Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Build AlloyDB-Connected Web Apps with Axios and CData Connect Cloud
Use CData Connect Cloud to connect to live AlloyDB data and build AlloyDB-connected web apps with Axios.
Axios is a JavaScript library that allows developers to make HTTP requests to servers from a web browser or Node.js. When paired with CData Connect Cloud, you get access to live AlloyDB data for your web apps. This article shows how to connect to AlloyDB and build web apps in Axios with access to live AlloyDB data.
Connect to AlloyDB from Axios
To work with AlloyDB in Axios, we need to connect to AlloyDB from Connect Cloud, provide user access to the connection, and create a Workspace for the AlloyDB data.
Connect to AlloyDB from Connect Cloud
CData Connect Cloud uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources.
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Sources, and then click Add Connection
- Select "AlloyDB" from the Add Connection panel
-
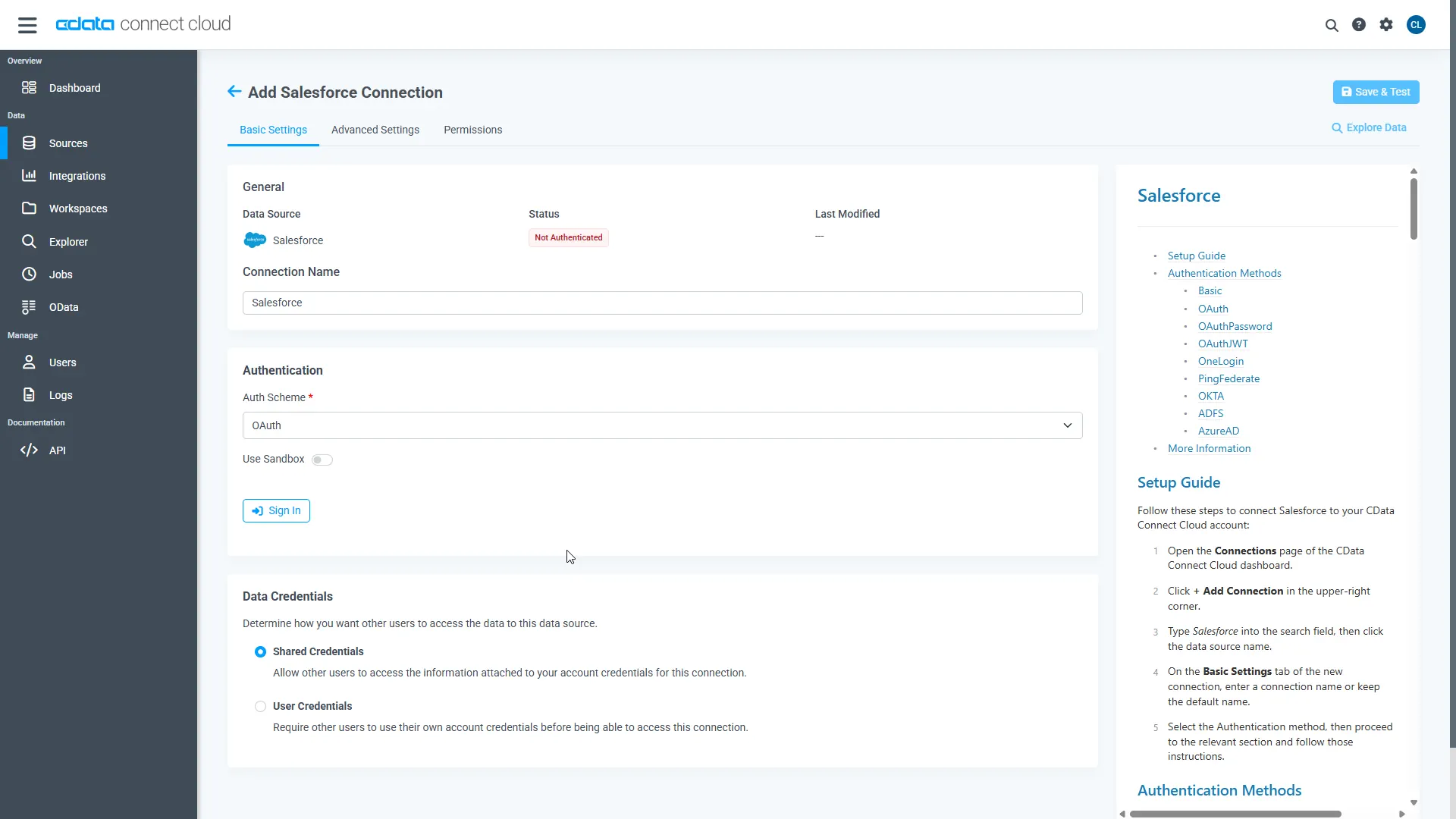
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to AlloyDB.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
- Click Create & Test
-
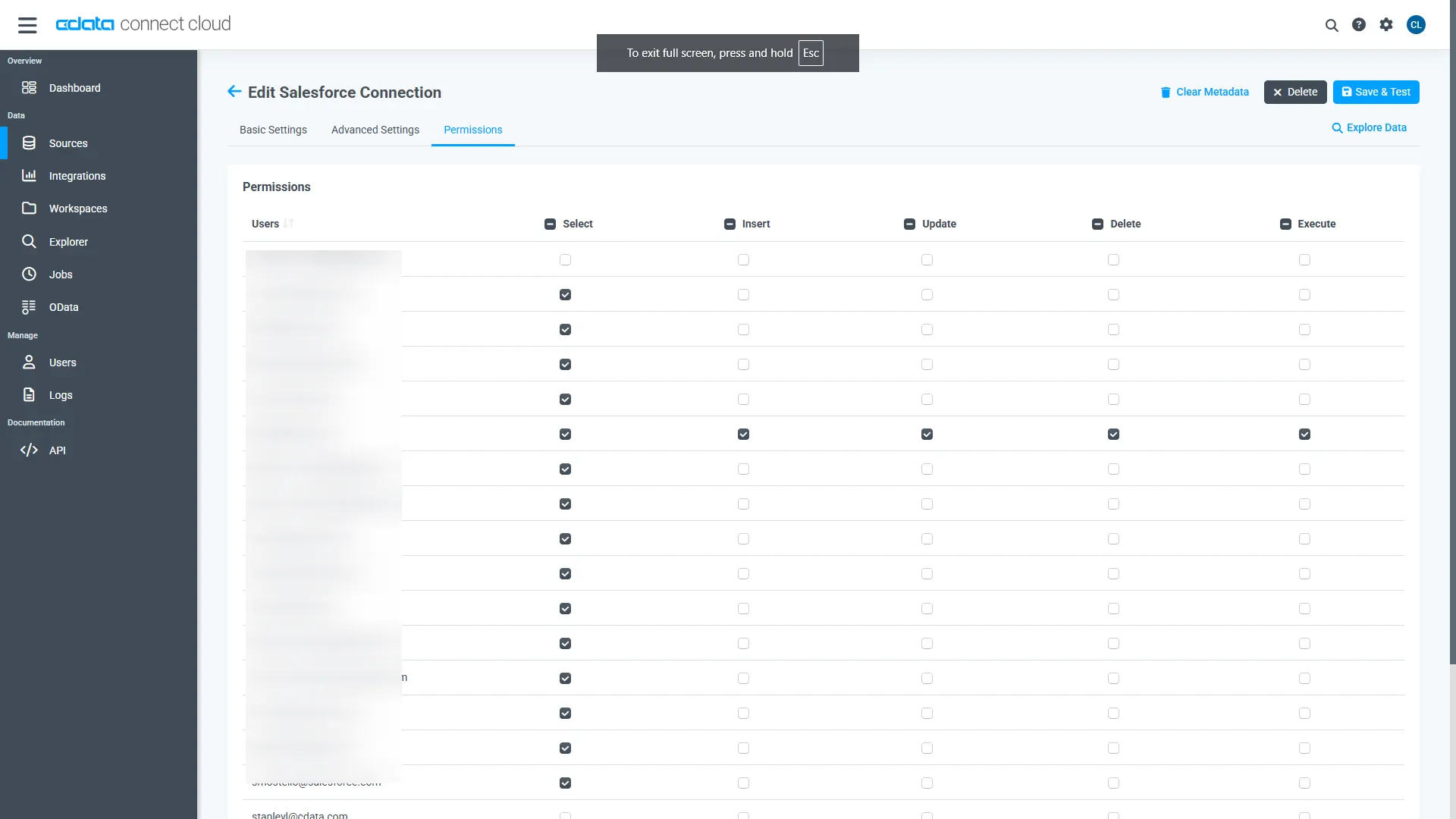
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add AlloyDB Connection page and update the User-based permissions.

Add a Personal Access Token
When connecting to Connect Cloud through the REST API, the OData API, or the Virtual SQL Server, a Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect Cloud. It is best practice to create a separate PAT for each service to maintain granularity of access.
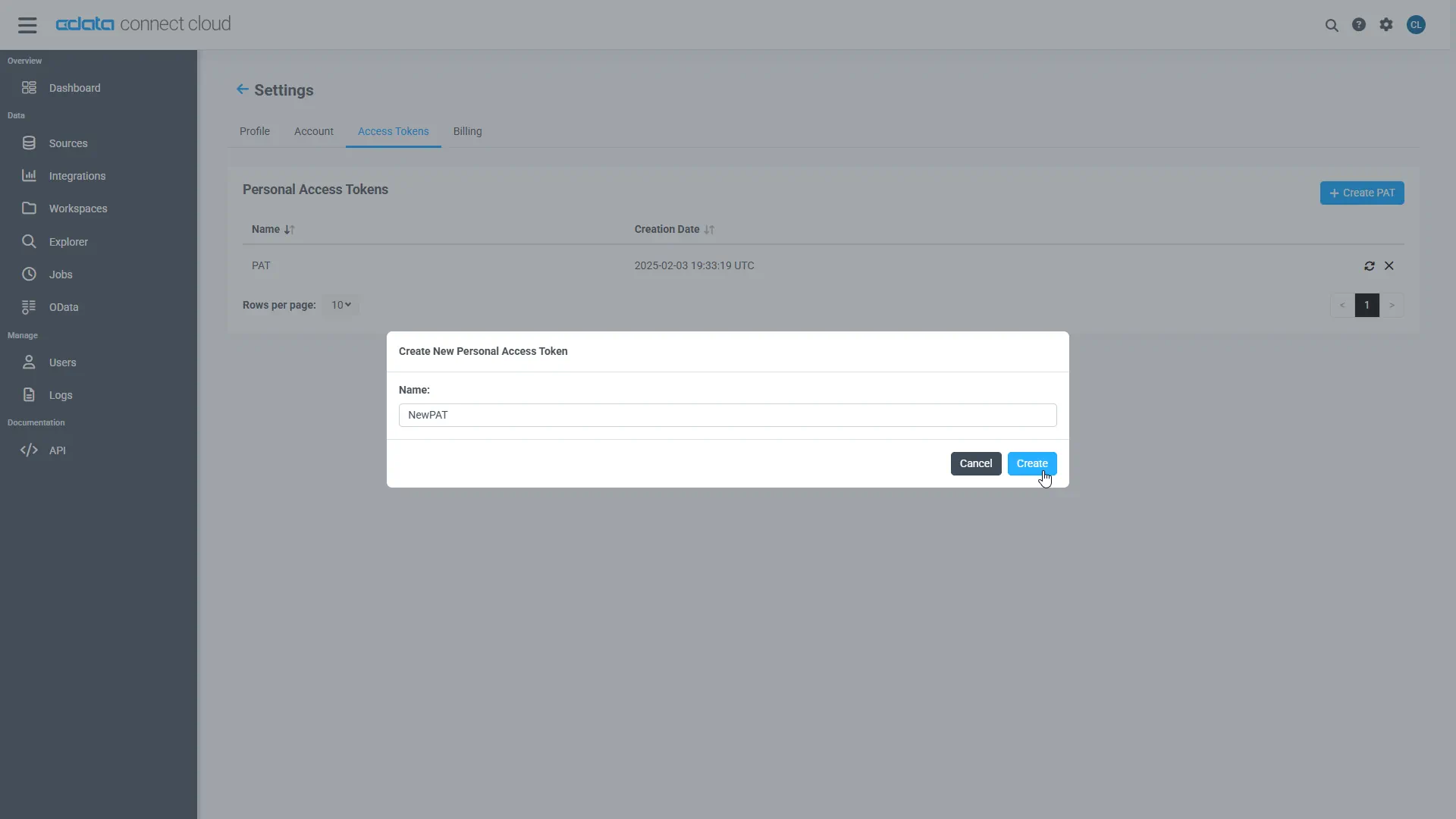
- Click on the Gear icon () at the top right of the Connect Cloud app to open the settings page.
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
-
Give the PAT a name and click Create.
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
Configure AlloyDB Endpoints for Axios
After connecting to AlloyDB, create a workspace for your desired table(s).
-
Navigate to the Workspaces page and click Add to create a new Workspace (or select an existing workspace).
- Click Add to add new assets to the Workspace.
-
Select the AlloyDB connection (e.g. AlloyDB1) and click Next.
-
Select the table(s) you wish to work with and click Confirm.
- Make note of the OData Service URL for your workspace, e.g. https://cloud.cdata.com/api/odata/{workspace_name}
With the connection, PAT, and Workspace configured, you are ready to connect to AlloyDB data from Axios.
Connect to AlloyDB Data in Axios Workflows
To establish a connection from Axios to CData Connect Cloud using the OData protocol, follow these steps.
- Create a project directory for your web app. For example: ~/connect_cloud/
- Open a terminal, navigate the the project directory and initialize a node project using the command:
npm init -y
- Install the Axios dependency in the project using the following command:
npm install axios
In your project directory, create a file called server.js that contains the following code. Provide your CData Connect Cloud username (e.g. [email protected]) and PAT (the PAT you created in the prerequisites). You must also provide a query for your data, such as SELECT * FROM AlloyDB1.SCHEMA.Orders.
server.js code
const axios = require('axios') const user = '[email protected]' const pat = '***********************************'; //Your API endpoint const url = 'https://cloud.cdata.com/api/odata/{workspace_name}'; //Your data to be sent in the POST request const data = { "query":"SELECT * FROM {workspace_name}.SCHEMA.Orders" }; axios.post(url, data, { auth: { username: user, password: pat } }) .then(response => { const rows = response.data.results[0].rows; const schema = response.data.results[0].schema; //Create an array of column names const columnNames = schema.map(col => col.columnName); //Loop through each row and log the column name with its value rows.forEach(row => { const rowObject = {}; row.forEach((value, index) => { const columnName = columnNames[index]; rowObject[columnName] = value; }); console.log(rowObject); }) }) .catch(error => { console.error('Error:', error); });- In the terminal, execute the following command to run the server:
node server.js
The query results will appear:{ ID: 1, VALUE: -2 } { ID: 2, VALUE: 1 } { ID: 11, VALUE: null } { ID: 3, VALUE: 2 } { ID: 4, VALUE: 5 } ...
Simplified Access to AlloyDB Data from Cloud Applications
At this point, you have a direct connection to live AlloyDB data from Axios. For more information on gaining simplified access to data from more than 100 SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources in cloud applications like Axios, refer to our Connect Cloud page.


