Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Connect to AlloyDB Data Using the Script Function in Claris FileMaker Pro
Use the CData ODBC Driver for AlloyDB and the Script function in FileMaker Pro to connect to AlloyDB and work with AlloyDB data in your FileMaker application.
Claris FileMaker is a low-code database application development tool that enables users to create custom apps for managing and organizing data. It combines a powerful relational database engine with an intuitive interface, allowing both technical and non-technical users to design and deploy applications across desktop, web, and mobile platforms.
In this article, we'll explore how to use the CData ODBC Driver for AlloyDB and FileMaker scripting to connect to AlloyDB data.
Create an ODBC Data Source for AlloyDB
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Connect and Sync AlloyDB data with FileMaker Using Scripts
In this section, we walk through the steps to connect live AlloyDB data to FileMaker using the CData ODBC Driver for AlloyDB and the Script function. During the initial import, FileMaker brings in all data from the external data source. From the second import onward, it updates only the data that has changed in the external source (a differential update). You can also replace the data in the current record order and schedule these differential updates for automated syncing.
You can download and install the latest version of FileMaker Pro for your Mac/Windows/Linux systems from this link.
Connect and sync AlloyDB data with FileMaker using scripts
Scripting in FileMaker automates complex tasks and workflows by running a sequence of actions with a single command. By using scripting to integrate with AlloyDB, you can automatically connect to, import, update, and replace AlloyDB data within your FileMaker applications, streamlining data management and improving efficiency.
First-time importing and adding AlloyDB data using script
In this section, we'll use scripts to import AlloyDB data into FileMaker by following these steps:
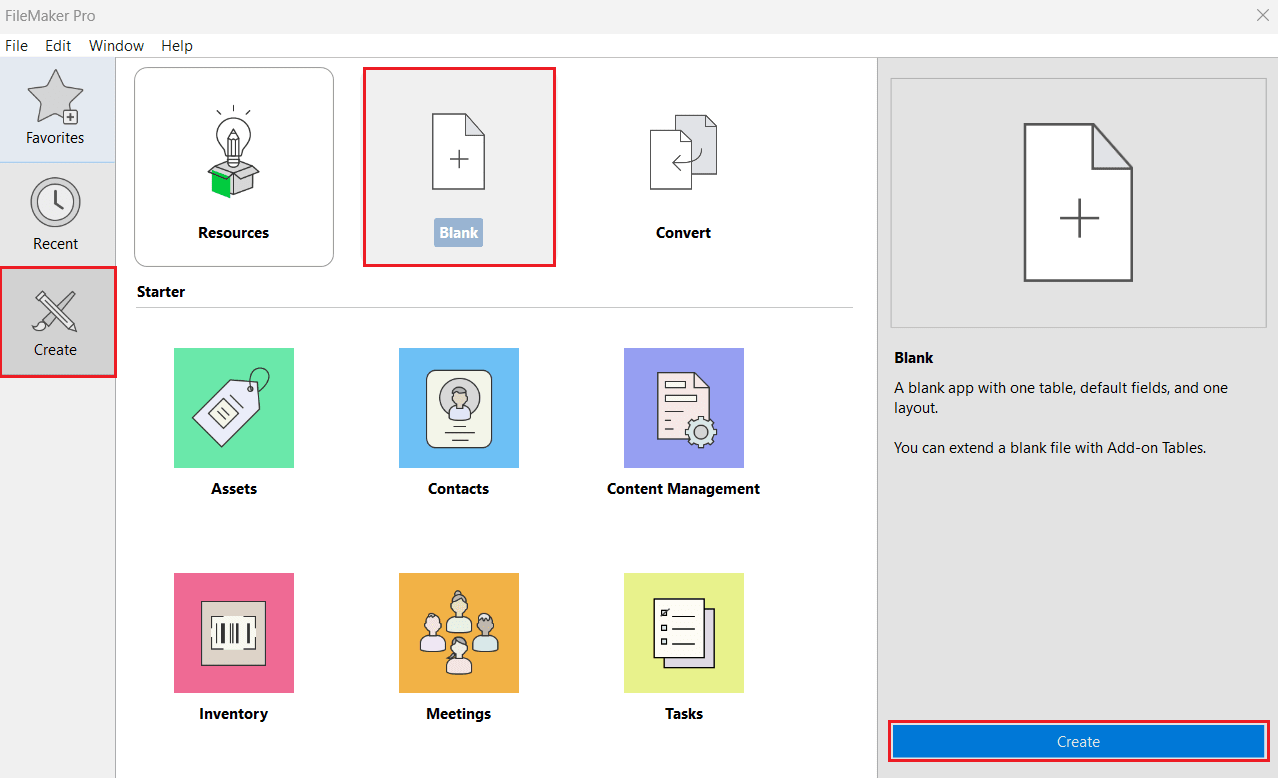
- Open FileMaker Pro. Navigate to Create from the left panel and select Blank > Create.
- Enter a filename of your choice and click Save.
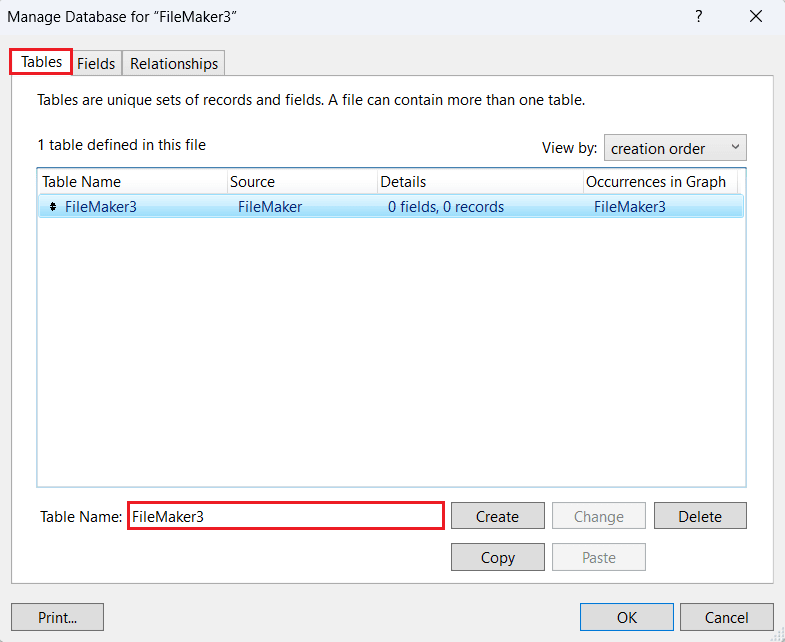
- In the Manage Database window, go to the Tables tab and create or rename the table where you want to display the AlloyDB data.
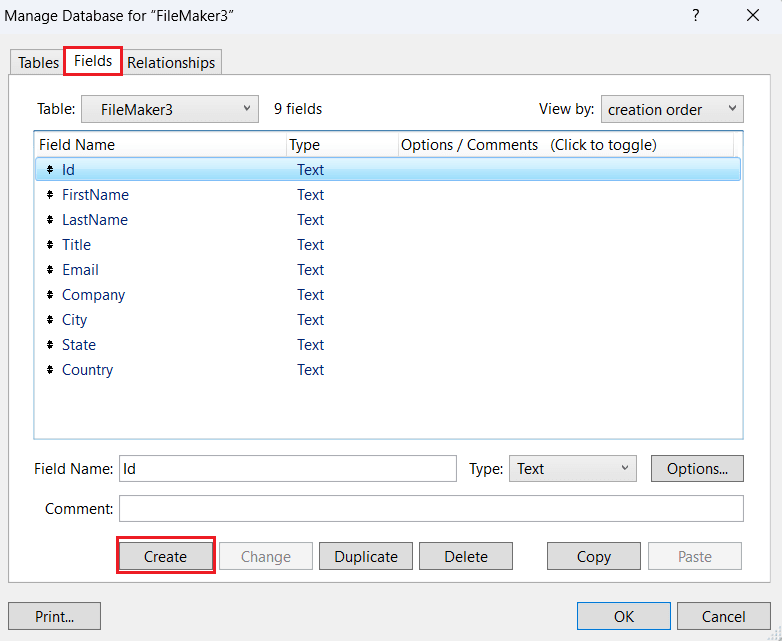
- In the Fields tab, create and add the fields you want to use in the table.
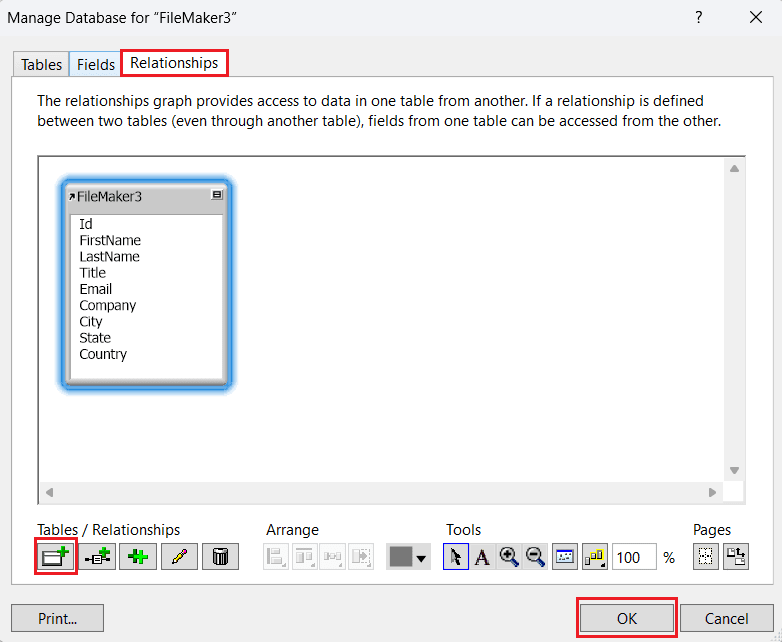
- In the Relationships tab, add table relationships if there are multiple tables, then click OK.
- To reopen and modify the table structure, go to File > Manage > Database.
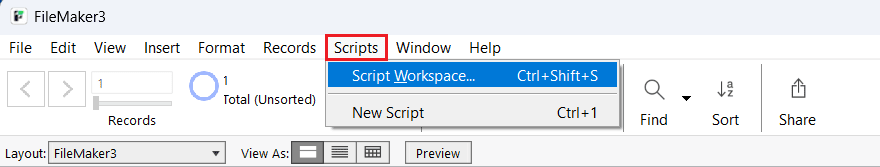
- Navigate to Scripts > Script Workspace.
- Select New Script to open a new script workspace.
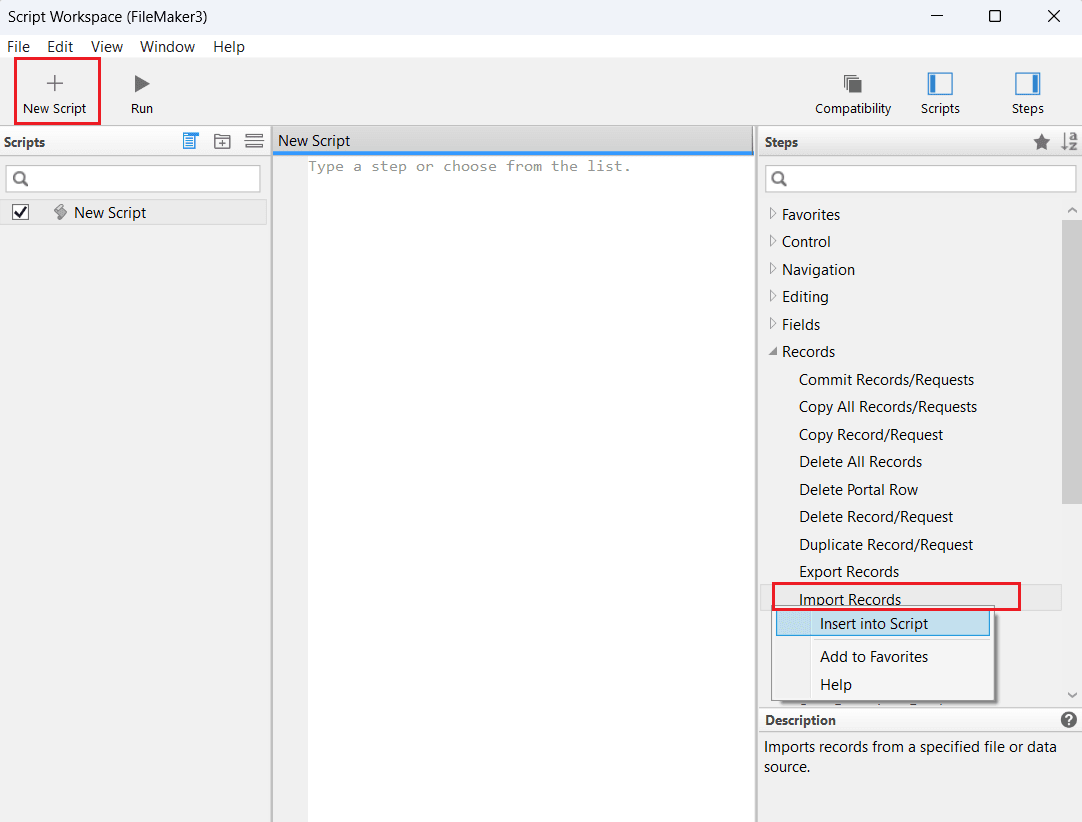
- From the Steps panel on the right, select Records > Import Records > Insert into Script.
- In the Specify Data Source dropdown, choose ODBC Data.
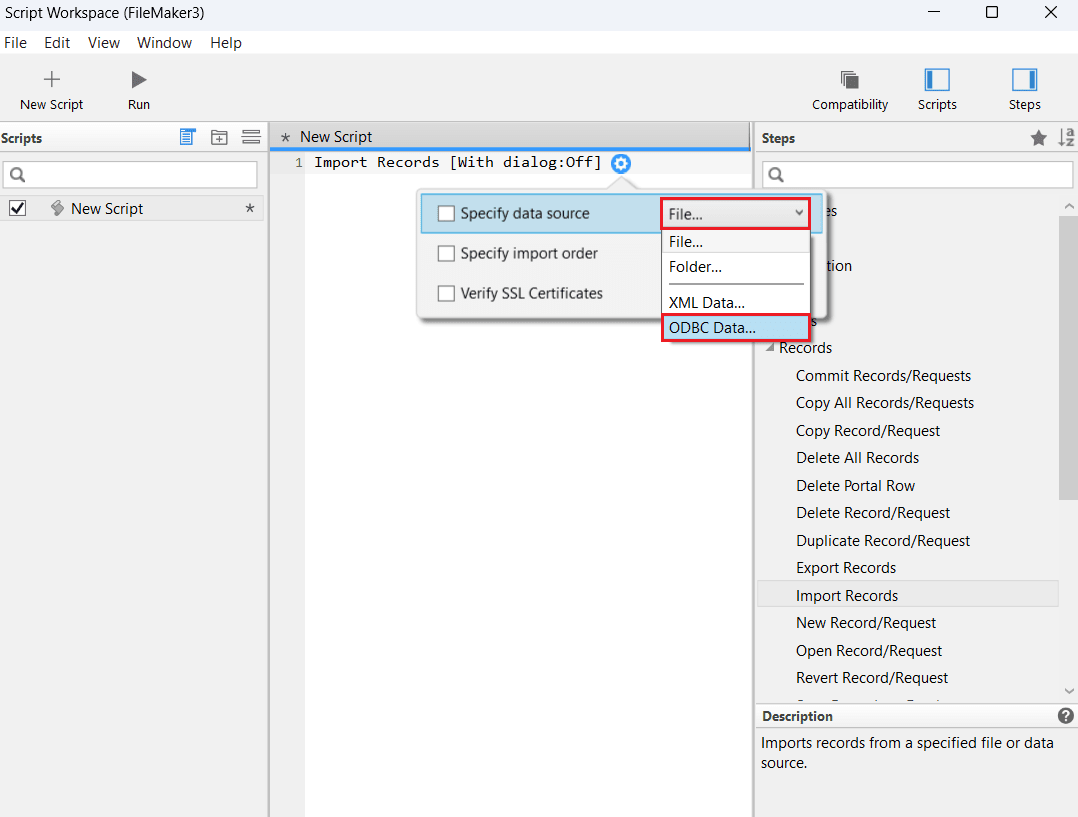
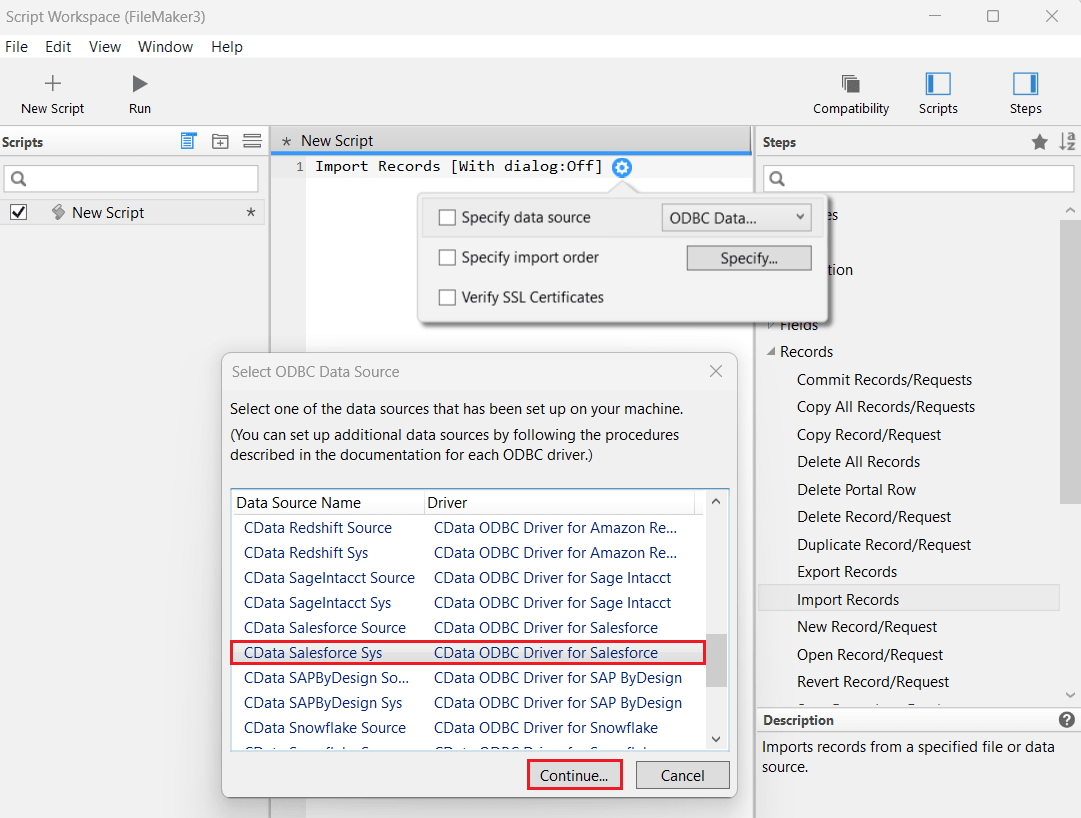
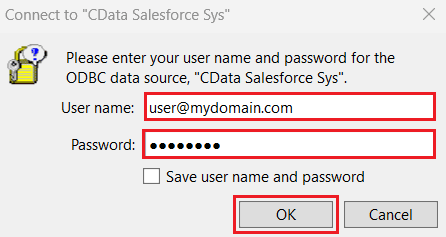
- Select CData AlloyDB Sys from the Select ODBC Data Source window, and click Continue. Enter your AlloyDB credentials and click OK.
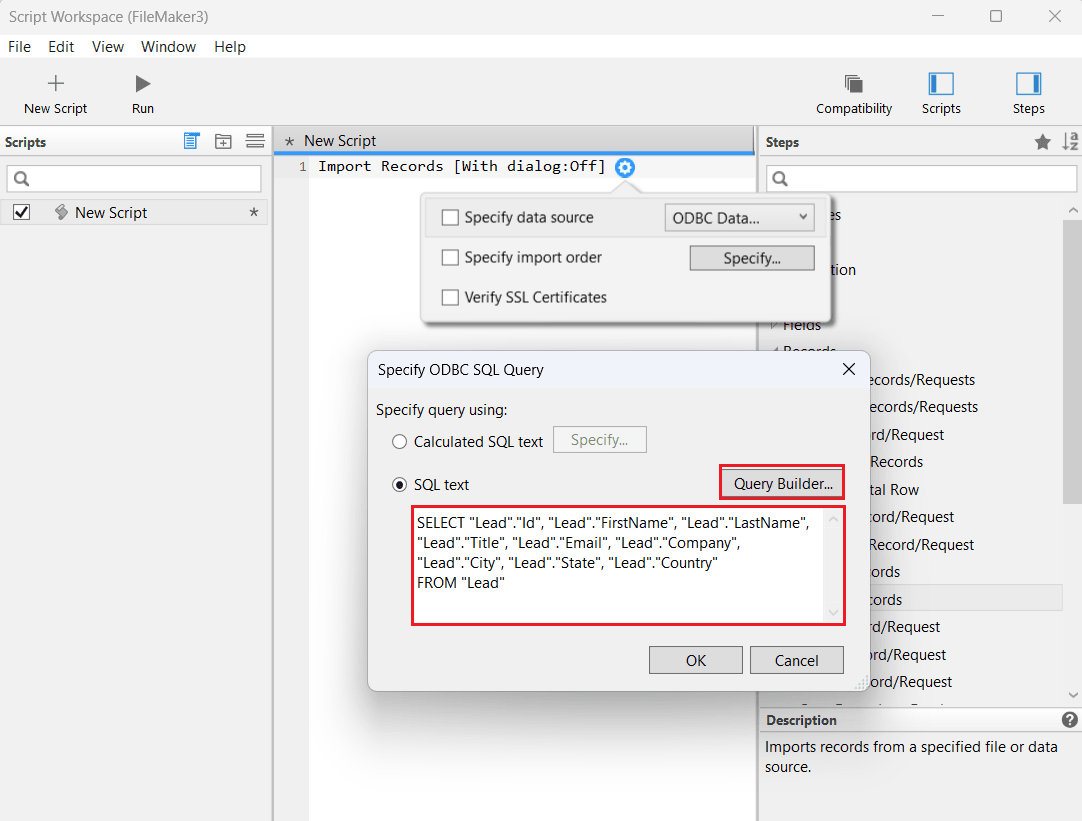
- In the Specify ODBC SQL Query dialog, enter the SQL query in the SQL text editor to import the desired AlloyDB data.
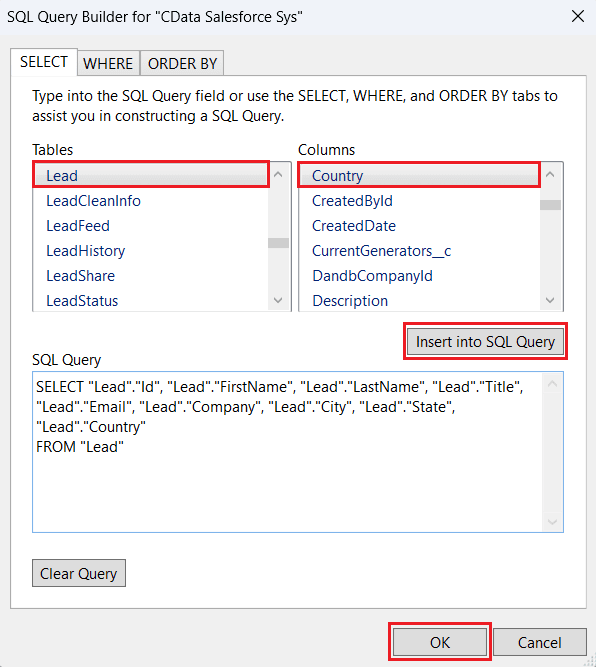
- Alternatively, select Query Builder to open the SQL Query Builder window. Choose the target table from the Tables section and relevant columns from the Columns section. Click Insert into SQL Query after each selection to auto-generate the query. You can also manually edit the query using WHERE and ORDER BY clauses or the designated tabs. Click OK to finalize the query.
- Click OK.
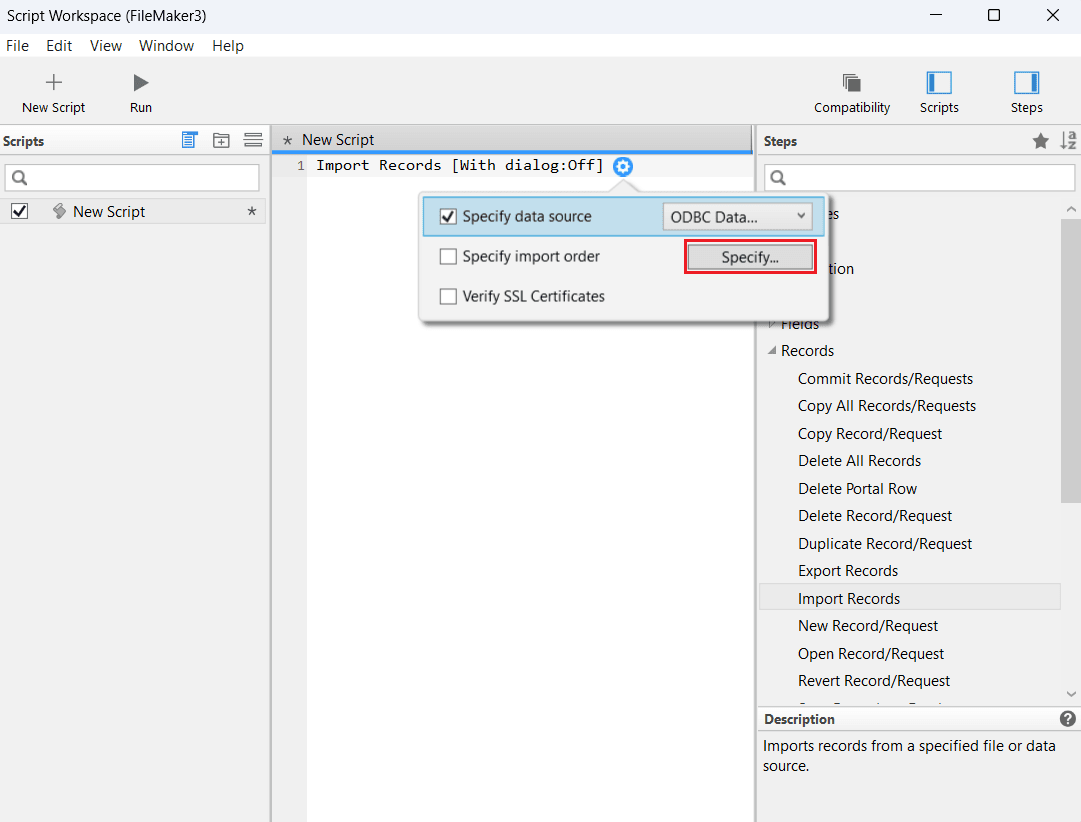
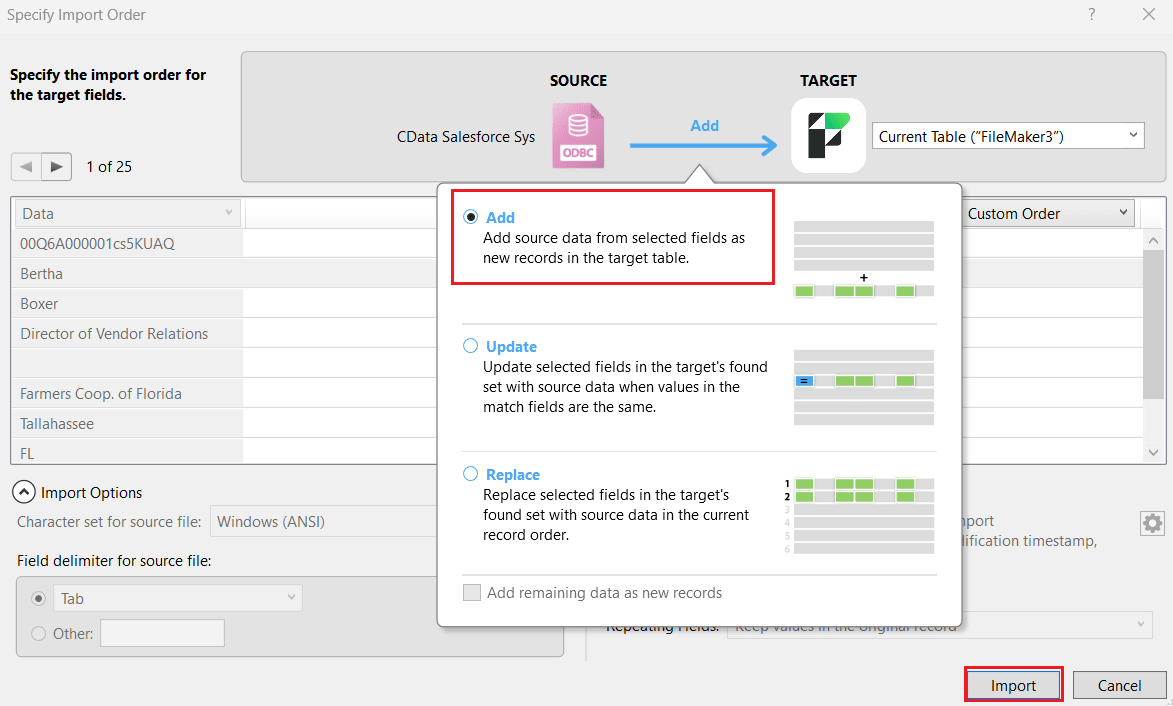
- In the Specify import order option, click Specify and enter the AlloyDB credentials.
- In the Specify Import Order window, define the import order for the target fields you added earlier. Select Add between the source and target fields to insert the AlloyDB data as new records in the table. Click Import.
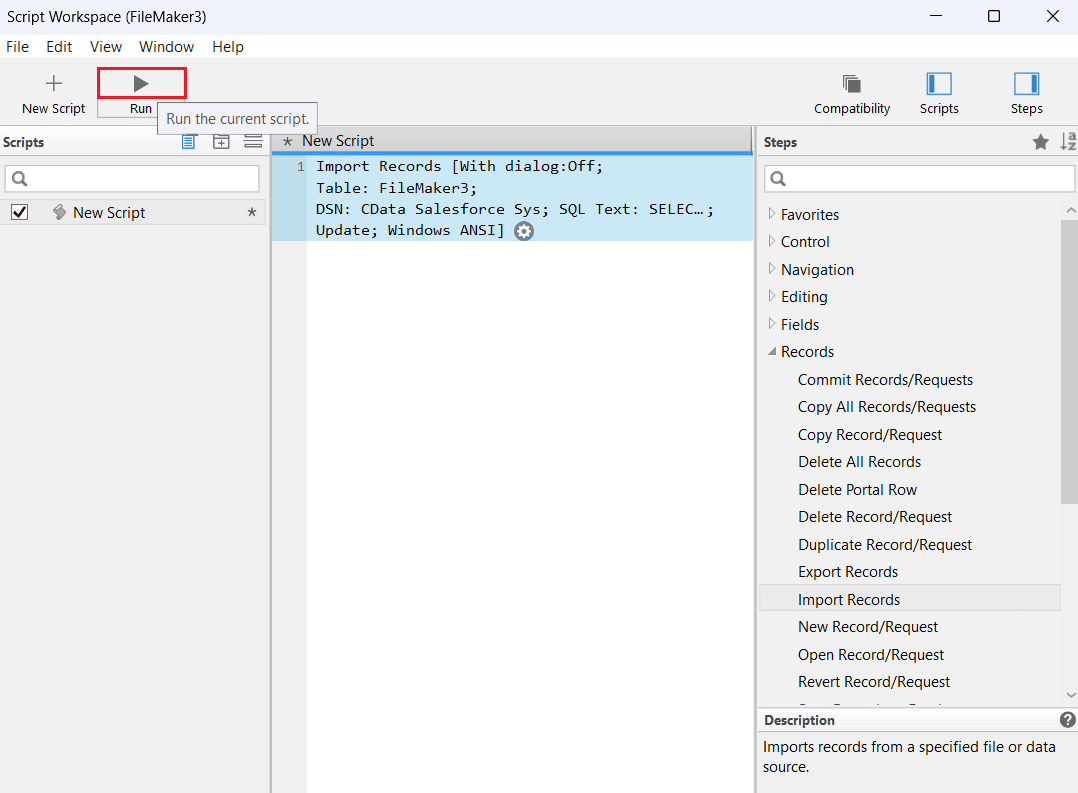
- The script now appears in the workspace. Click Run to execute the script and process the import.
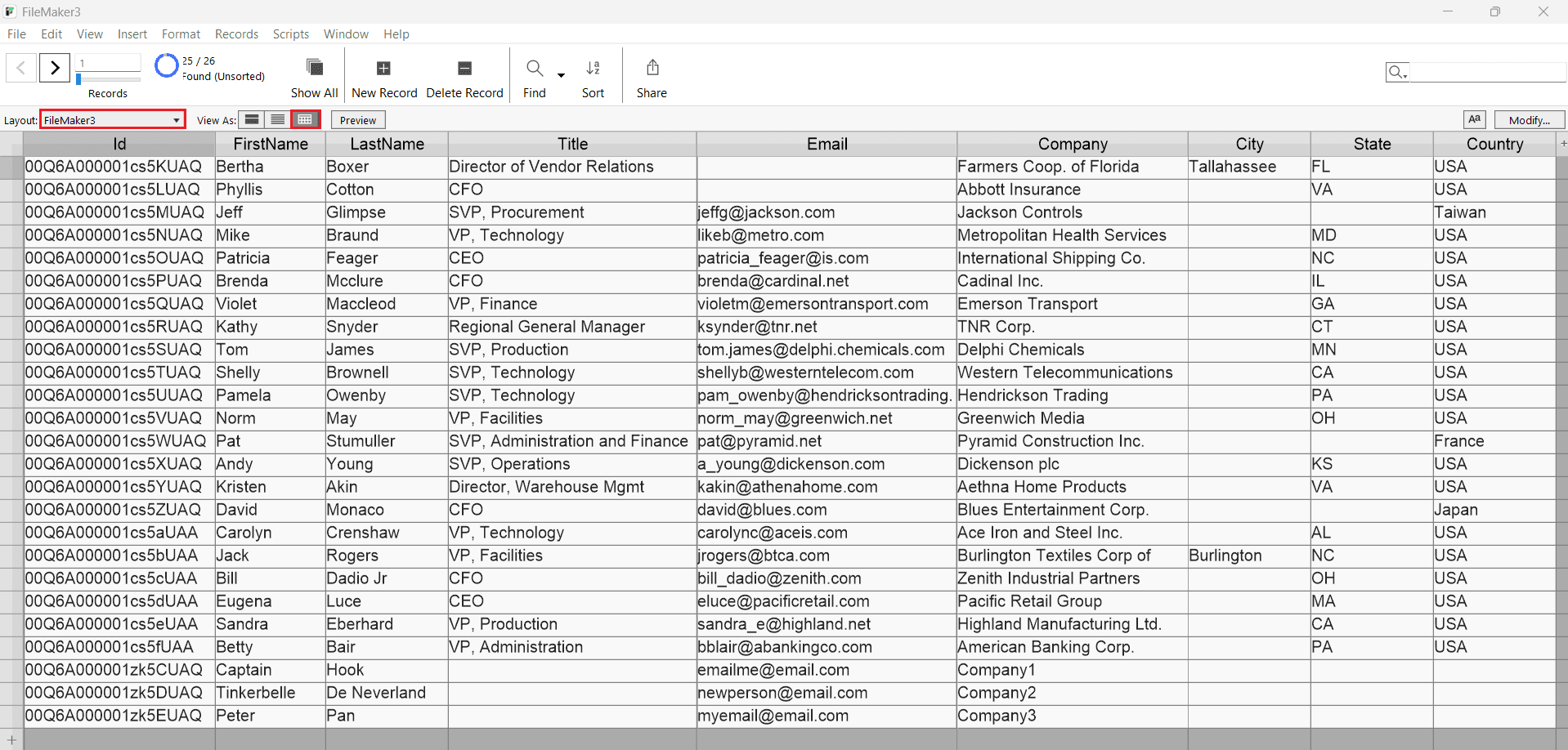
- FileMaker imports the AlloyDB data as a table.
Update or Replace Imported AlloyDB data Using a Script
After importing the AlloyDB data into FileMaker, use scripts to update or replace any changes made in AlloyDB by following this process:
- Go back to the Script Workspace by following the steps mentioned in the earlier section.
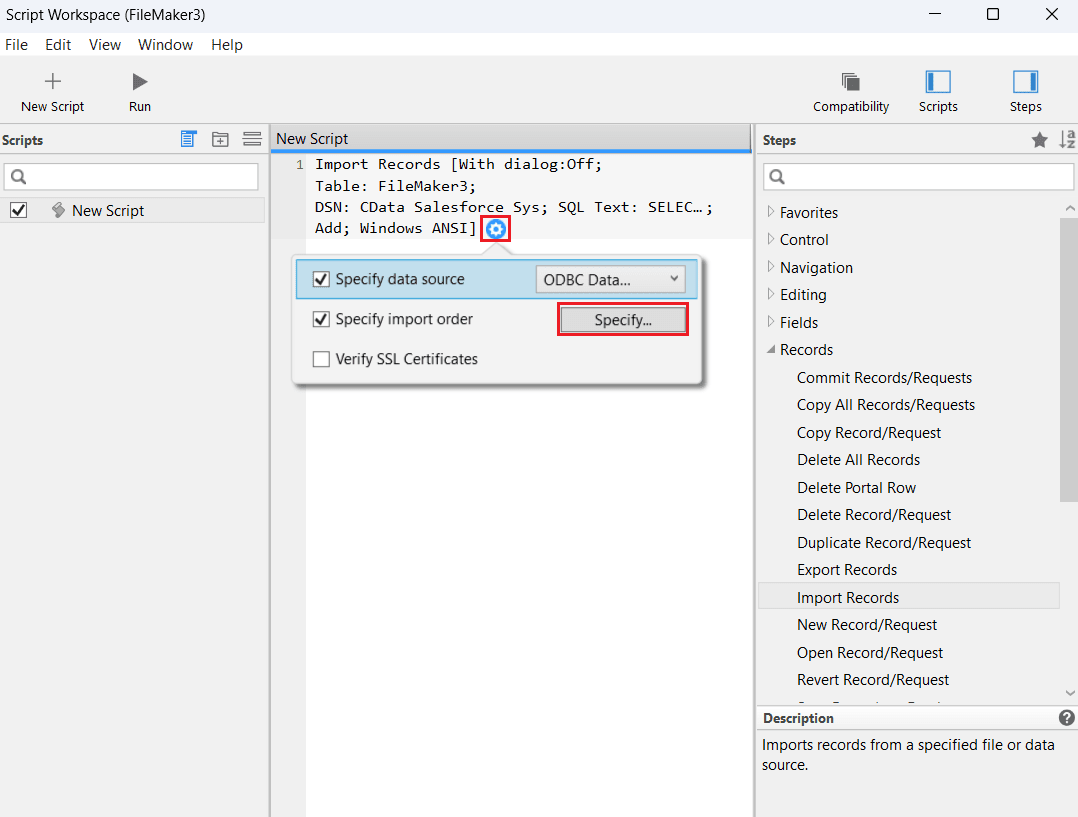
- Select the existing script, click the settings button, choose Specify under Specify Import Order, and re-enter the AlloyDB credentials to authenticate.
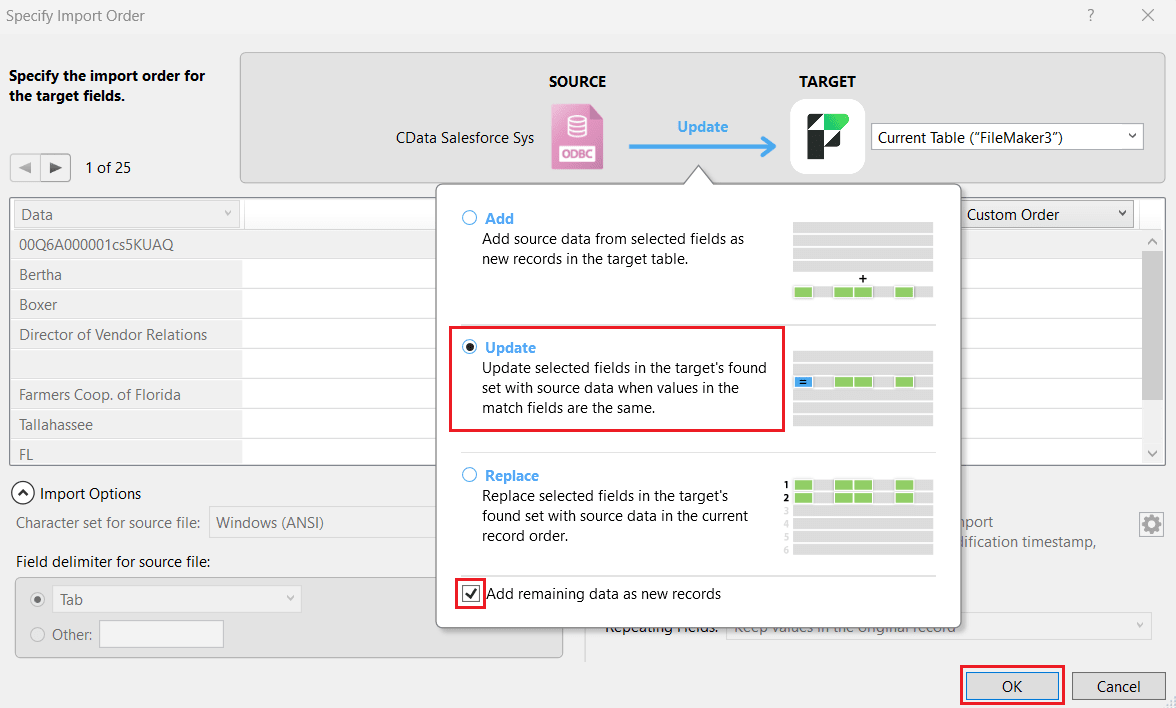
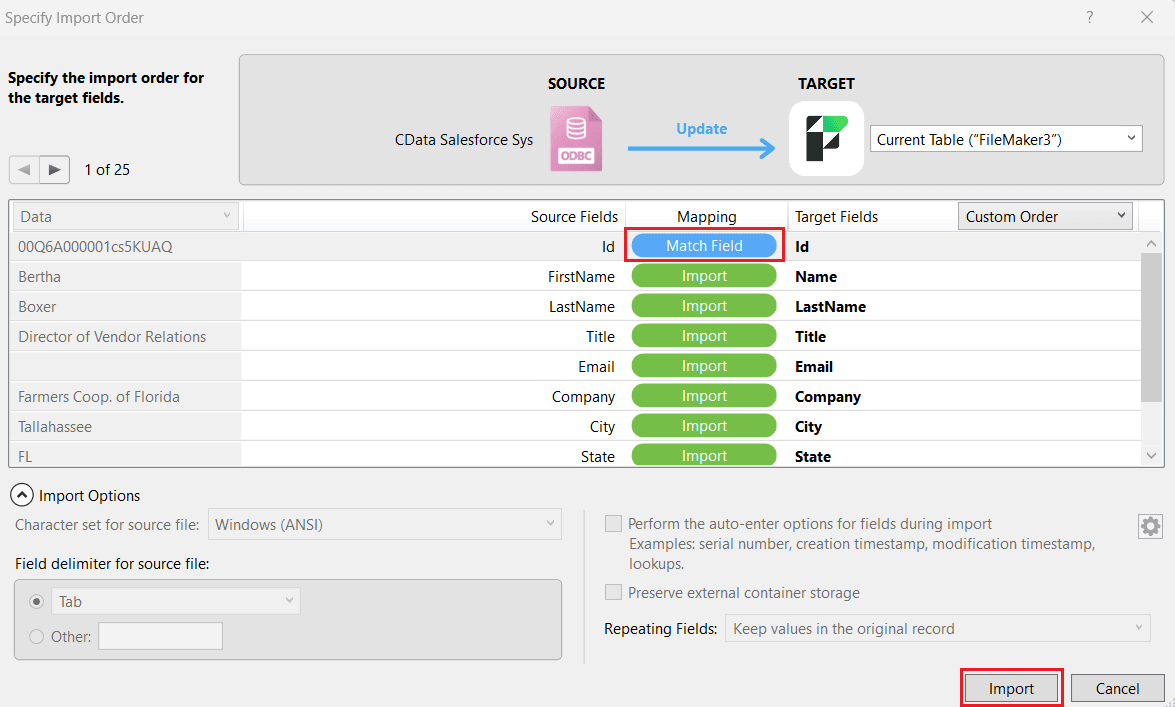
- In the Specify Import Order window, choose Update between source and target to update the imported AlloyDB data. This updates the target's found set with AlloyDB data values from selected fields when the match fields have the same values. You must define at least one match field in the mapping and select the checkbox Add remaining data as new records. Click Import.
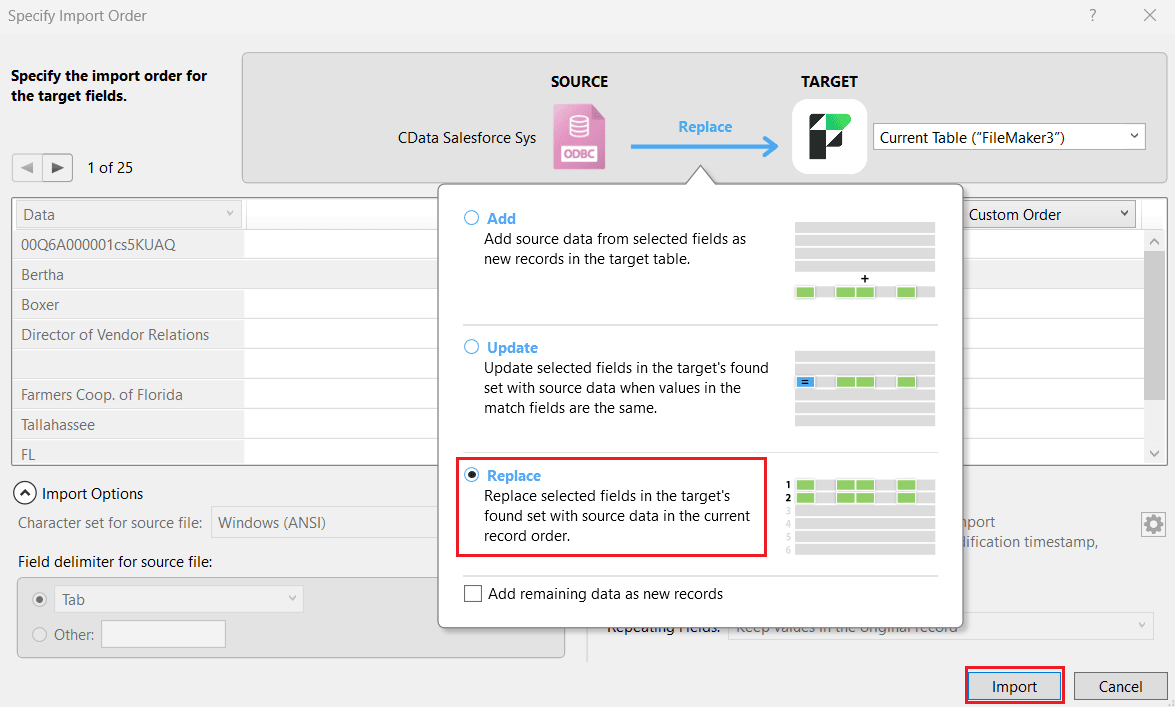
- Alternatively, choose the Replace option instead of Update, based on your use case. This replaces the selected fields in the target's found set with AlloyDB data in the current record order. Click Import.
- FileMaker adds the script to the workspace. Click Run to execute the script and process the import query.
- FileMaker imports the updated or replaced AlloyDB data as a table.
Get Started Today
Download a free 30-day trial of CData ODBC Driver for AlloyDB to integrate AlloyDB data into Claris FileMaker and work with AlloyDB data in your FileMaker applications.
Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.


