Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Trigger AlloyDB IFTTT Flows in Azure App Service
This article shows how to automate IFTTT (if-this-then-that) workflows with standard wizards in Logic Apps.
Through standards-based interfaces like OData and Swagger, the CData API Server provides a native experience in Logic Apps and Power Automate with AlloyDB. OData enables real-time connectivity to data; Swagger enables scaffolding, or code generation, of wizards in Logic Apps and Power Automate, as well as scaffolding Power Apps. This article shows how to add AlloyDB to an IFTTT (if-this-then-that) workflow in a Logic App.
Set Up the API Server
If you have not already done so, download the CData API Server. Once you have installed the API Server, follow the steps below to begin producing secure AlloyDB OData services:
Connect to AlloyDB
To work with AlloyDB data in a Logic App, we start by creating and configuring a AlloyDB connection. Follow the steps below to configure the API Server to connect to AlloyDB data:
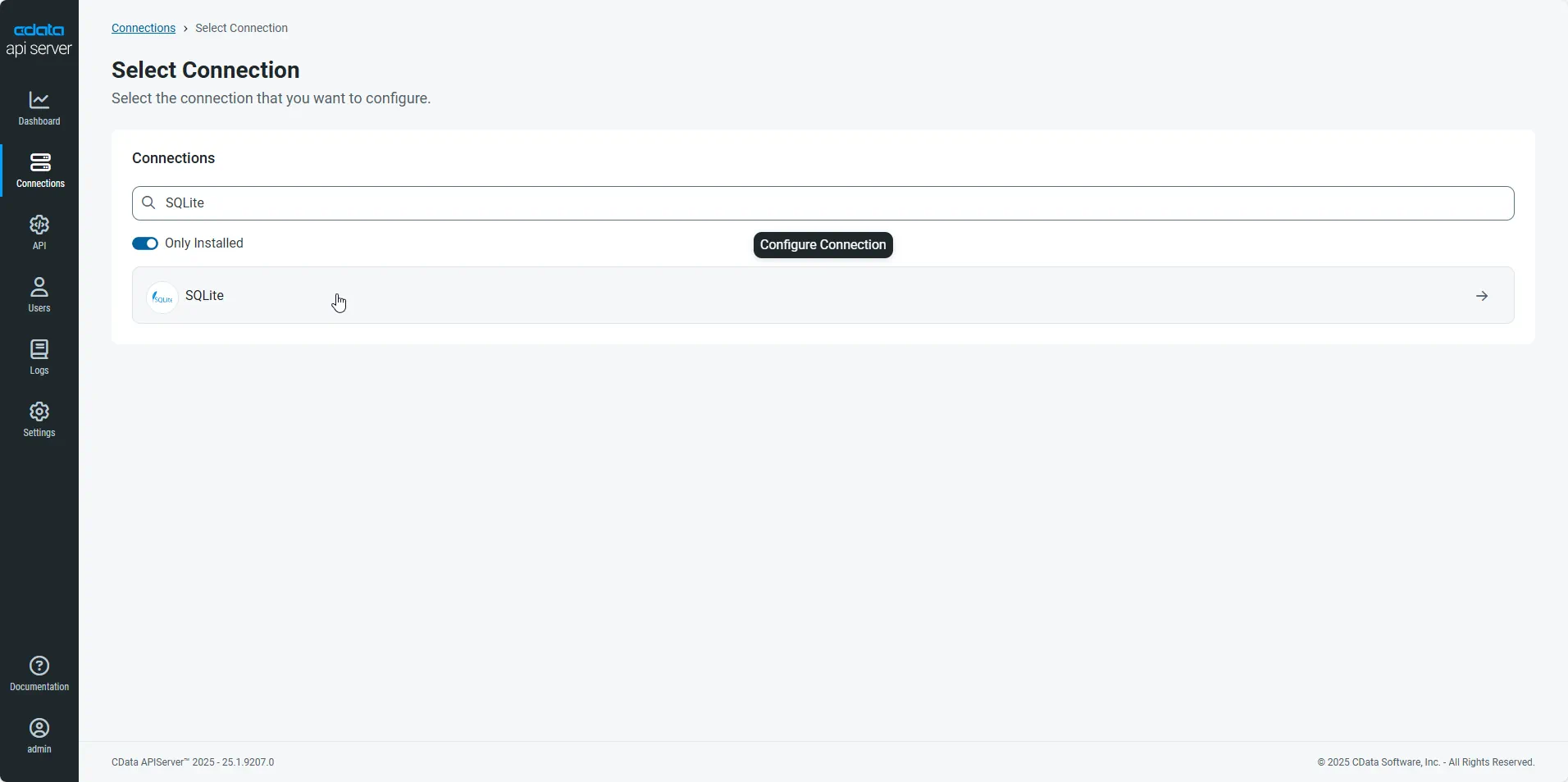
- First, navigate to the Connections page.
-
Click Add Connection and then search for and select the AlloyDB connection.
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to AlloyDB.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
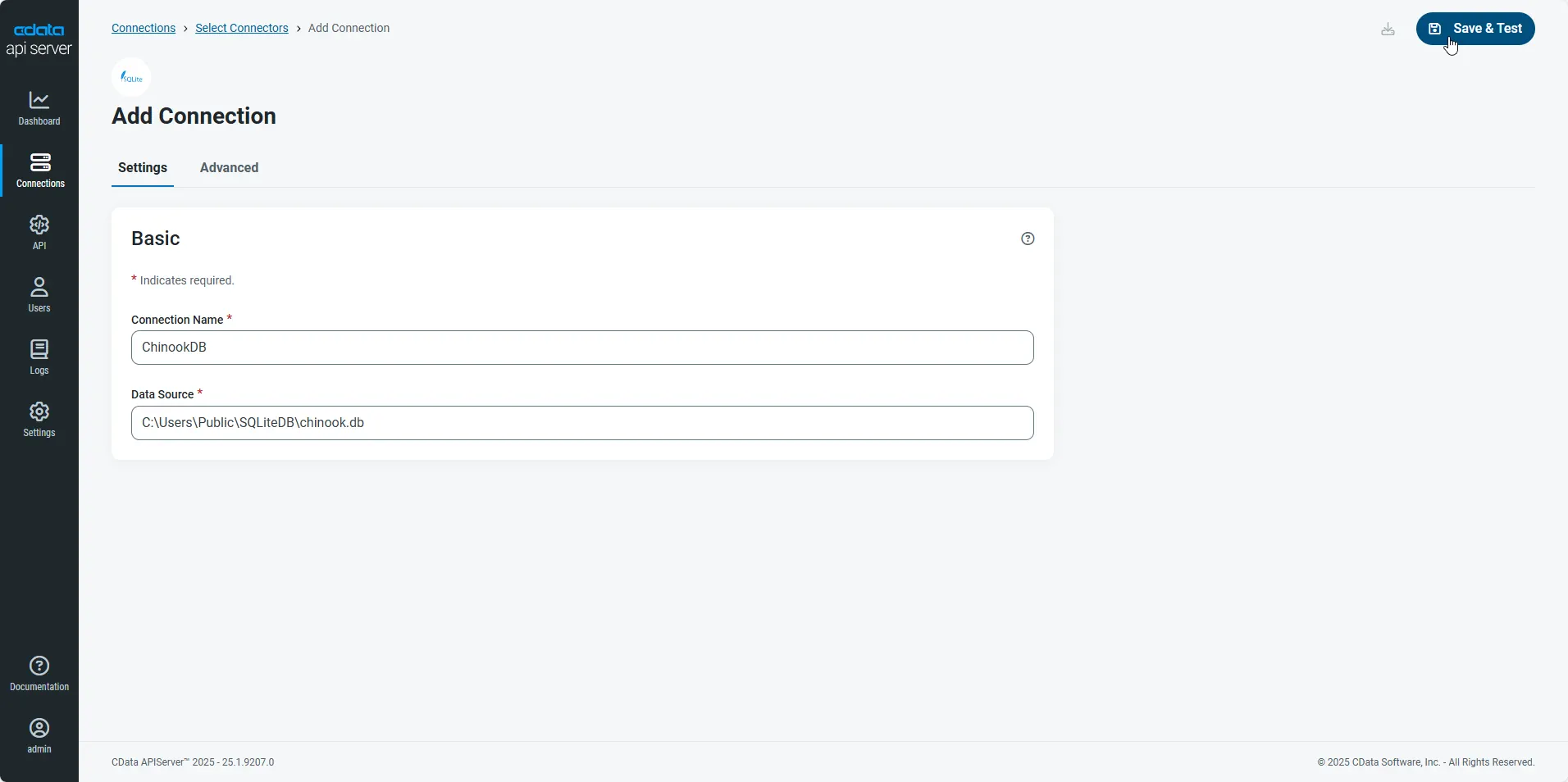
- After configuring the connection, click Save & Test to confirm a successful connection.
Configure API Server Users
Next, create a user to access your AlloyDB data through the API Server. You can add and configure users on the Users page. Follow the steps below to configure and create a user:
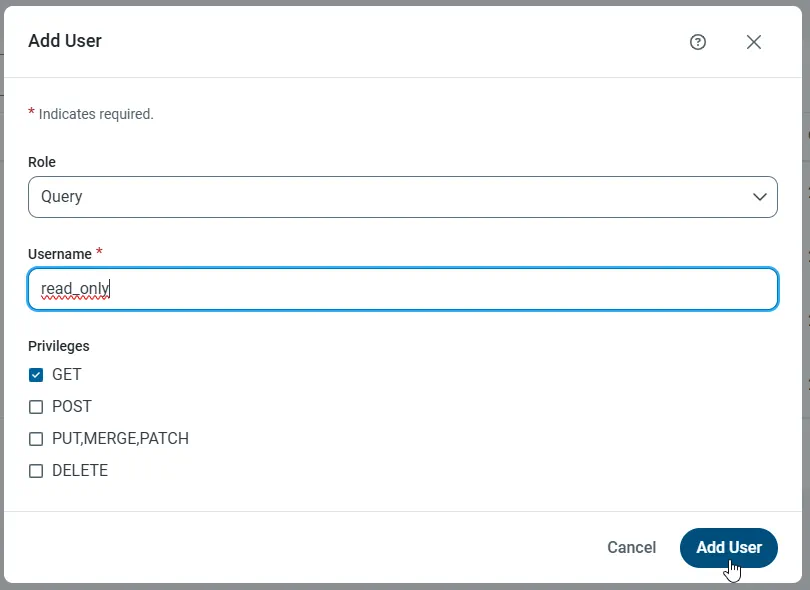
- On the Users page, click Add User to open the Add User dialog.
-
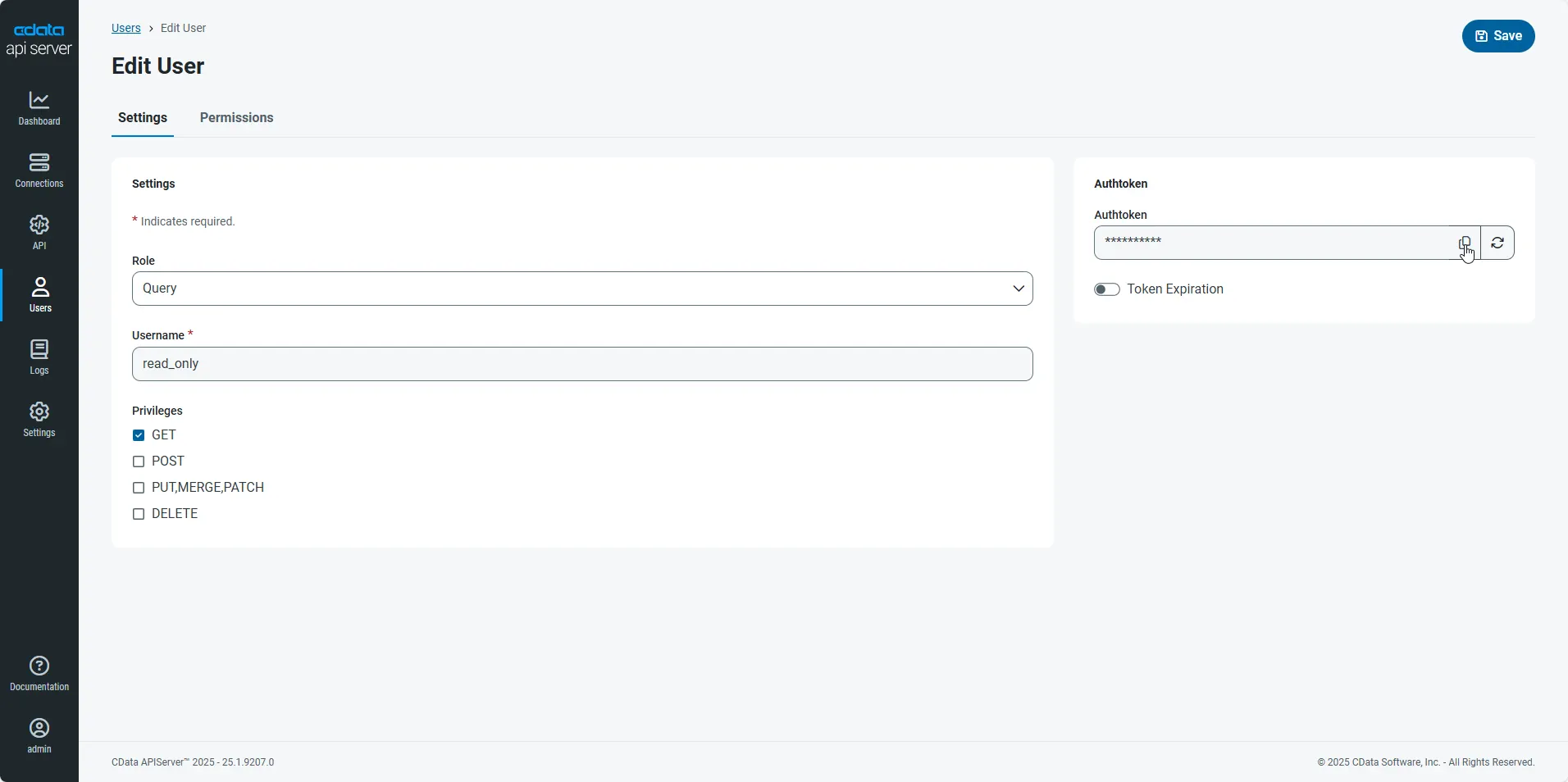
Next, set the Role, Username, and Privileges properties and then click Add User.
-
An Authtoken is then generated for the user. You can find the Authtoken and other information for each user on the Users page:
Creating API Endpoints for AlloyDB
Having created a user, you are ready to create API endpoints for the AlloyDB tables:
-
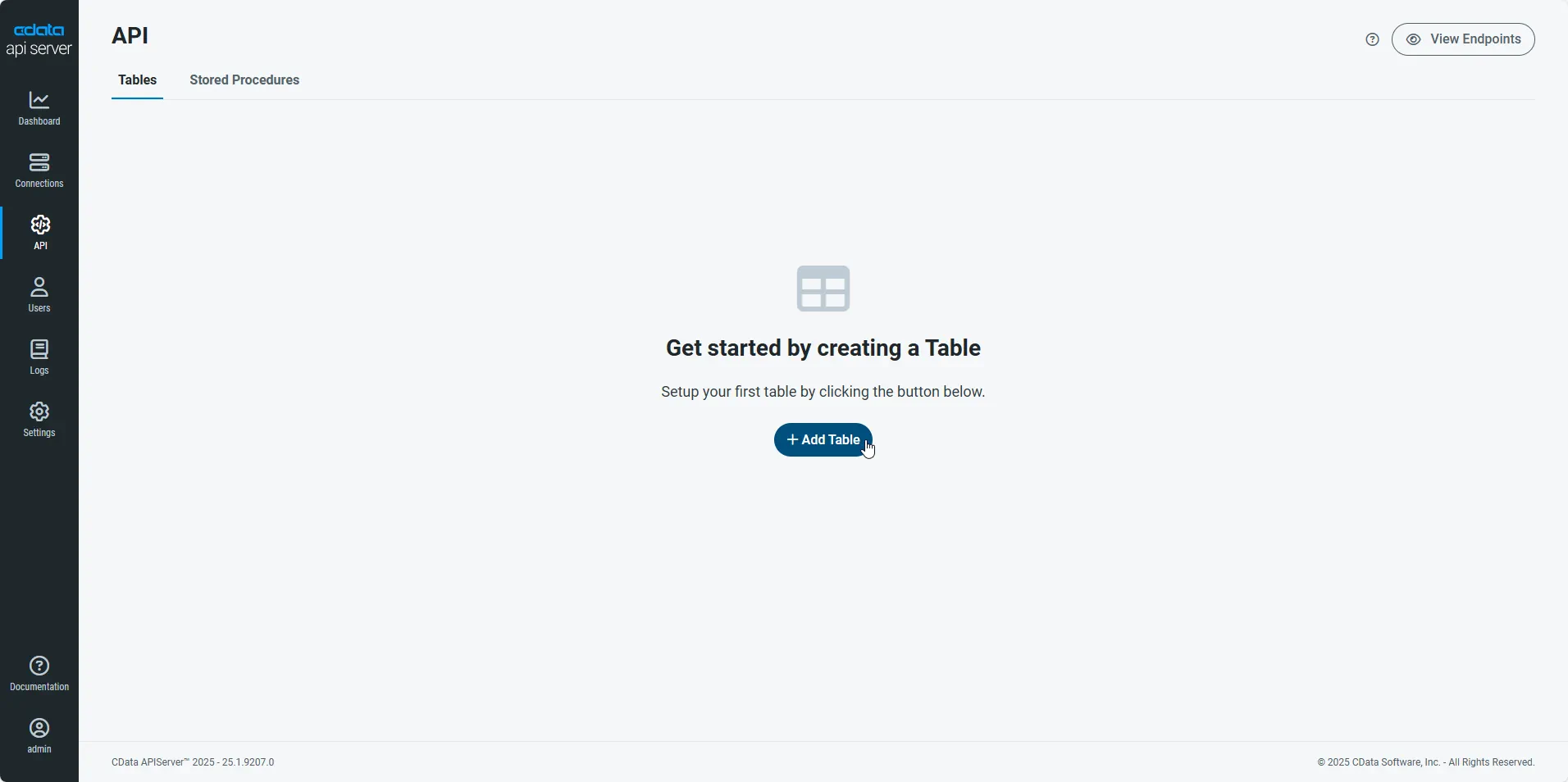
First, navigate to the API page and then click
Add Table
.
-
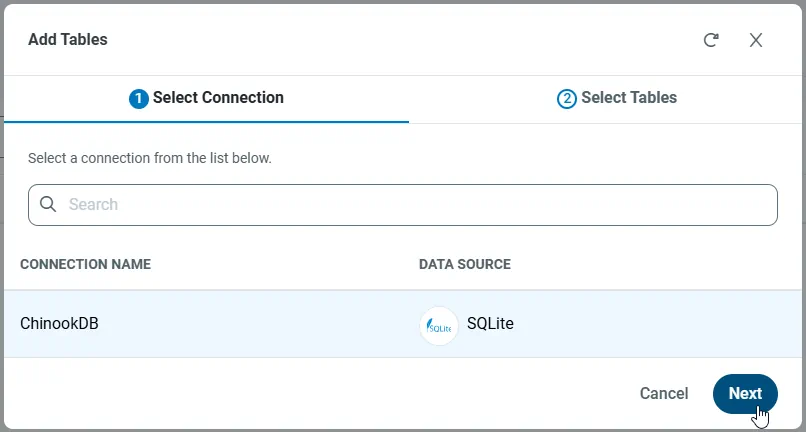
Select the connection you wish to access and click Next.
-
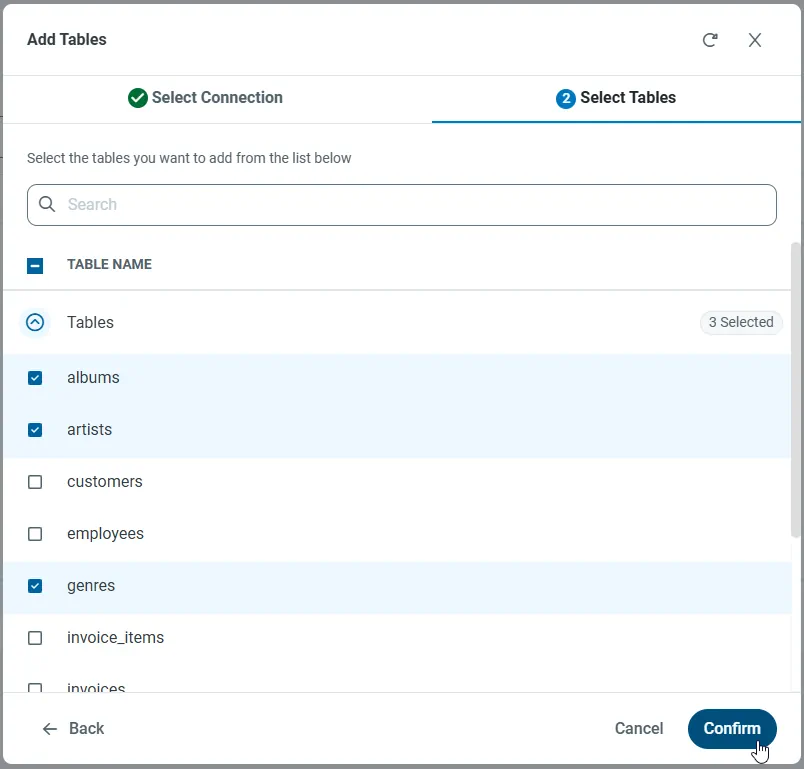
With the connection selected, create endpoints by selecting each table and then clicking Confirm.
Gather the OData Url
Having configured a connection to AlloyDB data, created a user, and added resources to the API Server, you now have an easily accessible REST API based on the OData protocol for those resources. From the API page in API Server, you can view and copy the API Endpoints for the API:
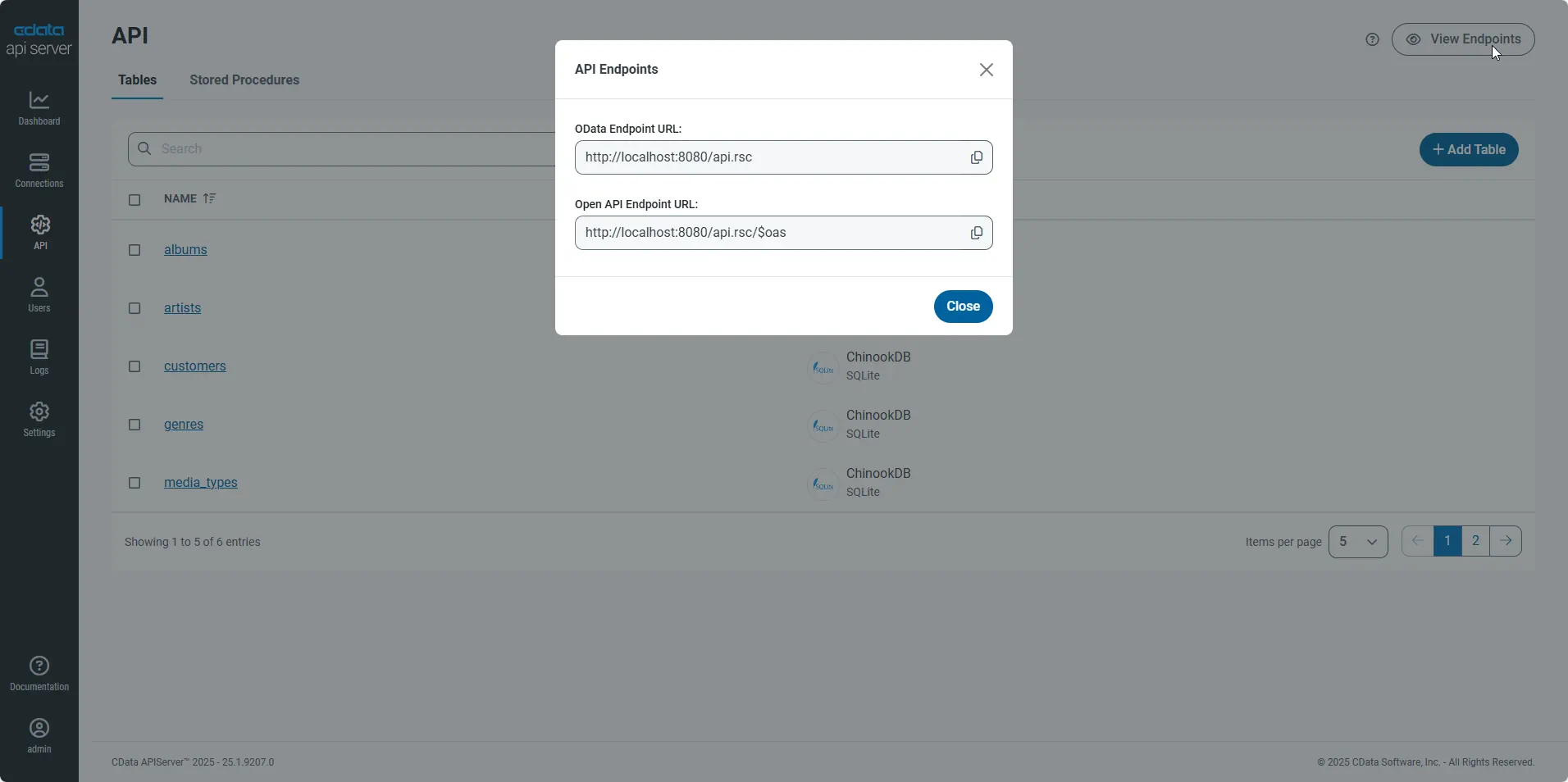
Access AlloyDB in a Logic App
You can use the API Server in a Logic App to create process flows around AlloyDB data. The HTTP + Swagger action provides a wizard to define the operations you want to execute to AlloyDB. The following steps below show how to retrieve AlloyDB data in a Logic App.
If your table has a column containing the creation date of a record, you can follow the steps below to write a function to check the column values for any new records. Otherwise, skip to the Create a Logic App section to send out emails to entities that match a filter.
Check for New AlloyDB Entities
To find new AlloyDB entities since a certain time, you can write a function that retrieves a datetime value for the start of the interval:
- In the Azure Portal, click New -> Function App -> Create.
- Enter a name and select the subscription, resource group, App Service plan, and storage account.
- Select your Function App and select the Webhook + API scenario.
- Select the language. This article uses JavaScript.
- Add the following code to return the previous hour in a JSON object:
module.exports = function (context, data) { var d = new Date(); d.setHours(d.getHours()-1); // Response of the function to be used later. context.res = { body: { start: d } }; context.done(); };
Add AlloyDB to a Trigger
Follow the steps below to create a trigger that searches AlloyDB for results that match a filter. If you created the function above, you can search for objects that were created after the start of the interval returned.
- In the Azure Portal, click New and in the Web + Mobile section select Logic App and select a resource group and App Service plan.
- You can then use the wizards available in the Logic App Designer, which can be accessed from the settings blade for the Logic App. Select the Blank Logic App template.
- Add a Recurrence action that will poll for the AlloyDB objects. This article polls every hour. Select the timezone -- the default is UTC.
- Add a function action: Expand the menu in the Add Action dialog and select the option to show Azure functions in the same region. Select the Function App you created earlier and select the function that returns the interval start.
- Enter an empty pair of curly brackets, "{}", to pass an empty payload object to the function.
- Add the HTTP + Swagger action and enter the swagger URL of the API Server:
http://MySite:MyPort/api.rsc/@MyAuthtoken/$oas
- Select the "Return Orders" operation.
Use the descriptions for each property to specify additional parameters such as the columns to retrieve, filters, etc. Below is an example filter:
ShipCountry eq 'USA'
The API Server returns the descriptions and other documentation in the swagger document. You can find more information on using the OData API and supported OData in the API Server help documentation.
To use the datetime value returned from the getInterval function, use the "ge" operator with a datetime column in the Orders table and select the Body parameter in the dialog. Note that quotes must be used to surround the datetime value.
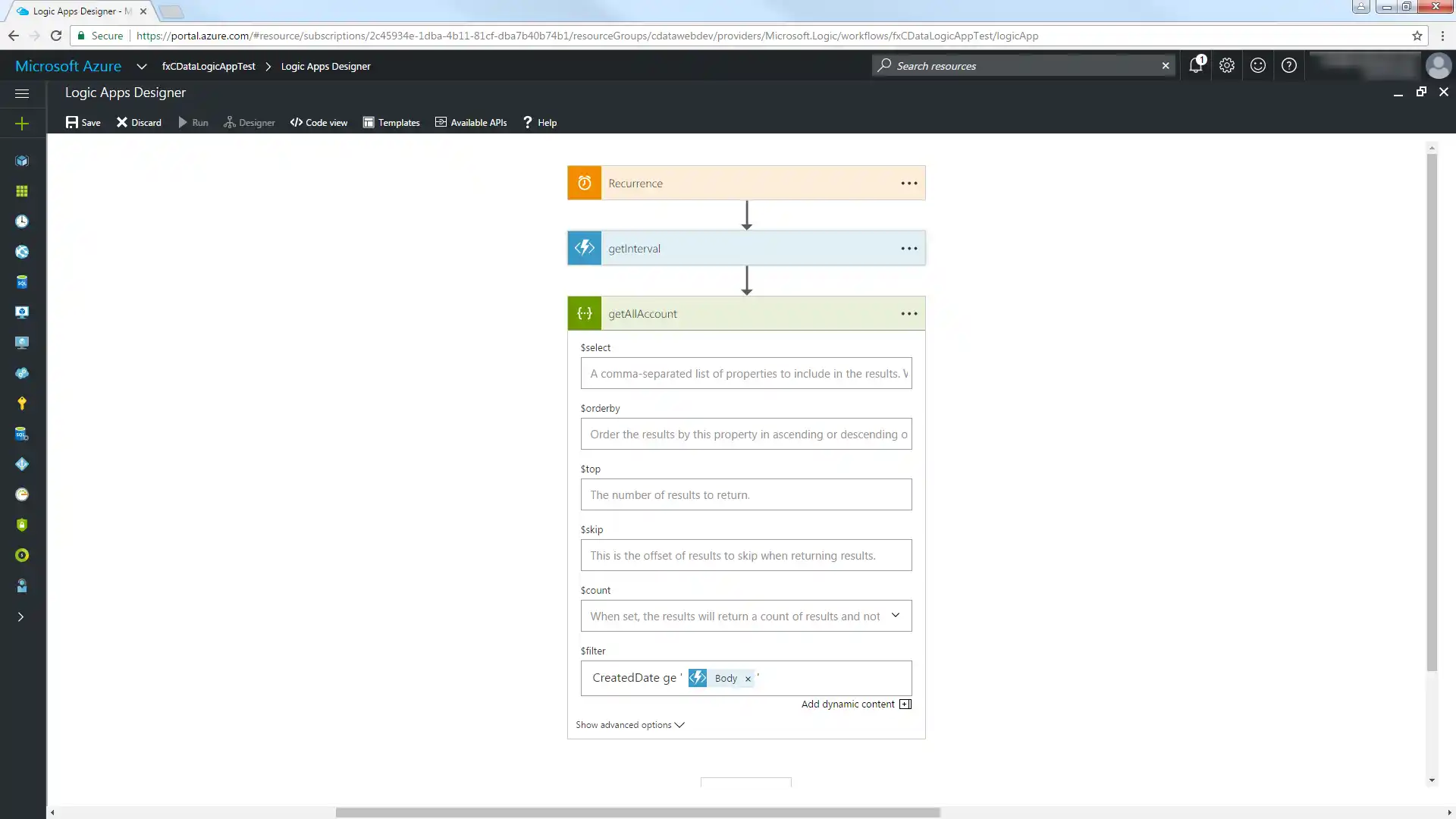
Switch to Code View and modify the $filter expression to extract the property containing the start of the interval. Use the syntax '@{body('MyFunc')['MyProp']'.
"getAllAccount": { "inputs": { "method": "get", "queries": { "$filter": "CreatedDate ge '@{body('getInterval')['start']}'" }, "uri": "https://MySite:MyPort/api.rsc/@MyAuthtoken/Orders" }
You can now access AlloyDB as data sources and destinations in your workflows.
Email New Records
Follow the steps below to email a report with any new Orders entities.
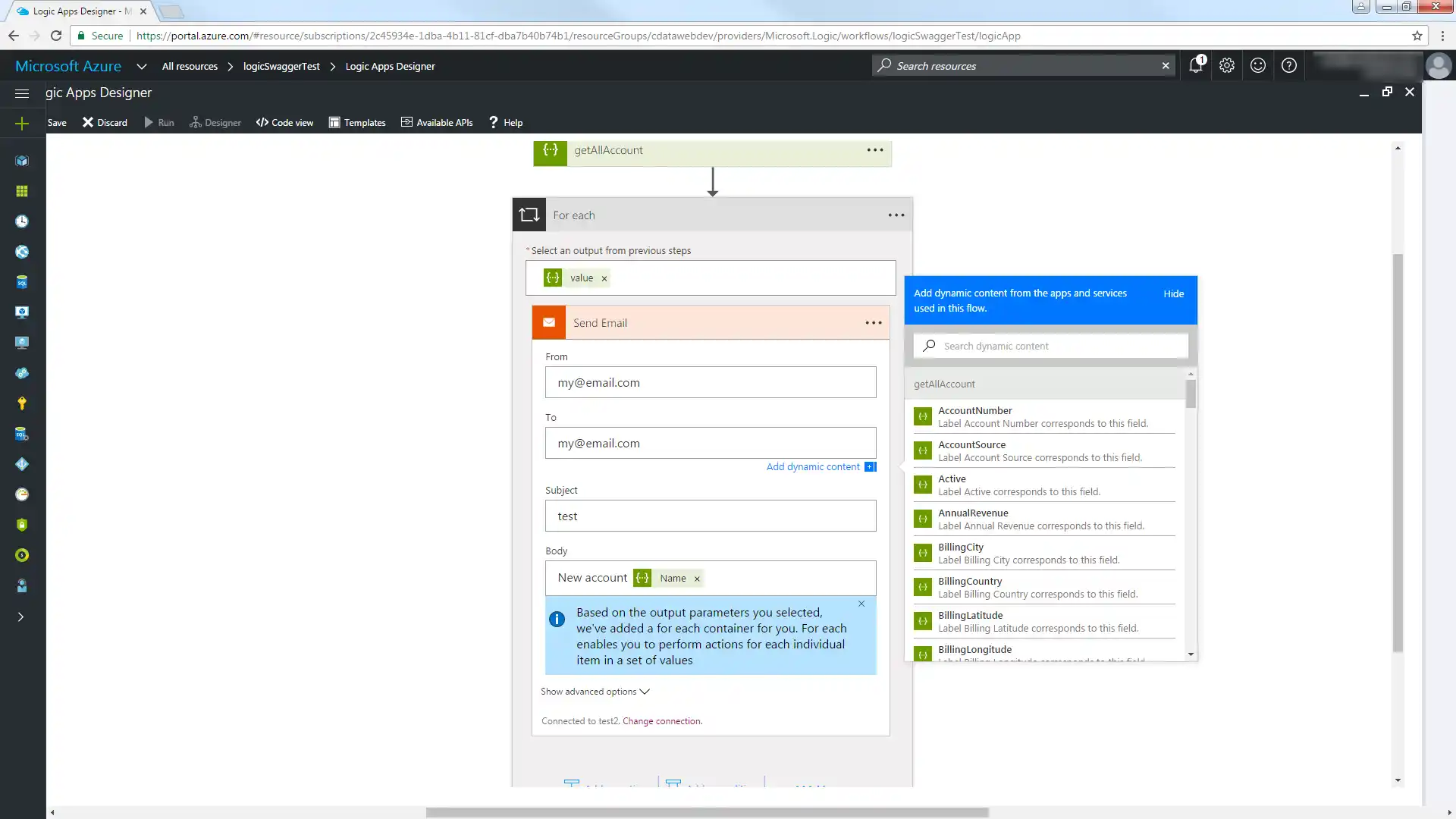
- In the Logic Apps Designer, add an SMTP - Send Email action.
- Configure the necessary information for the SMTP server.
- Configure the From, To, Subject, and Body. You can add parameters from the AlloyDB columns returned.
Click Save and then click Run to send email notifications on any AlloyDB records created in the last hour.