Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Create Power BI Reports on Real-Time ADP Data
Use the CData ODBC Driver for ADP to visualize ADP data in Power BI Desktop.
With built-in support for ODBC on Microsoft Windows, the CData ODBC Drivers provide self-service integration with self-service analytics tools such as Microsoft Power BI. The CData ODBC Driver for ADP links your Power BI reports to operational ADP data. You can monitor ADP data through dashboards and ensure that your analysis reflects ADP data in real time by scheduling refreshes or refreshing on demand. This article details how to use the ODBC driver to create real-time visualizations of ADP data in Microsoft Power BI Desktop and then upload to Power BI.
The CData ODBC Drivers offer unmatched performance for interacting with live ADP data in Power BI due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from Power BI to ADP, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to ADP and utilizes the embedded SQL Engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze ADP data using native Power BI data types.
Connect to ADP as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
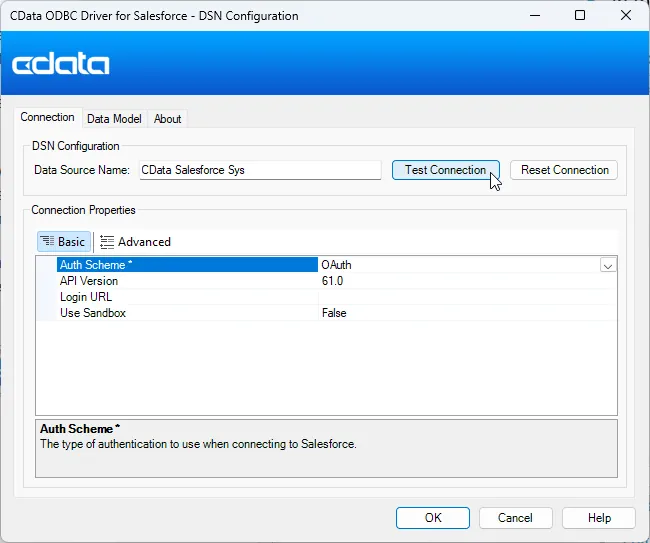
Connect to ADP by specifying the following properties:
- OAuthClientId: The client Id of the custom OAuth application you obtained from ADP.
- OAuthClientSecret: The custom OAuth application's client secret.
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the certificate provided during registration.
- SSLClientCertPassword: Set this to the password of the certificate.
- UseUAT: The connector makes requests to the production environment by default. If using a developer account, set UseUAT = true.
- RowScanDepth: The maximum number of rows to scan for the custom fields columns available in the table. The default value will be set to 100. Setting a high value may decrease performance.
The connector uses OAuth to authenticate with ADP. OAuth requires the authenticating user to interact with ADP using the browser. OAuth access can be configured in ADP through ADP API Central. For more information, refer ADP's API Central Quick Start Guide and the OAuth section in CData's Help documentation.
Create Data Visualizations
After creating an ODBC DSN, follow the steps below to connect to the ADP ODBC DSN from Power BI Desktop:
-
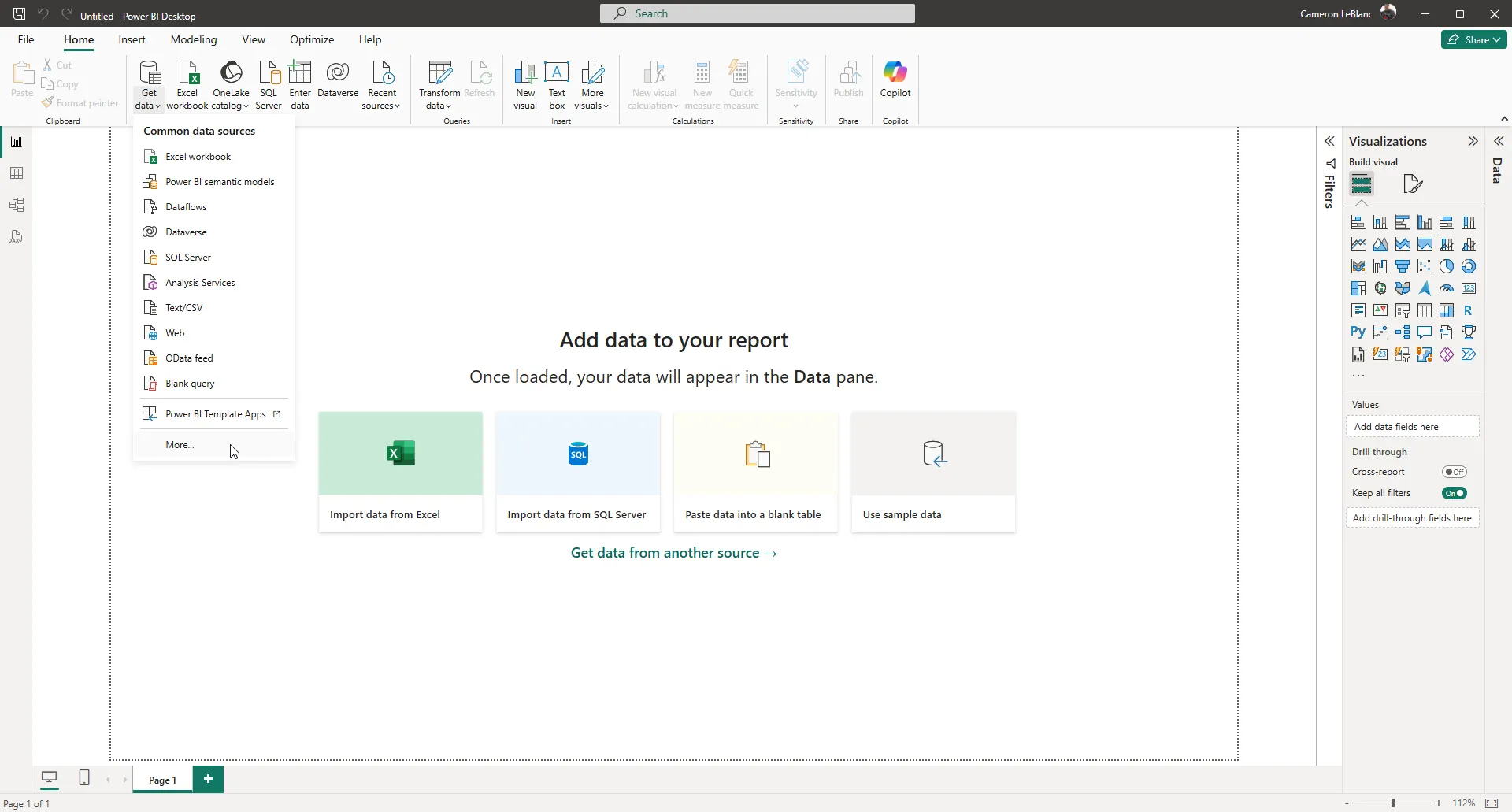
Open Power BI Desktop and click Get Data -> More... to open the Get Data window.
-
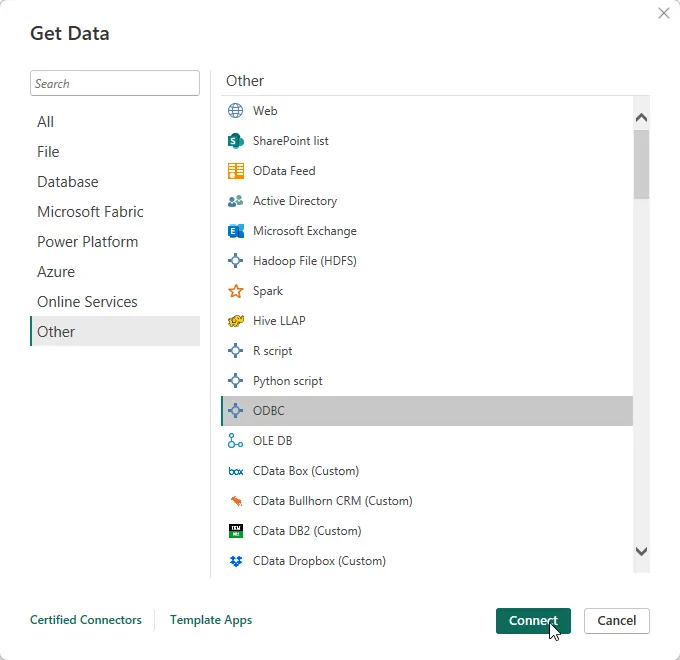
In the Get Data window select Other -> ODBC to open the next window.
-
Select the DSN in the menu. If you know the SQL query you want to use to import data, you can expand the Advanced options node and enter the query in the SQL Statement box. Otherwise, click OK to continue.

-
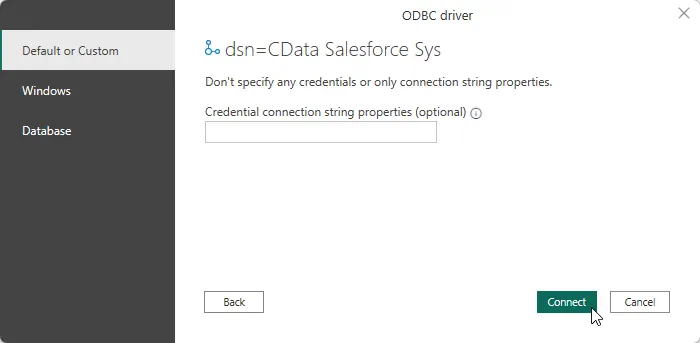
Choose Default or Custom as the authentication option and click Connect.
-
Select tables in the Navigator dialog.
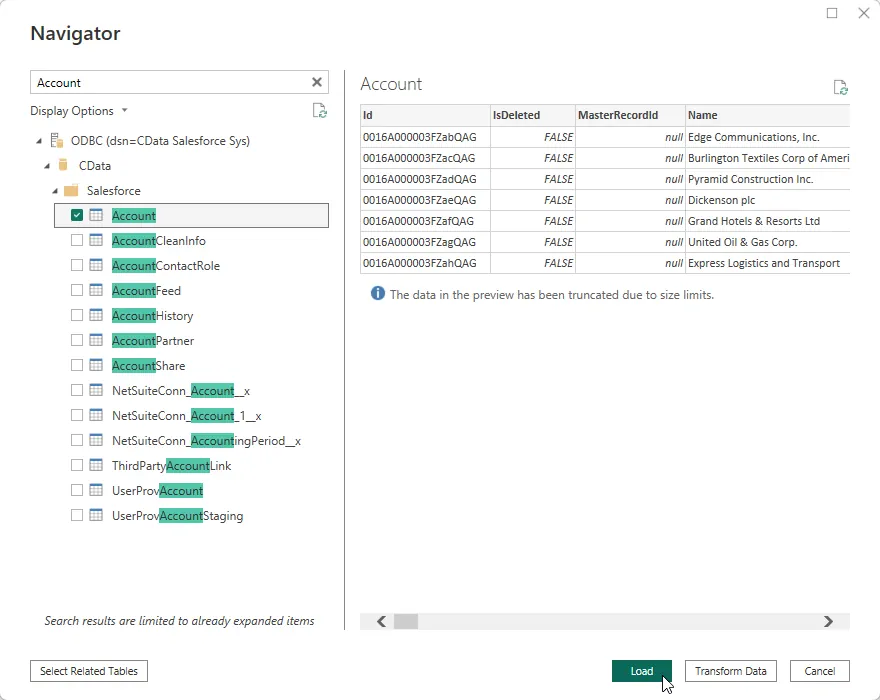
-
Click Transform Data to edit the query. The table you imported is displayed in the Power Query Editor. In the Power Query Editor, you can enrich your local copy of ADP data with other data sources, pivot ADP columns, and more. Power BI detects each column's data type from the ADP metadata retrieved by the driver.
Power BI records your modifications to the query in the Applied Steps section, adjusting the underlying data retrieval query that is executed to the remote ADP data. When you click Close and Apply, Power BI executes the data retrieval query.
Otherwise, click Load to pull the data into Power BI.
Create Data Visualizations
After pulling the data into Power BI, you can create data visualizations in the Report view by dragging fields from the Fields pane onto the canvas. Follow the steps below to create a pie chart (Salesforce shown):
- Select the pie chart icon in the Visualizations pane.
- Select a dimension in the Fields pane: for example, Name.
- Select a measure in the Fields pane: for example, Annual Revenue.
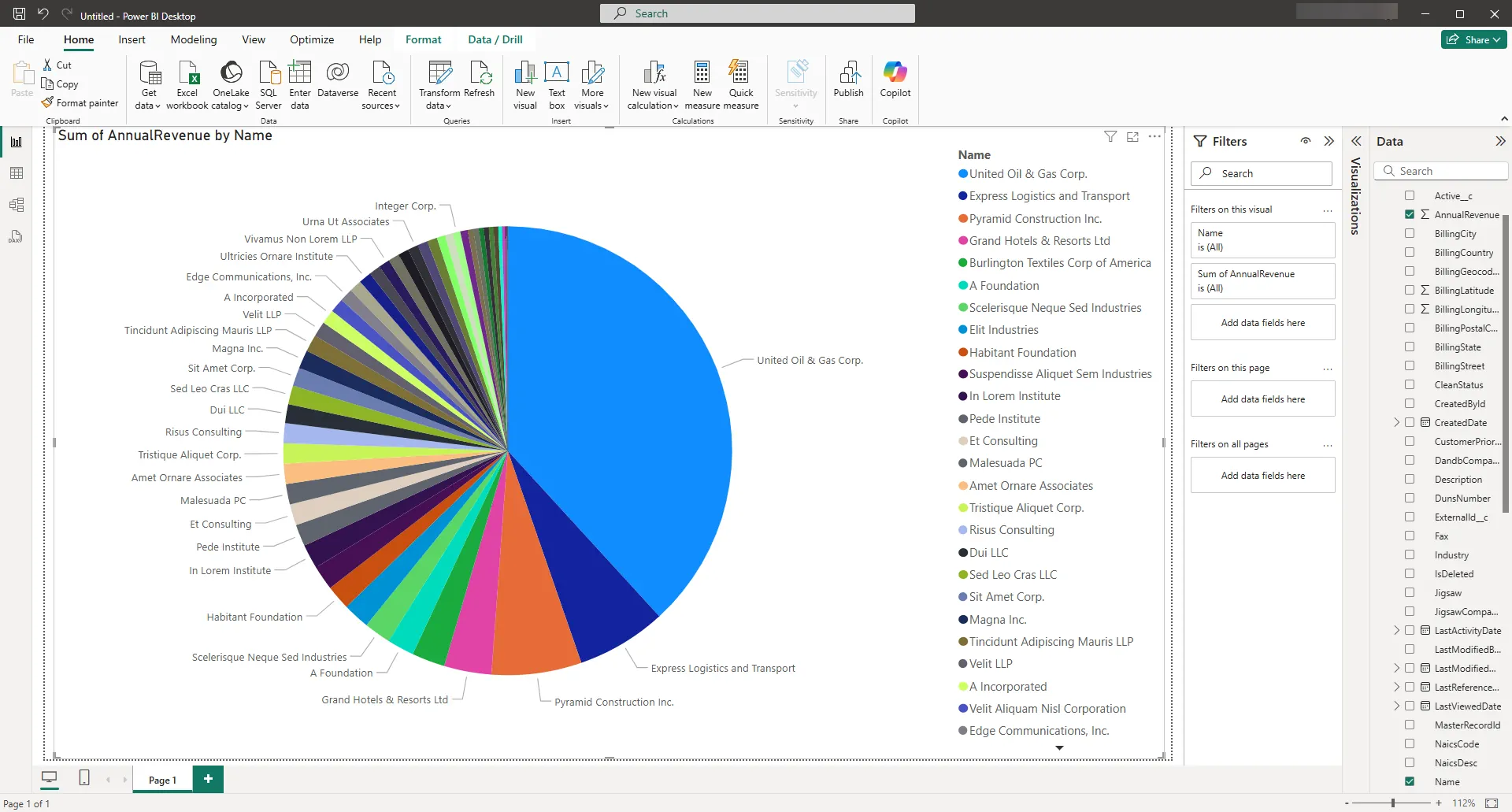
You can change sort options by clicking the ellipsis (...) button for the chart. Options to select the sort column and change the sort order are displayed.
You can use both highlighting and filtering to focus on data. Filtering removes unfocused data from visualizations; highlighting dims unfocused data. You can highlight fields by clicking them:
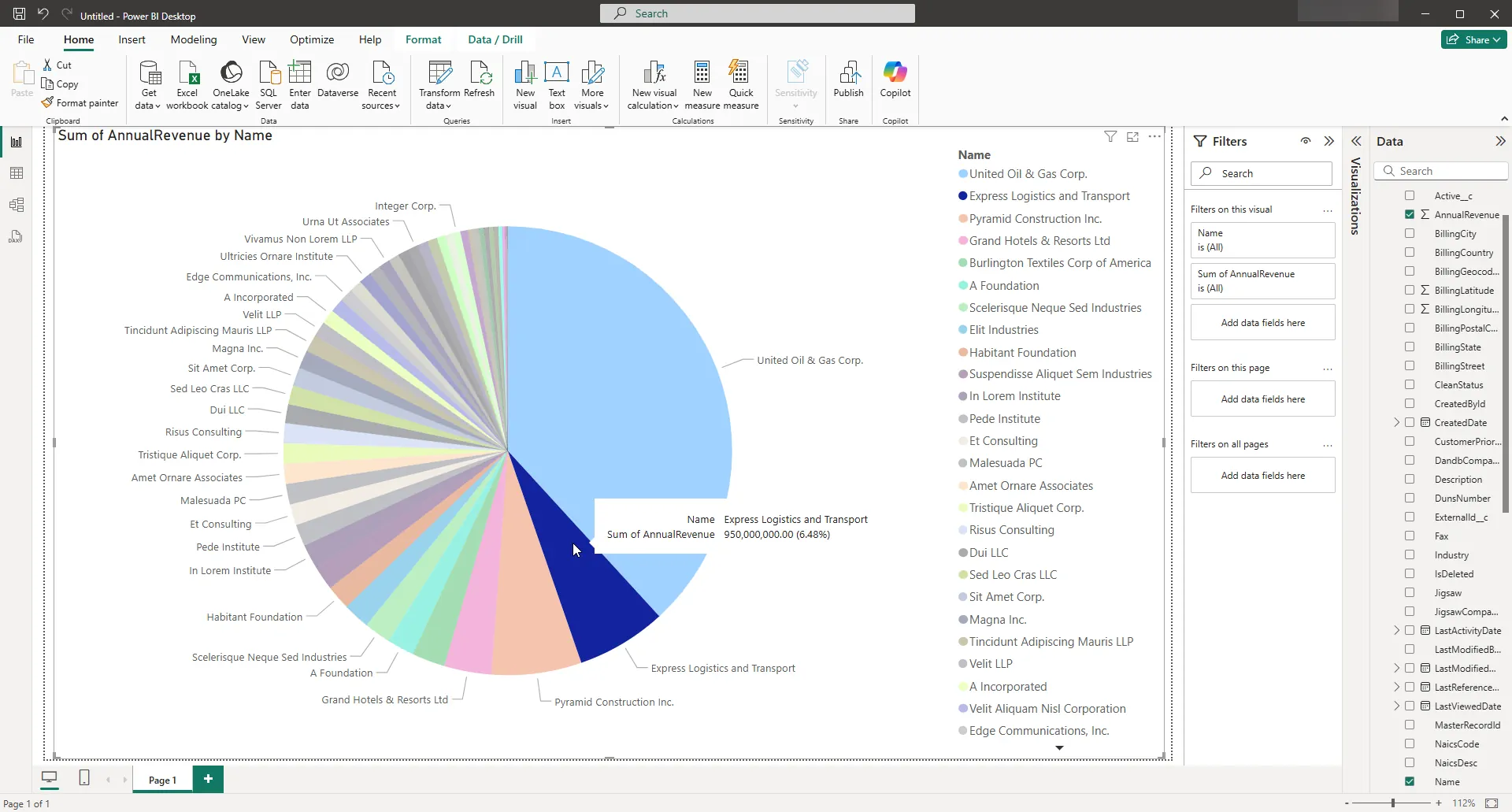
You can apply filters at the page level, at the report level, or to a single visualization by dragging fields onto the Filters pane. To filter on the field's value, select one of the values that are displayed in the Filters pane.
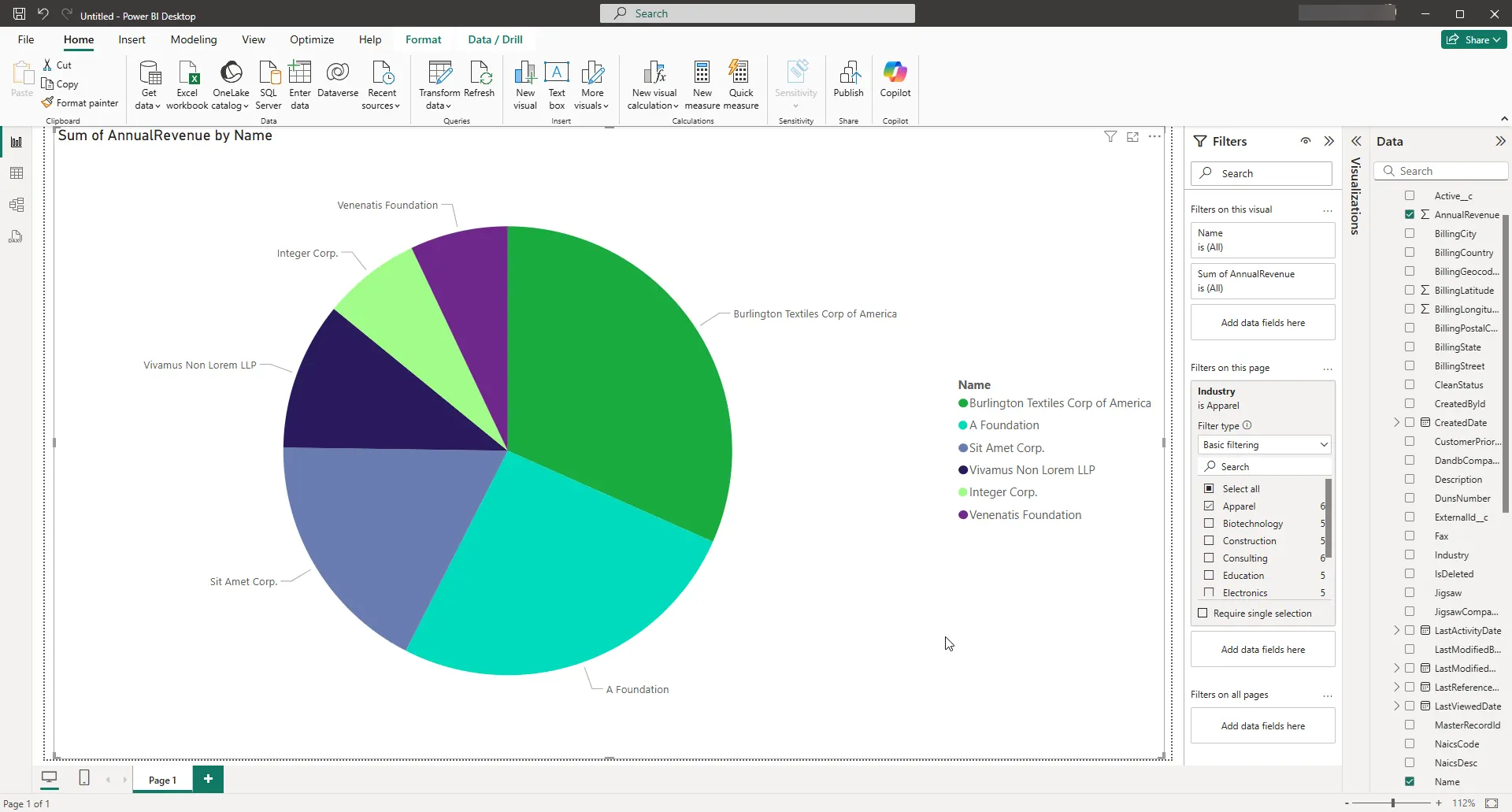
Click Refresh to synchronize your report with any changes to the data.
Free Trial & More Information
If you are interested in connecting to your ADP data from Microsoft Power BI, or any applications that support ODBC connectivity, download a free, 30-day trial of the CData ODBC Driver for ADP. As always, our world-class support team is ready to answer any questions you may have.


