Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Configure the CData JDBC Driver for Adobe Target in a Connection Pool in Tomcat
Connect to Adobe Target data from a connection pool in Tomcat.
The CData JDBC Drivers support standard JDBC interfaces to integrate with Web applications running on the JVM. This article details how to connect to Adobe Target data from a connection pool in Tomcat.
Connect to Adobe Target Data through a Connection Pool in Tomcat
- Copy the CData JAR and CData .lic file to $CATALINA_HOME/lib. The CData JAR is located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
- Add a definition of the resource to the context. Specify the JDBC URL here.
To connect to Adobe Target, you must provide the Tenant property along with OAuth connection properties mentioned below. Note that while other connection properties can influence processing behavior, they do not affect the ability to connect.
To determine your Tenant name:
- Log in to Adobe Experience. The URL will look similar to: "https://experience.adobe.com/#/@mycompanyname/preferences/general-section".
- Extract the value after the "/#/@". In this example, it is "mycompanyname".
- Set the Tenant connection property to that value.
User Accounts (OAuth)
You must set AuthScheme to OAuthClient for all user account flows.
Note: Adobe authentication via OAuth requires updating your token every two weeks.
All Applications
CData provides an embedded OAuth application that simplifies OAuth authentication. Alternatively, you can create a custom OAuth application. Review Creating a Custom OAuth App in the Help documentation for more information.Obtaining the OAuth Access Token
Set the following properties to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: Set to GETANDREFRESH to automatically perform the OAuth exchange and refresh the OAuthAccessToken as needed.
- OAuthClientId : Set to the client Id assigned when you registered your app.
- OAuthClientSecret : Set to the client secret assigned when you registered your app.
- CallbackURL : Set to the redirect URI defined when you registered your app. For example: https://localhost:3333
With these settings, the provider obtains an access token from Adobe Target, which it uses to request data. The OAuth values are stored in the location specified by OAuthSettingsLocation, ensuring they persist across connections.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Adobe Target JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.adobetarget.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
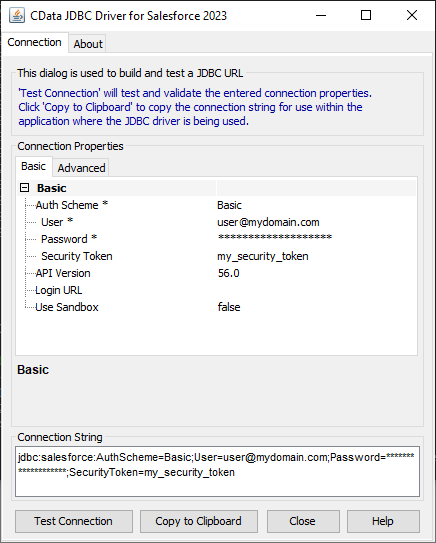
You can see the JDBC URL specified in the resource definition below.
<Resource name="jdbc/adobetarget" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource" driverClassName="cdata.jdbc.adobetarget.AdobeTargetDriver" factory="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSourceFactory" url="jdbc:adobetarget:Tenant=mycompanyname;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH" maxActive="20" maxIdle="10" maxWait="-1" />
To allow a single application to access Adobe Target data, add the code above to the context.xml in the application's META-INF directory.
For a shared resource configuration, add the code above to the context.xml located in $CATALINA_BASE/conf. A shared resource configuration provides connectivity to Adobe Target for all applications.
- Add a reference to the resource to the web.xml for the application.
Adobe Target data JSP jdbc/AdobeTarget javax.sql.DataSource Container
-
Initialize connections from the connection pool:
Context initContext = new InitialContext(); Context envContext = (Context)initContext.lookup("java:/comp/env"); DataSource ds = (DataSource)envContext.lookup("jdbc/AdobeTarget"); Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
More Tomcat Integration
The steps above show how to connect to Adobe Target data in a simple connection pooling scenario. For more use cases and information, see the JNDI Datasource How-To in the Tomcat documentation.


