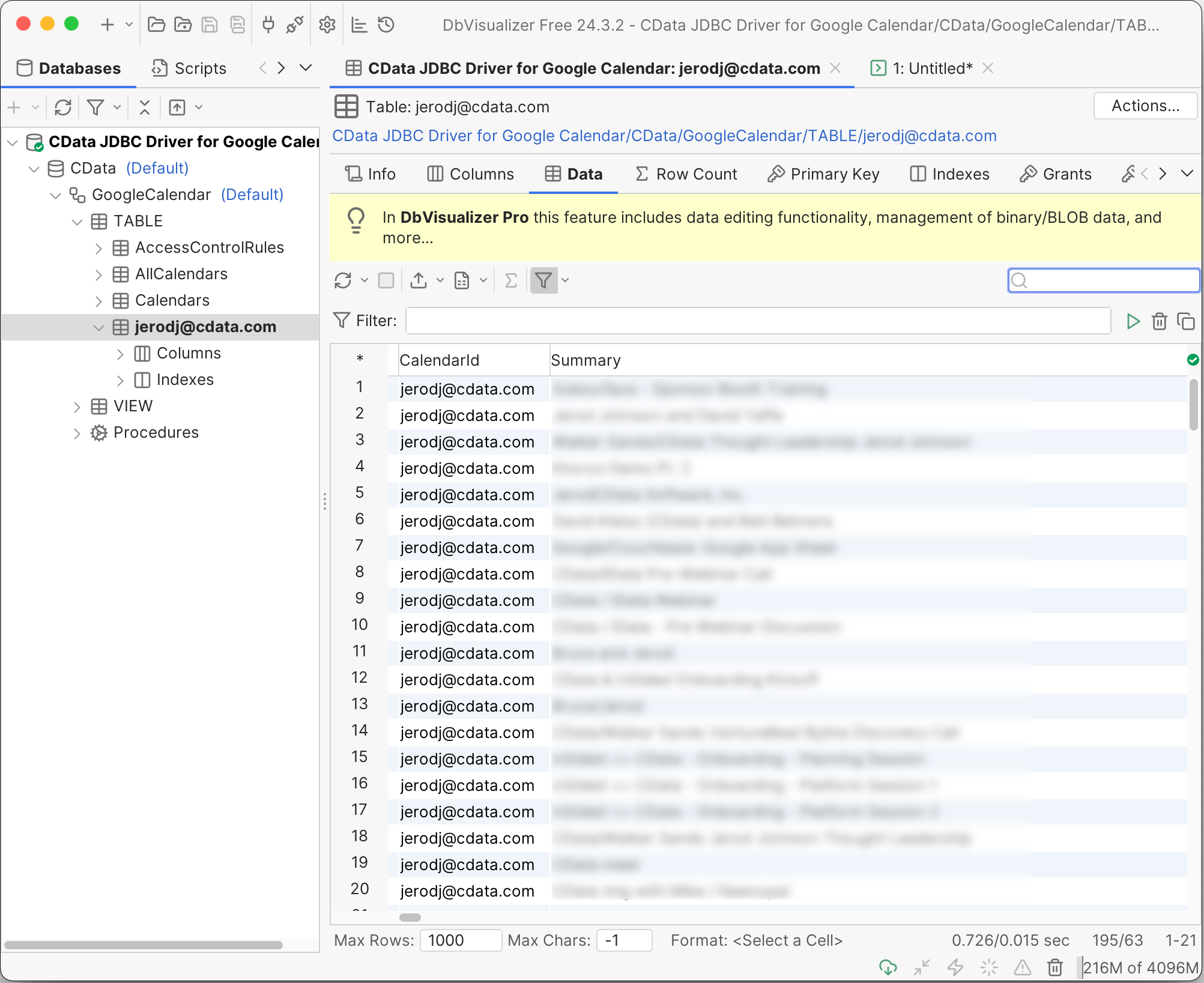
At this point, you can work with live Google Calendar data through the service account, based on the calendar permissions granted to the service account.
Free Trials & More Information
You can find the latest version of our Google Calendar drivers here. All of our drivers include a free, 30-day trial. Also, if you'd like to learn more about using our drivers with your existing tools or applications, explore our Knowledge Base.
As always, our world-class Support Team is ready to answer any questions you may have.


