Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Ingest Data into Salesforce Data Cloud Using CData JDBC Driver
Salesforce Data Cloud (SFDC) is a hyperscale data platform built on Salesforce's core infrastructure. It enables organizations to unify customer data from various systems into a single, real-time customer profile. This unified view allows marketing, sales, and service teams to activate customer data across every interaction, whether through email campaigns, service workflows, or digital advertising. With Data Cloud, businesses can move from insight to action in milliseconds, delivering personalization at scale.
This article demonstrates how to ingest (write) data from external data sources into SFDC using the CData Salesforce Data Cloud JDBC Driver (2025).
Prerequisites
- Create an account on Salesforce Data Cloud
- Download and install the CData Salesforce Data Cloud JDBC driver
- Install DBeaver and configure a database using the installed CData Salesforce Data Cloud JDBC driver
Step 1: Create an Ingestion API
In SFDC, an Ingestion API allows you to bring external data into Data Cloud from various systems (like web apps, CRMs, ERP systems, etc.) in a scalable and near-real-time manner. It is important for building a unified customer profile by ingesting data such as transactions, interactions, or custom events.
Follow the given process to create an Ingestion API in SFDC:
- Click the Setup menu on the top-right and click Data Cloud Setup
- Navigate to Ingestion API in the left panel under External Integrations or find it using Quick Search
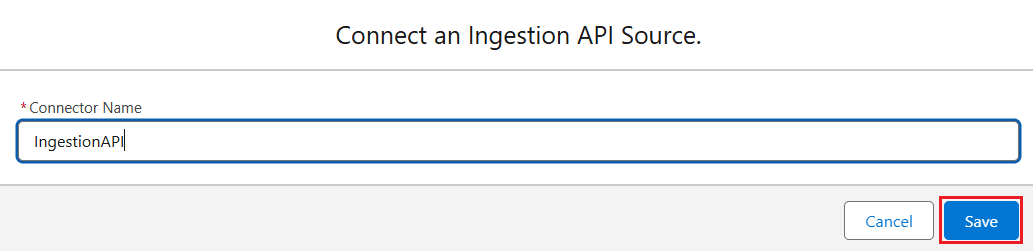
- Click New, enter a Connector Name, and click Save
- Once the Ingestion API is created, it should appear in the Ingestion API list
Step 2: Create an OpenAPI (OAS) Format File
Once you've set up your Ingestion API in SFDC, the next step is to generate an OpenAPI Specification (OAS) file. This file serves as a machine-readable description of your API, often used for integrations, automation, and client SDK generation.
- Based on the fields you need, construct the file using the sample format below:
openapi: 3.0.3
components:
schemas:
Order:
type: object
properties:
contact_name:
type: string
created_date:
type: string
format: date-time
id:
type: string
is_new:
type: boolean
modifie_date:
type: string
format: date-time
my_email:
type: string
format: email
total:
type: number
my_phone:
type: string
format: phone
my_url:
type: string
format: url
shipAddress:
type: string
taxExempt:
type: string
tax_rate:
type: number
my_percent:
type: string
format: percent
OrderItem:
type: object
properties:
cost:
type: number
createdDate:
type: string
format: date-time
quantity:
type: number
name:
type: string
orderId:
type: string
itemNumber:
type: number
SalesCustomer:
type: object
properties:
address:
type: string
age:
type: number
city:
type: string
country:
type: string
modifiedDate:
type: string
format: date-time
firstName:
type: string
gender:
type: string
id:
type: string
lastName:
type: string
createdDate:
type: string
format: date-time
You can also use GPT or similar tools to generate an OpenAPI (OAS) or .yaml file based on required fields, or convert JSON responses into schemas using Java code.
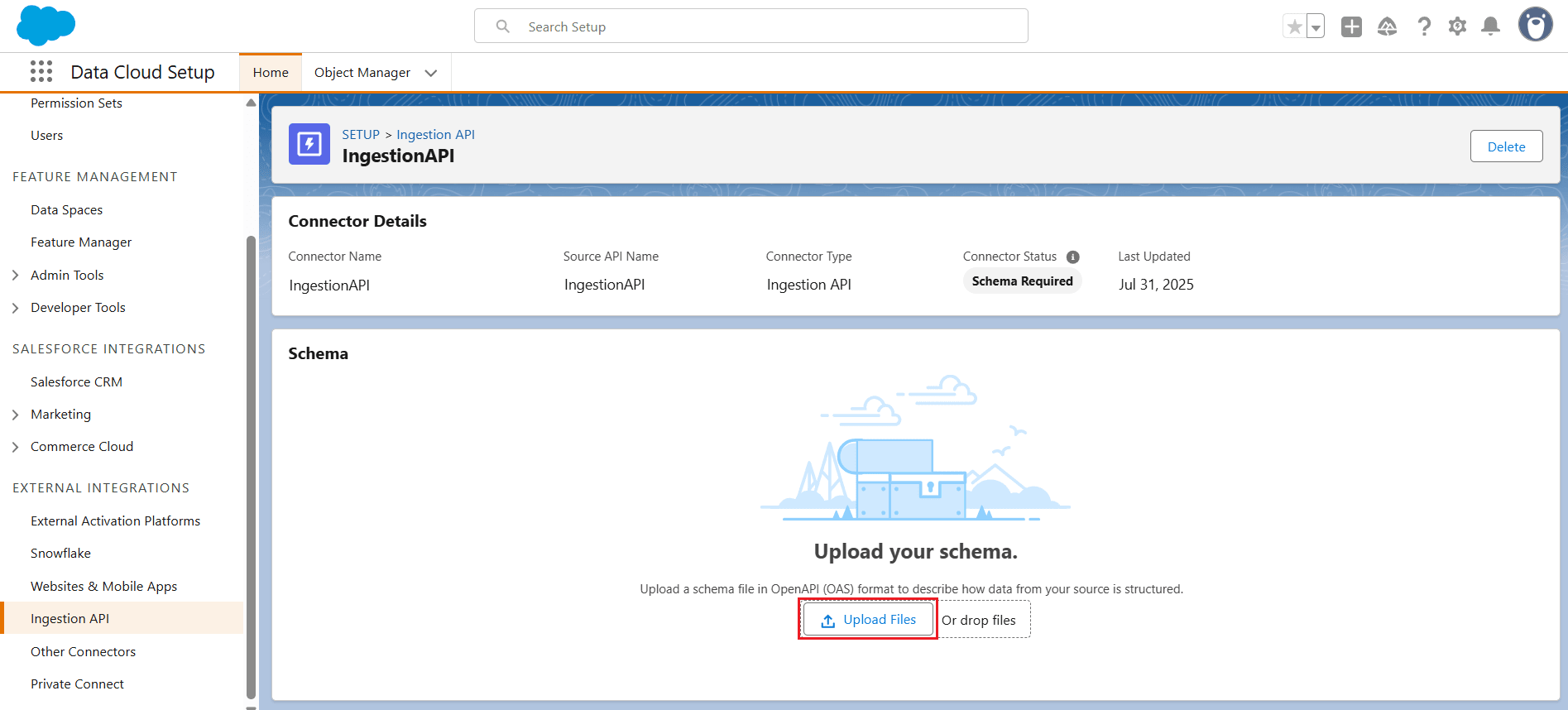
- Once the file is generated, upload the schema using Upload Files in the Ingestion API connector
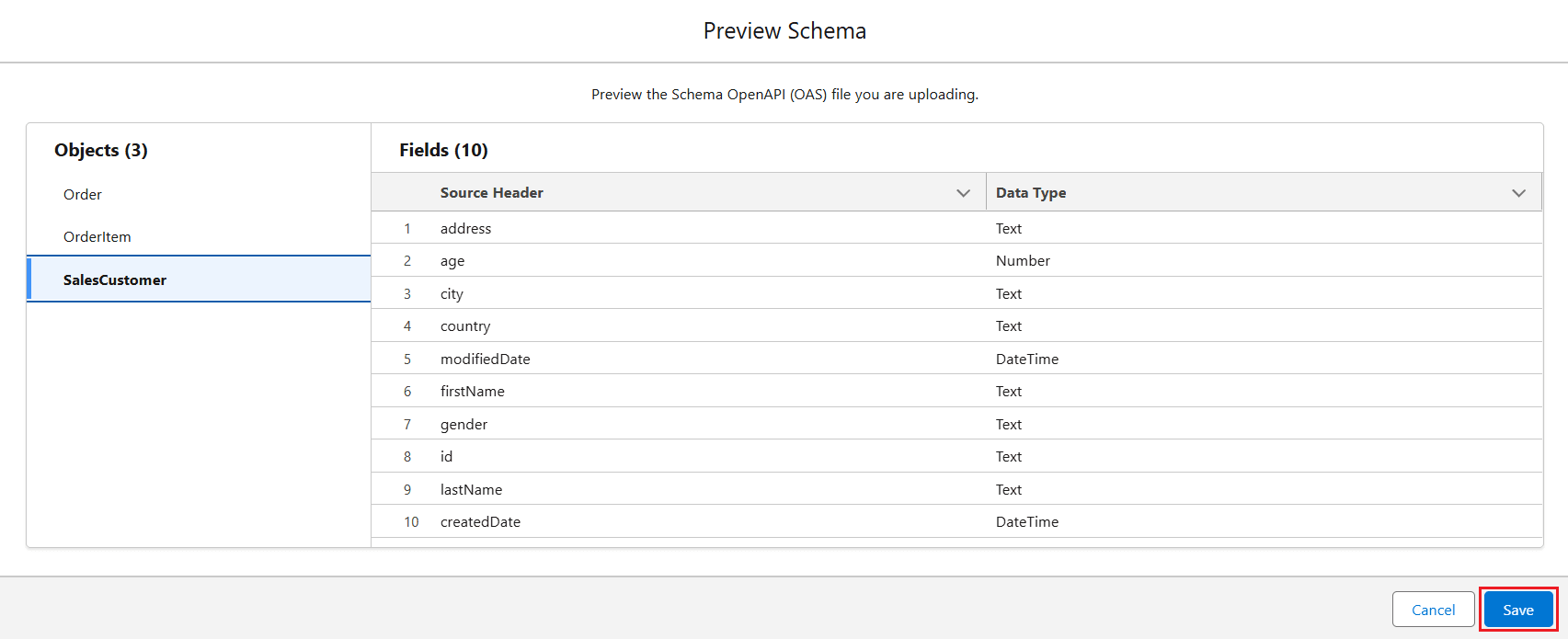
- The Preview Schema screen appears, where you can review the data. Click Save
Step 3: Create a Data Stream
Once the Ingestion API is fully set up with the OpenAPI schema, the next step is to create a Data Stream in SFDC to enable actual data ingestion. Follow these steps:
- Begin by clicking the 3x3 App Launcher grid in the upper-left corner of the Salesforce interface. In the search bar that appears, type Data Cloud and select it from the list of available apps.
- Inside the Data Cloud app, navigate to the Data Streams tab in the navigation panel. This is where all data ingress activities are managed. Click the Create New button to begin configuring a new data stream.
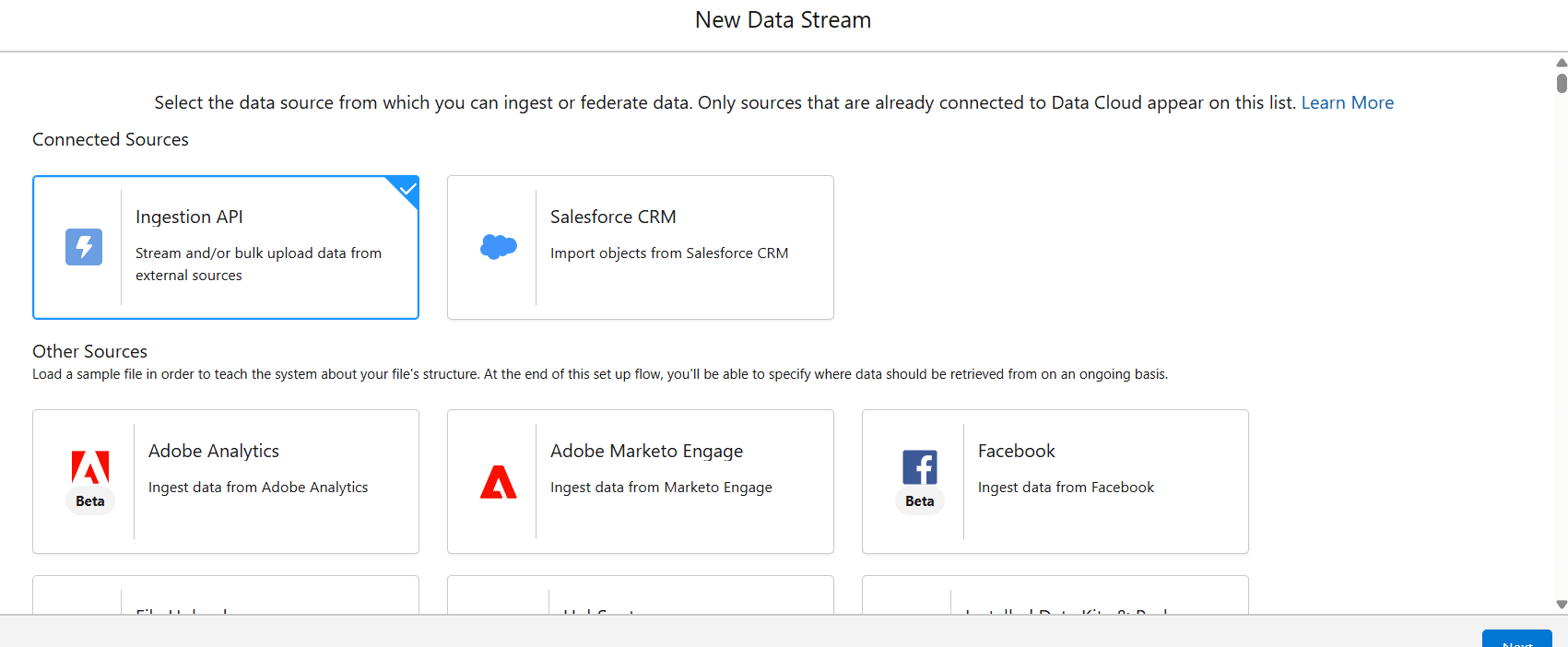
- In the New Data Stream window, select Ingestion API from the Connected Sources and click Next.
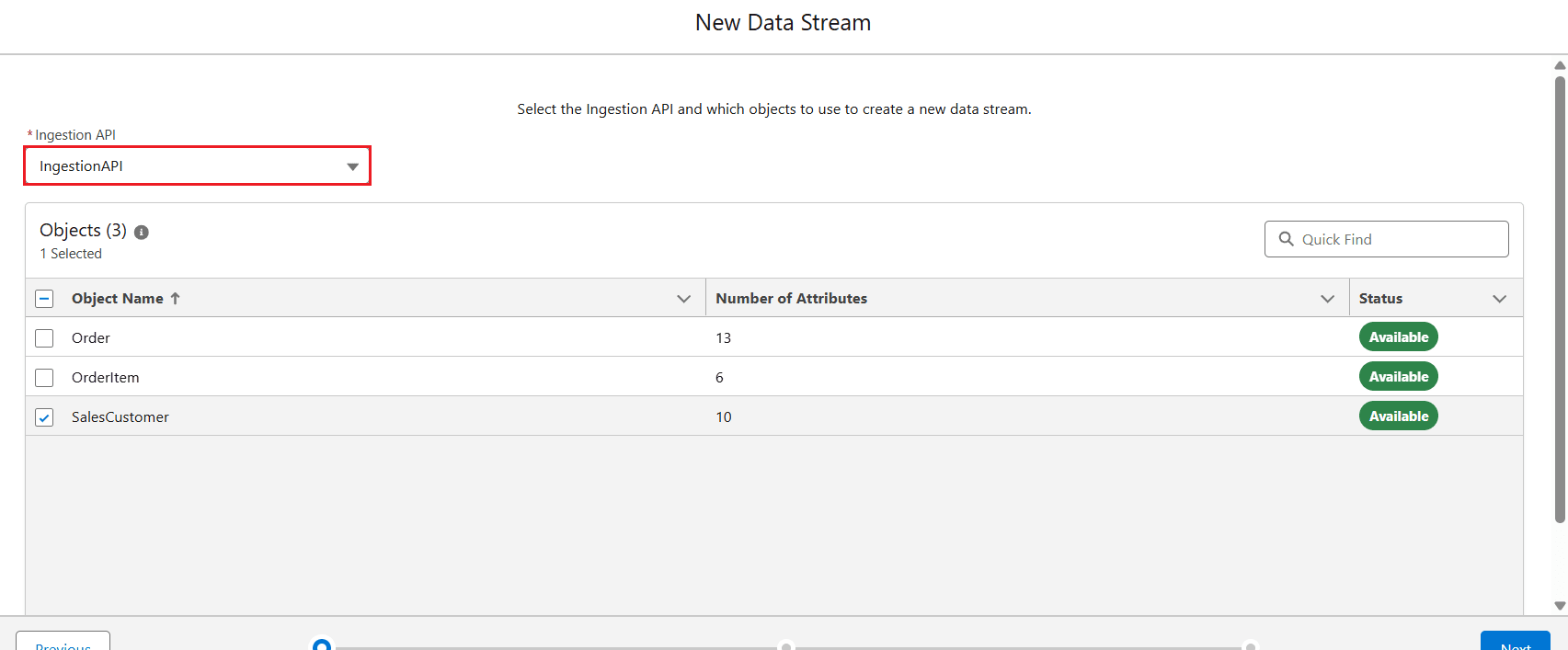
- In the next step, select the Ingestion API you recently created from the dropdown and choose an object defined in the previously generated OpenAPI (OAS) file. Click Next.
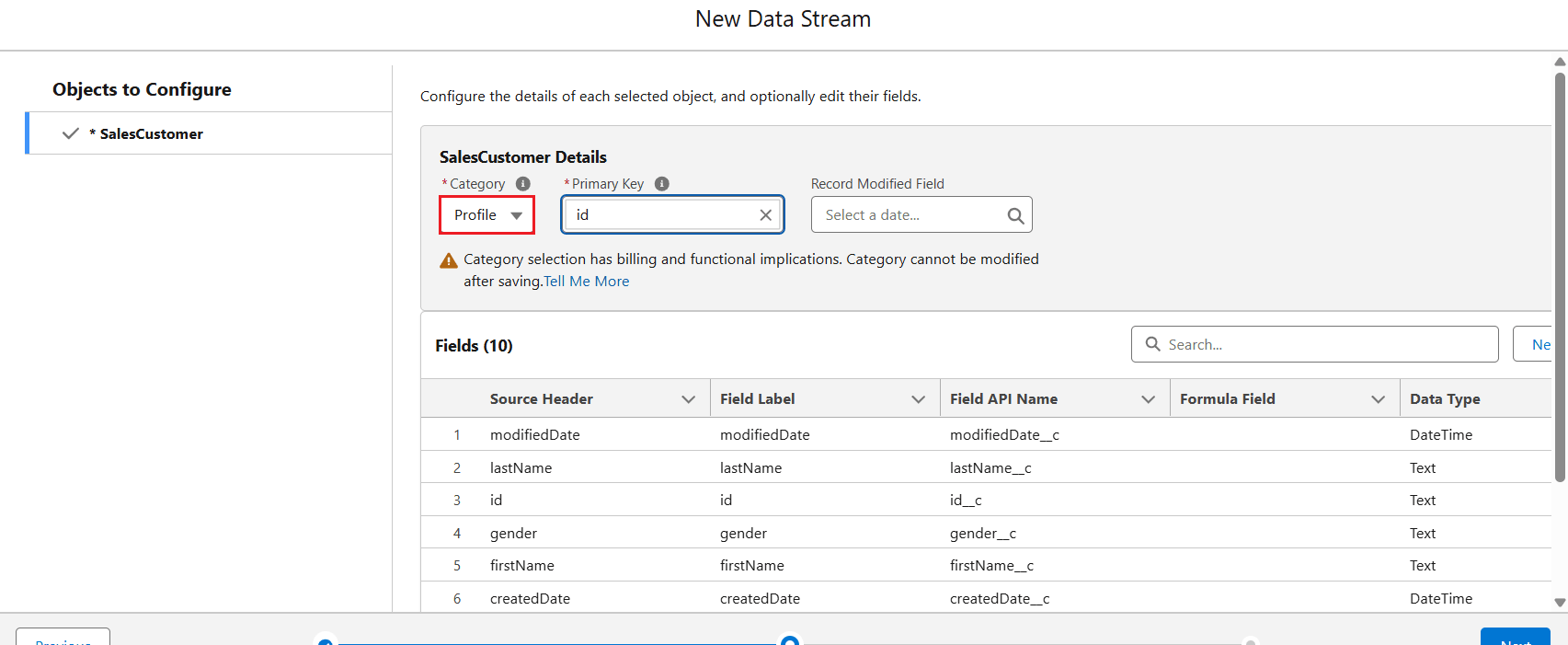
- Now, configure the selected object by adding the Category and Primary Key, then click Next.
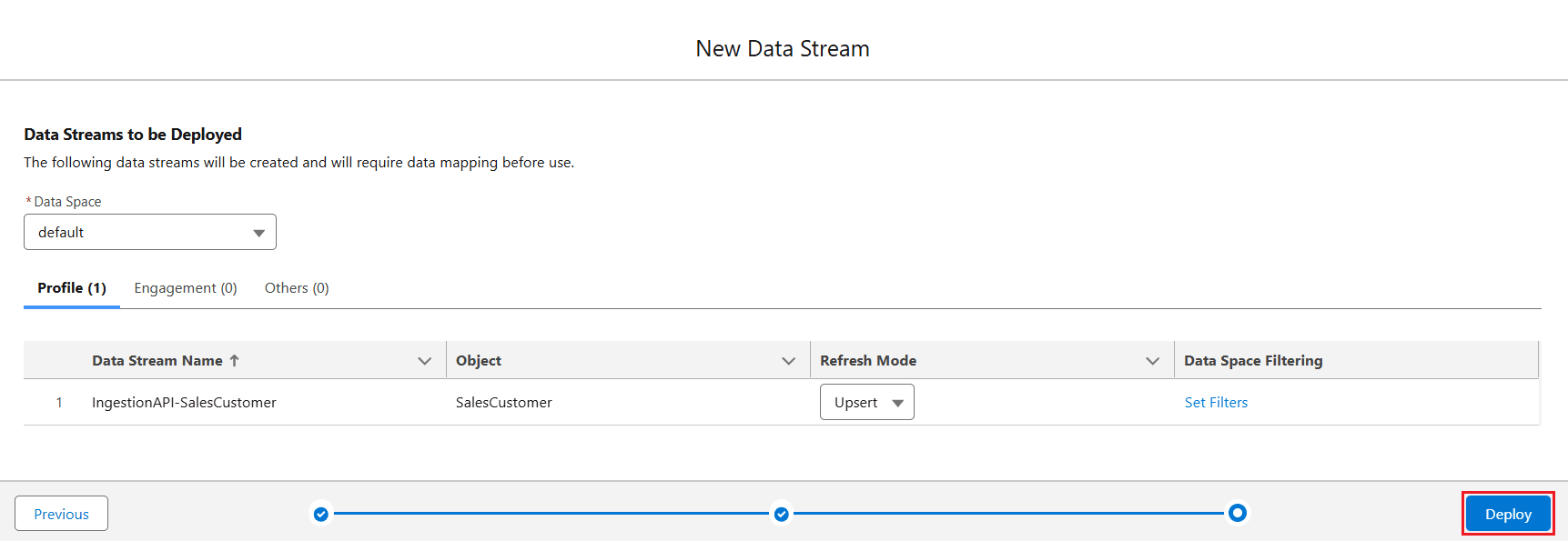
- In the following window, the object appears in the list of the associated category (Profile, Engagement, or Others). Select the Refresh Mode as Upsert and click Deploy.
- The Data Stream is now created.
Step 4: Create a Data Mapping
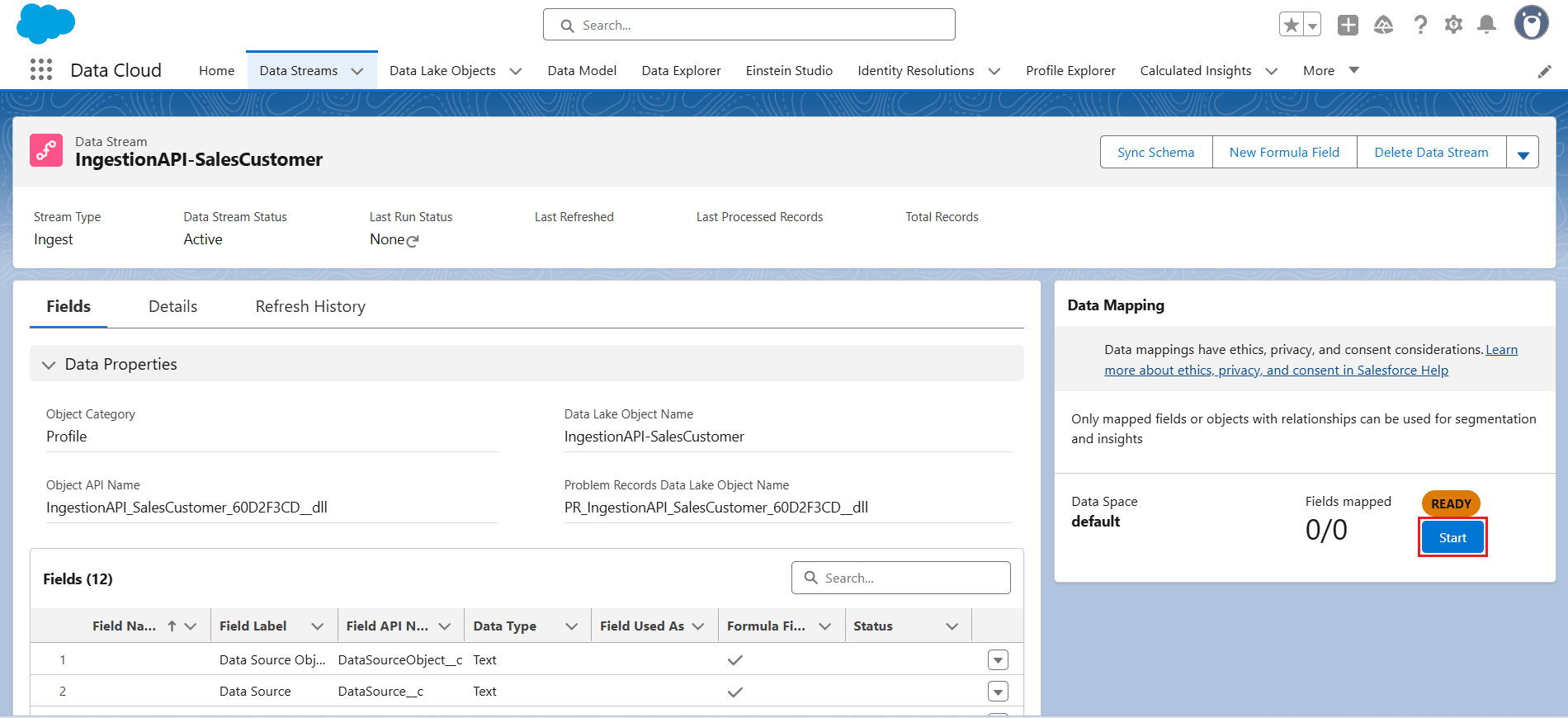
- Once the Data Stream is created, click Start under Data Mapping.
- In the Data Mapping screen, the unmapped metadata from the object uploaded via the Ingestion API appears on the left panel. This metadata needs to be mapped to a Data Model Object (DMO), which can be selected from a Standard Data Model or created as a Custom Object based on the input data.
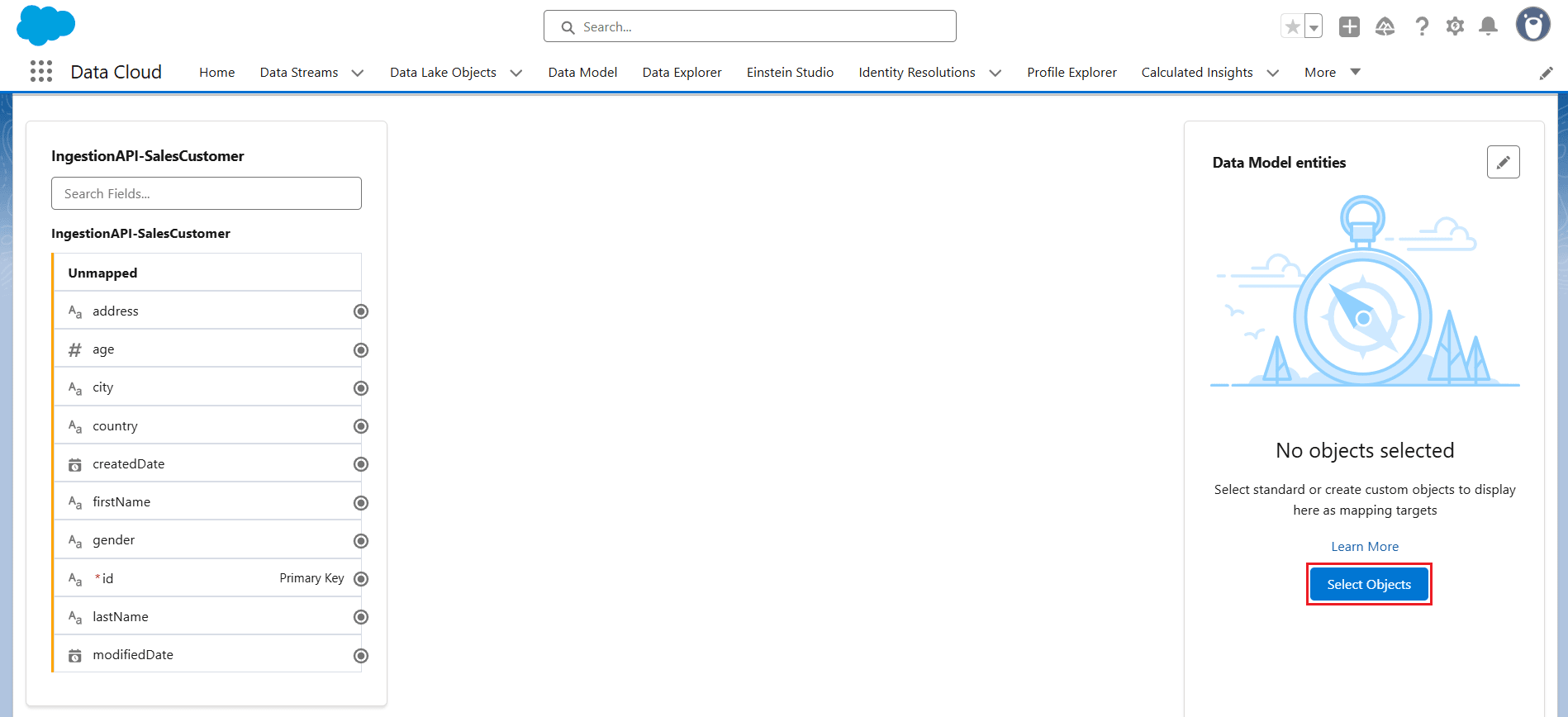
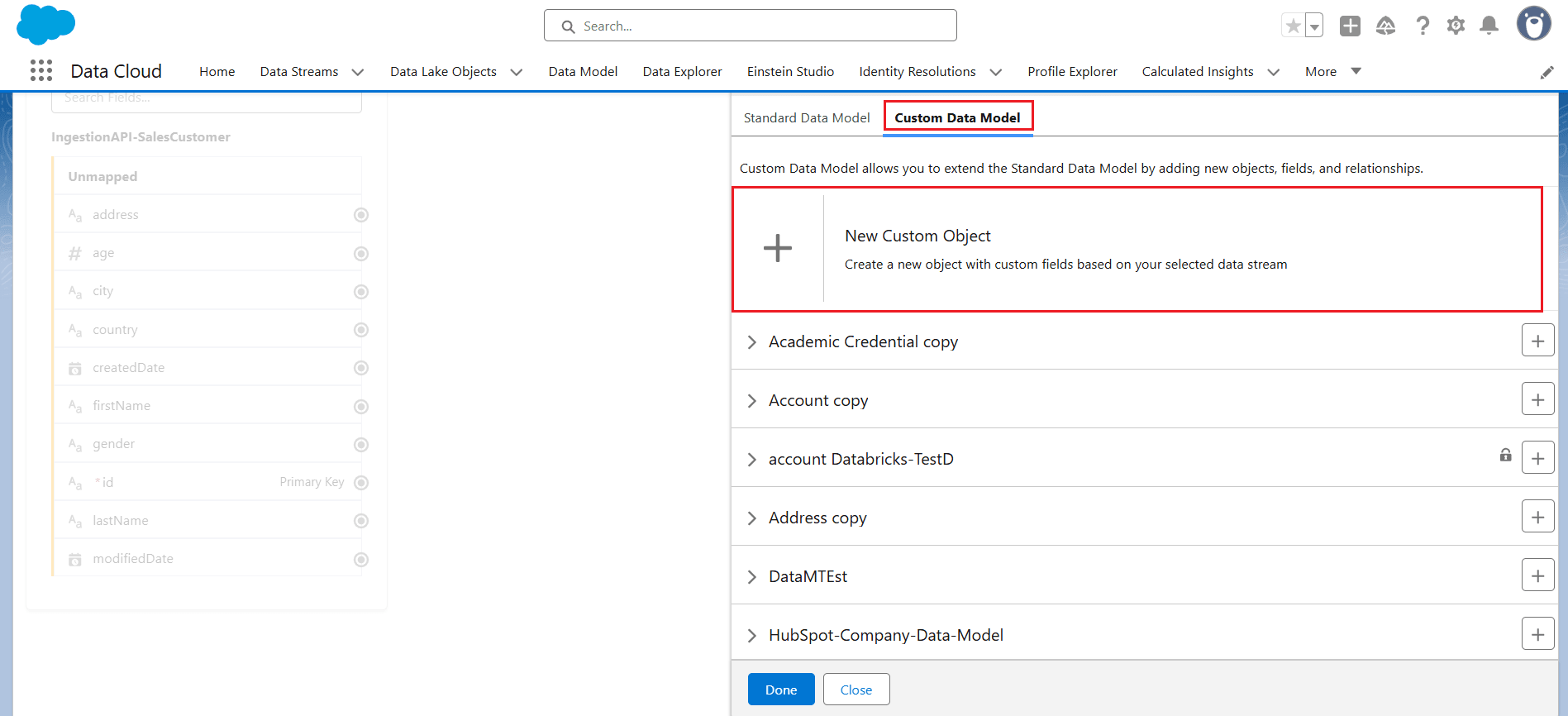
- Click Select Objects under Data Model entities and choose Custom Data Model > New Custom Object.
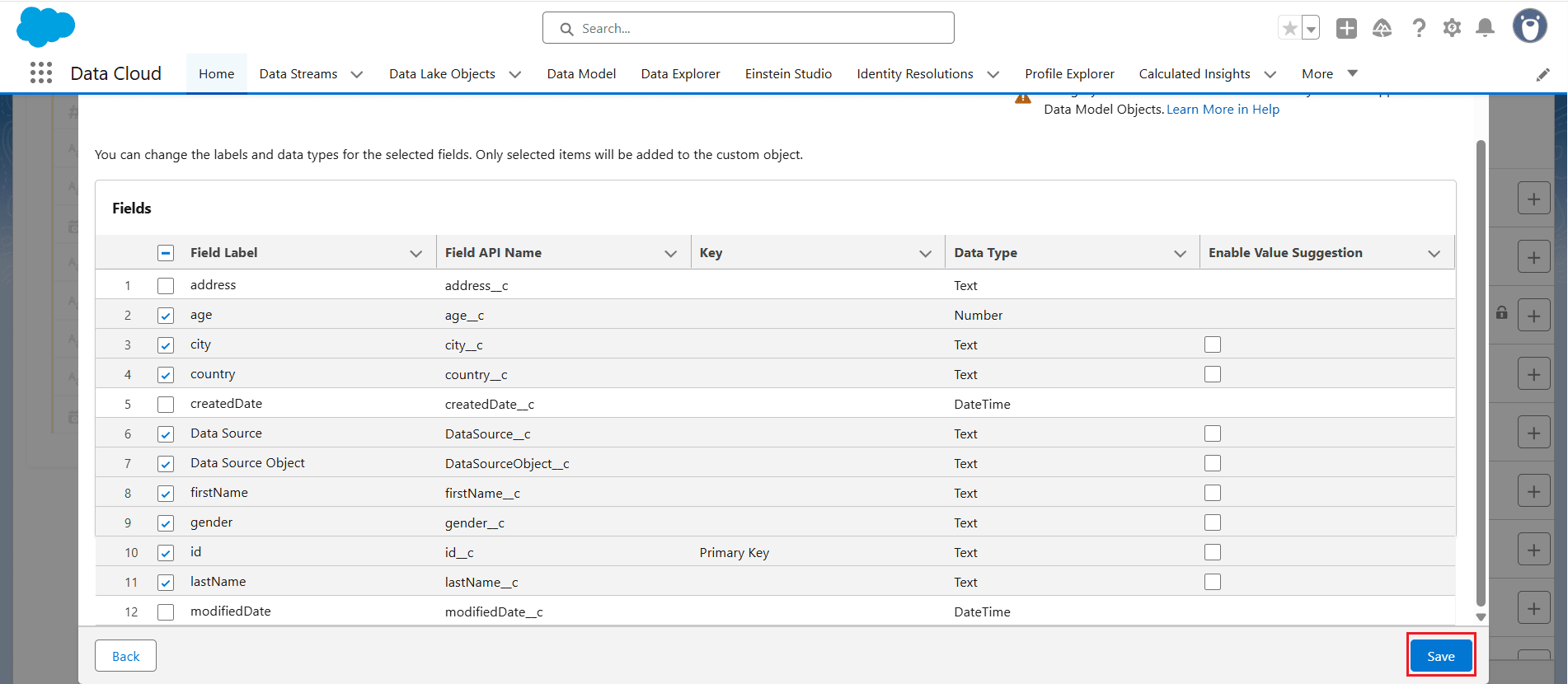
- Select the required fields you want to receive from the input object, making sure to include the Primary Key field. Then click Save.
- Click Save & Close to save the mappings.
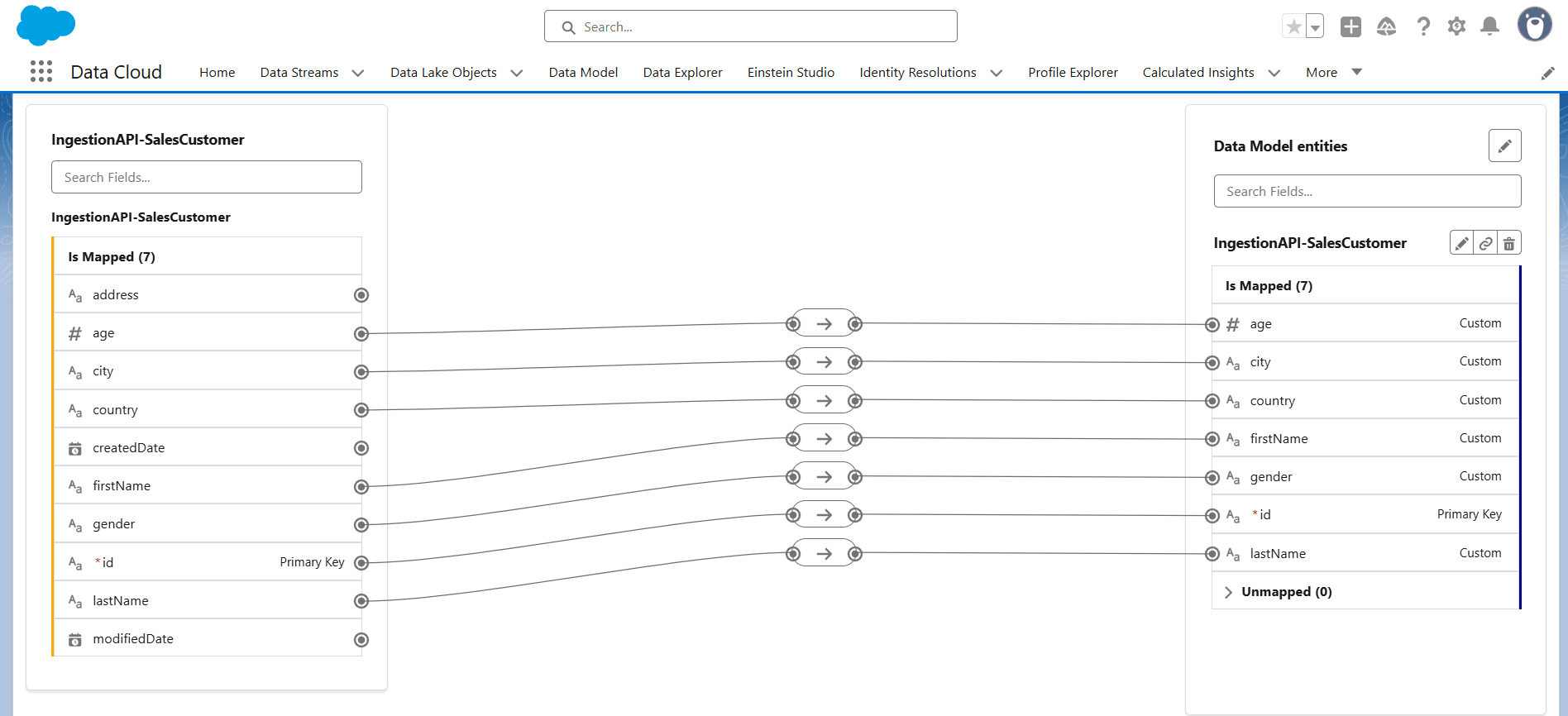
- The mappings are now successfully added.
- Select Data Lake Objects, click on the created Data Stream, and review the mappings to ensure they are correct.
Step 5: Connect to Salesforce Data Cloud with CData
Generate a JDBC URL for connecting to Salesforce, beginning with jdbc:salesforcedatacloud:, followed by a series of semicolon-separated connection string properties.
There are several authentication methods available for connecting to SFDC: OAuth, OAuthClient, OAuthPassword, OAuthJWT, and OAuthPKCE.
Select OAuth authentication, and set InitiateOAuth to GETANDREFRESH. Under Connection Properties, click Advanced and set Enable As Upsert under Miscellaneous to 'ALL'. Now, click Test Connection to check and confirm the connection with SFDC.
See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for more information.
Built-in Connection String Designer
To help construct the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Salesforce JDBC Driver. You can either double-click the JAR file or execute it from the command line:
java -jar cdata.jdbc.salesforce.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the generated connection string to your clipboard.
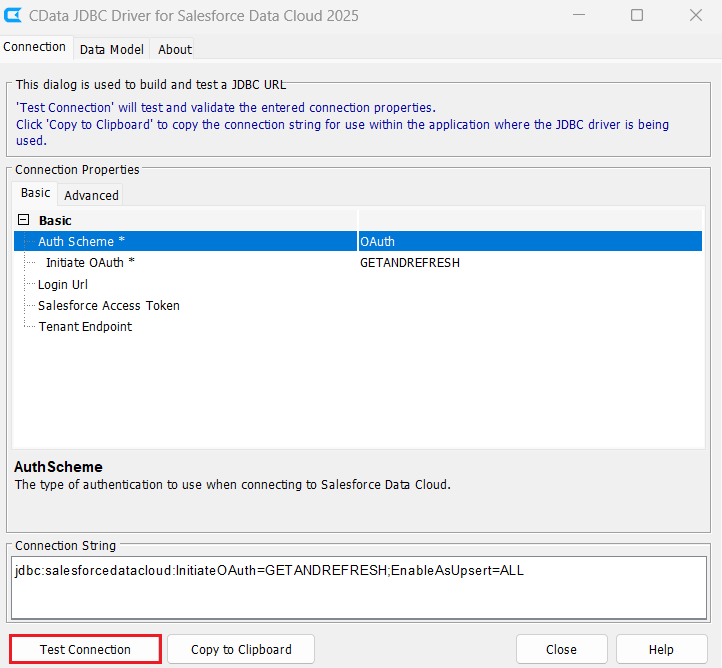
A typical JDBC URL is shown below:
jdbc:salesforcedatacloud:InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH;EnableAsUpsert=ALL
Step 6: Ingesting Data into Salesforce Data Cloud
Once all settings are configured in SFDC and a successful connection is made using the CData Salesforce Data Cloud JDBC driver, create a database connection in DBeaver using the JDBC URL. Then follow these steps to ingest data into SFDC:
- Expand the SalesforceDataCloud database created in DBeaver.
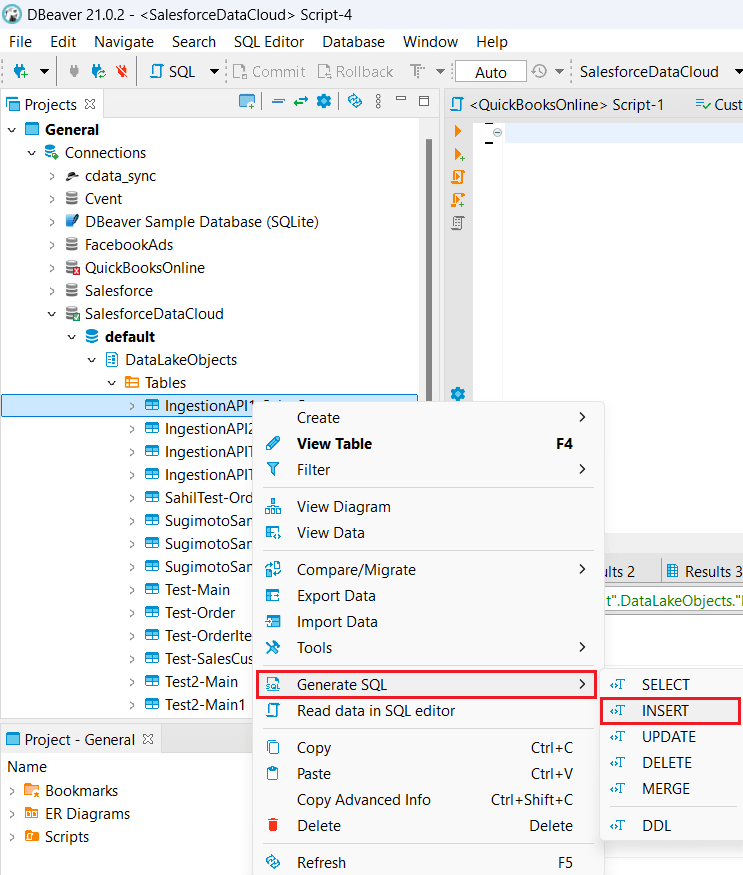
- Under DataLakeObjects, click the Tables dropdown, right-click the Data Stream you created, and select Generate SQL > INSERT.
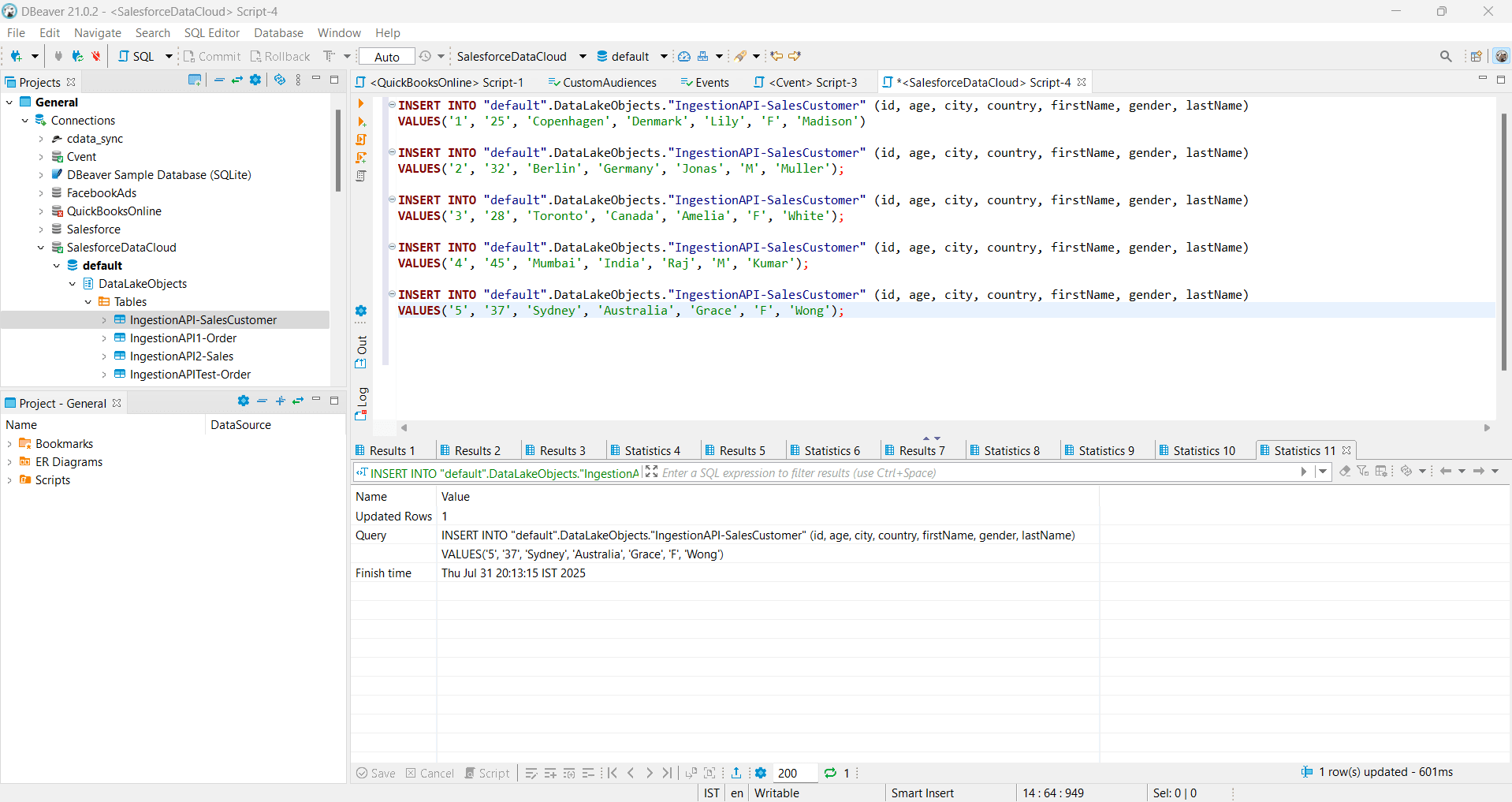
- Copy the generated INSERT statement from the SQL Preview, open an SQL Script, paste the query, and modify it to insert the required data.
- Execute the SQL statement. It typically takes ~3 minutes to insert the data into SFDC.
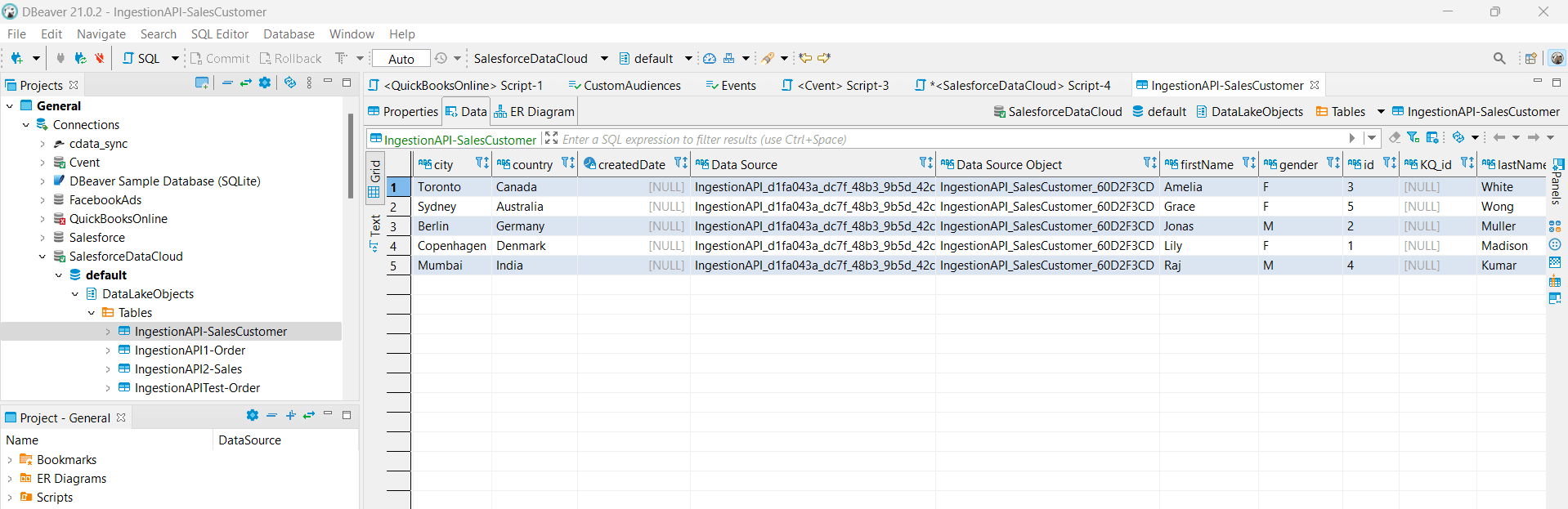
By following this process and using the Ingestion API in SFDC, you can ingest data from any external data source into Salesforce Data Cloud.
Effortlessly Ingest Data into Salesforce Data Cloud with CData Connectivity
In this walkthrough, we successfully established a streamlined data ingestion pipeline into Salesforce Data Cloud using the CData Salesforce Data Cloud JDBC driver. By leveraging CData's robust connectivity framework, we can integrate external data sources directly into Salesforce's real-time Customer Data Platform (CDP), eliminating the need for manual ETL processes or intermediate storage layers.
Ready to get started? Download a free 30-day trial of the CData Salesforce Data Cloud JDBC driver today. As always, our world-class Support Team is available to help with any questions you may have.


