Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Build Apps with Live Amazon Athena Data Using the Low-Code Development Platform of Mendix
Connect Amazon Athena data with Mendix to build apps using the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Athena.
Mendix, developed by Siemens, is a low-code platform used to rapidly develop, test, and deploy web and mobile applications, facilitating digital transformation and enhancing business agility. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Athena, you can use your Amazon Athena data to create various applications using Mendix Studio Pro.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Amazon Athena data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Amazon Athena, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Amazon Athena and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Amazon Athena data using native data types.
This article shows how you can easily create an application that utilizes Amazon Athena data in Mendix by combining the JDBC interface provided by Mendix with the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Athena.
About Amazon Athena Data Integration
CData provides the easiest way to access and integrate live data from Amazon Athena. Customers use CData connectivity to:
- Authenticate securely using a variety of methods, including IAM credentials, access keys, and Instance Profiles, catering to diverse security needs and simplifying the authentication process.
- Streamline their setup and quickly resolve issue with detailed error messaging.
- Enhance performance and minimize strain on client resources with server-side query execution.
Users frequently integrate Athena with analytics tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Excel for in-depth analytics from their preferred tools.
To learn more about unique Amazon Athena use cases with CData, check out our blog post: https://www.cdata.com/blog/amazon-athena-use-cases.
Getting Started
Preparing the Mendix environment
In this section, we will explore how to develop an app using Mendix Studio Pro, as previously introduced, with Amazon Athena data. Be sure to install Mendix Studio Pro beforehand.
Install the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Athena
First, install the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Athena on the same machine as Mendix. The JDBC Driver will be installed in the following path:
C:\Program Files\CData\CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Athena 20xx\lib\cdata.jdbc.amazonathena.jar
Create an application
Now let's start creating the app. First, let's make an app that has the Database Connector available.
- Launch Mendix Studio Pro and click 'Create New App.'
- Select the 'Blank Web App' option.
- Click 'Use this starting point' to proceed.
- Create an app with a name of your choice. Also, note down the "Disk location" information, for future reference.
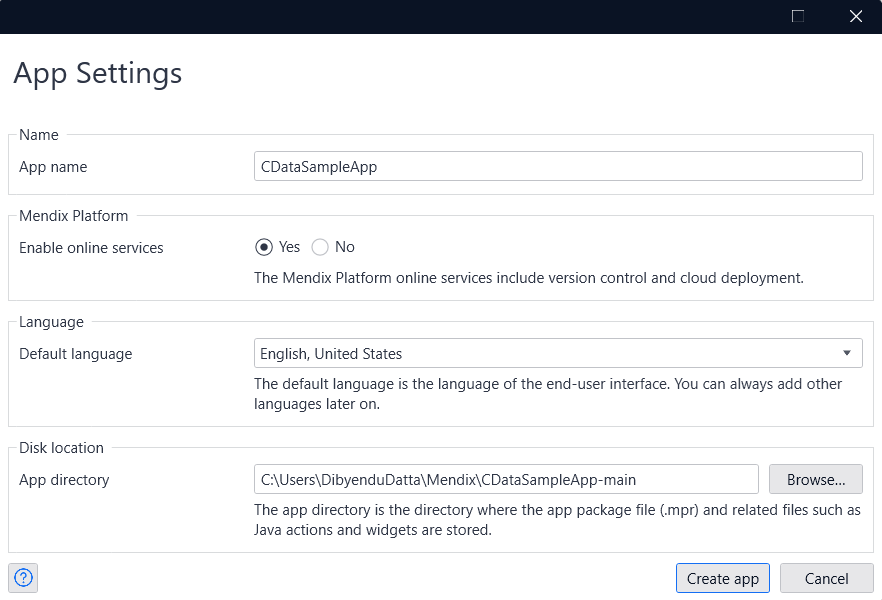
- You have now created a brand-new app.
Add the Database Connector to your application
Next, add the Database Connector module to the app you just created.
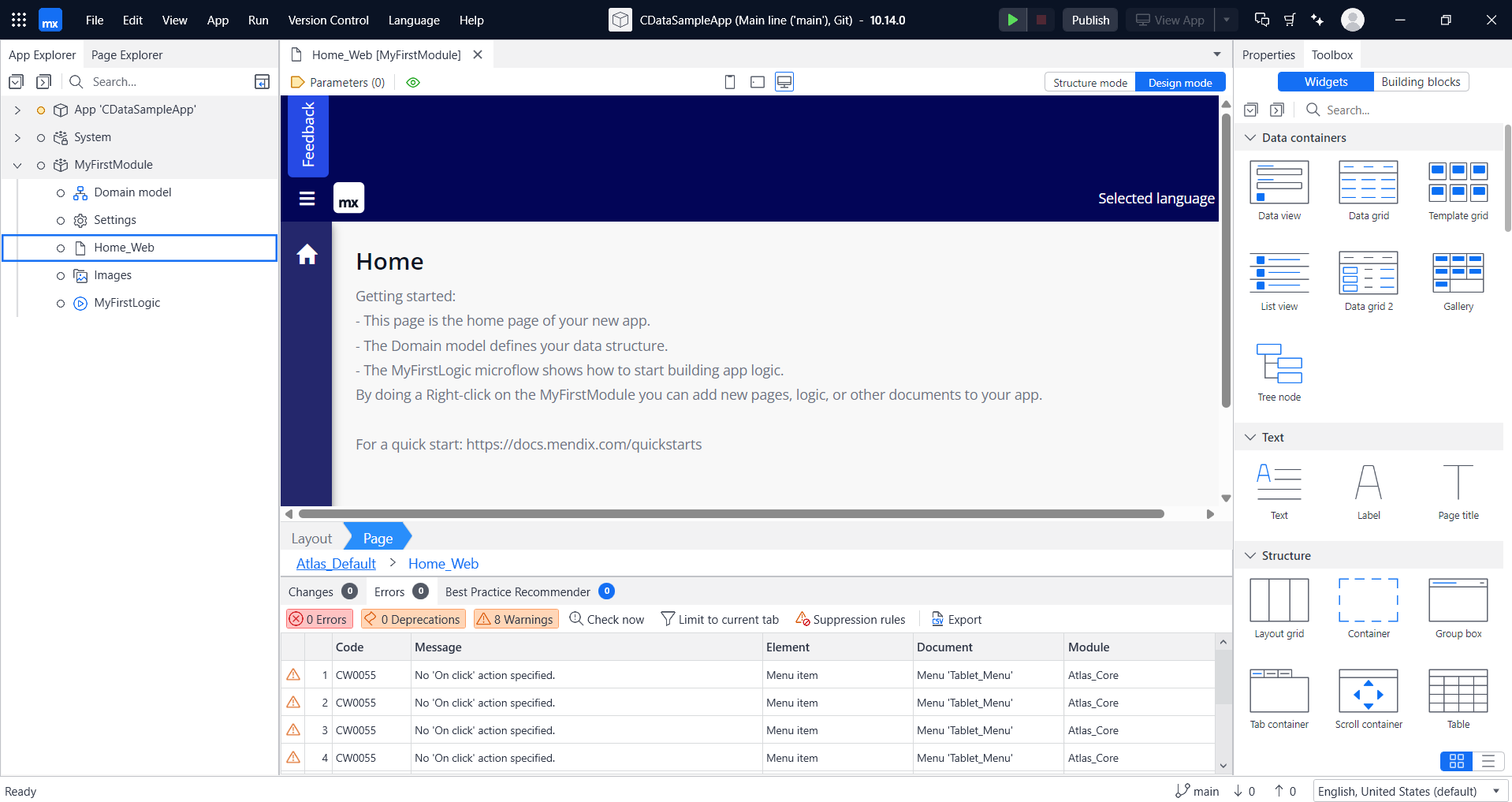
- On the top right, click on the Marketplace button.
- Search for Database Connector in the Marketplace search section and select it.
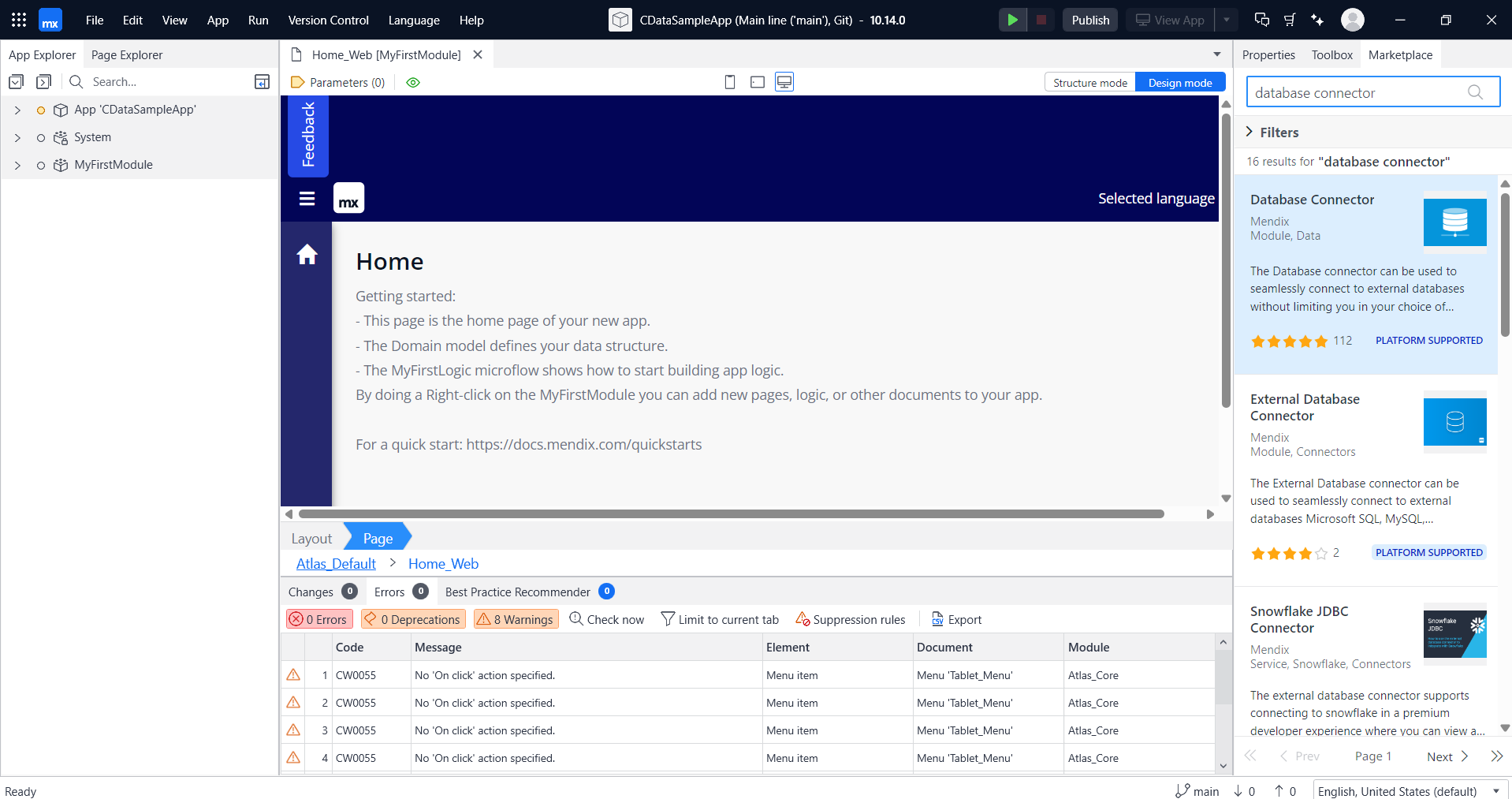
- Click on Download to download the latest Database Connector.
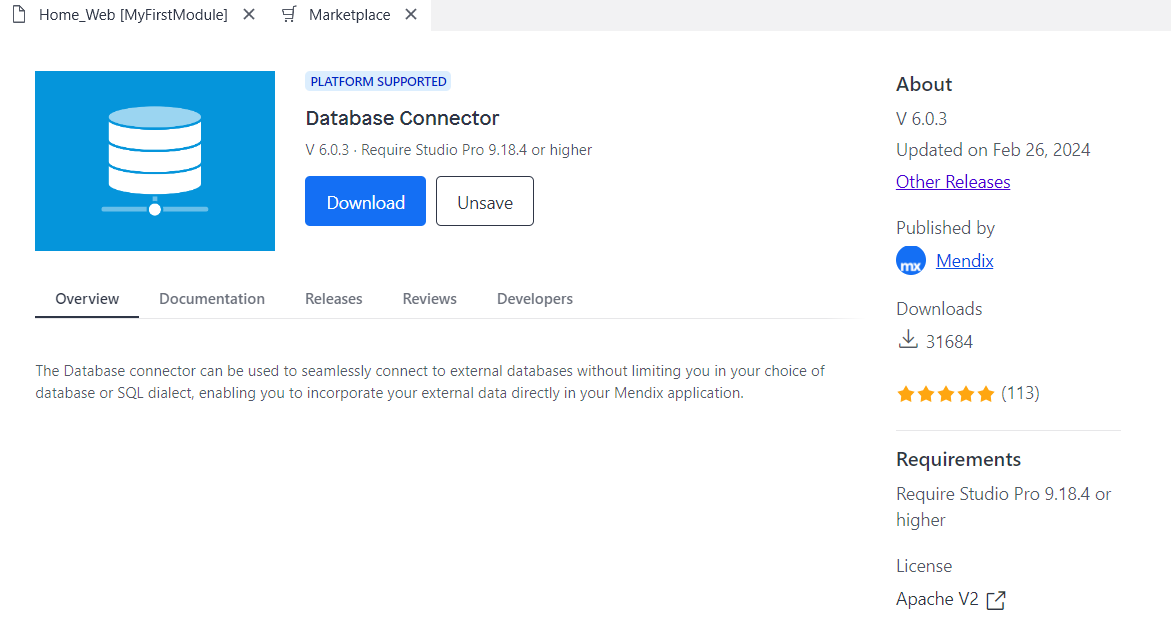
- In the Import Module window, select the Action as Add as a new module.
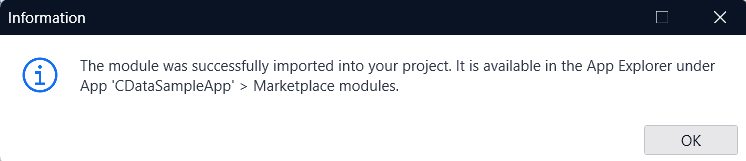
- If the Database Connector appears on the app screen, you are good to move on to the next steps.
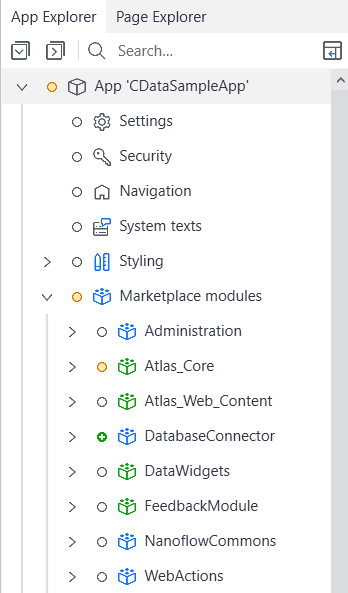
Adding the JDBC Driver to Mendix Studio Pro
To use the CData JDBC driver with this Database Connector, you must add the JDBC Driver JAR file to your project.
- In the Mendix project folder you noted earlier, there is a folder named 'userlib.' Place the two files, 'cdata.jdbc.amazonathena.jar' and 'cdata.jdbc.amazonathena.lic,' into that folder.
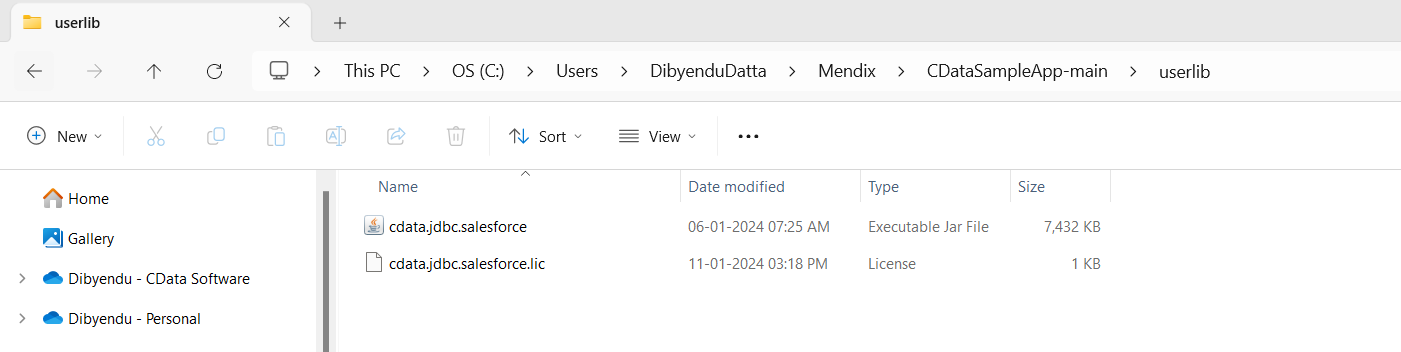
- You can now use the CData JDBC Driver with the Database Connector.
Create a Data Model
Now, let's create an app. We first need to define a data model to load data from the Database Connector and display it on the list screen. Let's create the data model before loading the data.
- Add an Entity to the 'Domain model' of MyFirstModule.
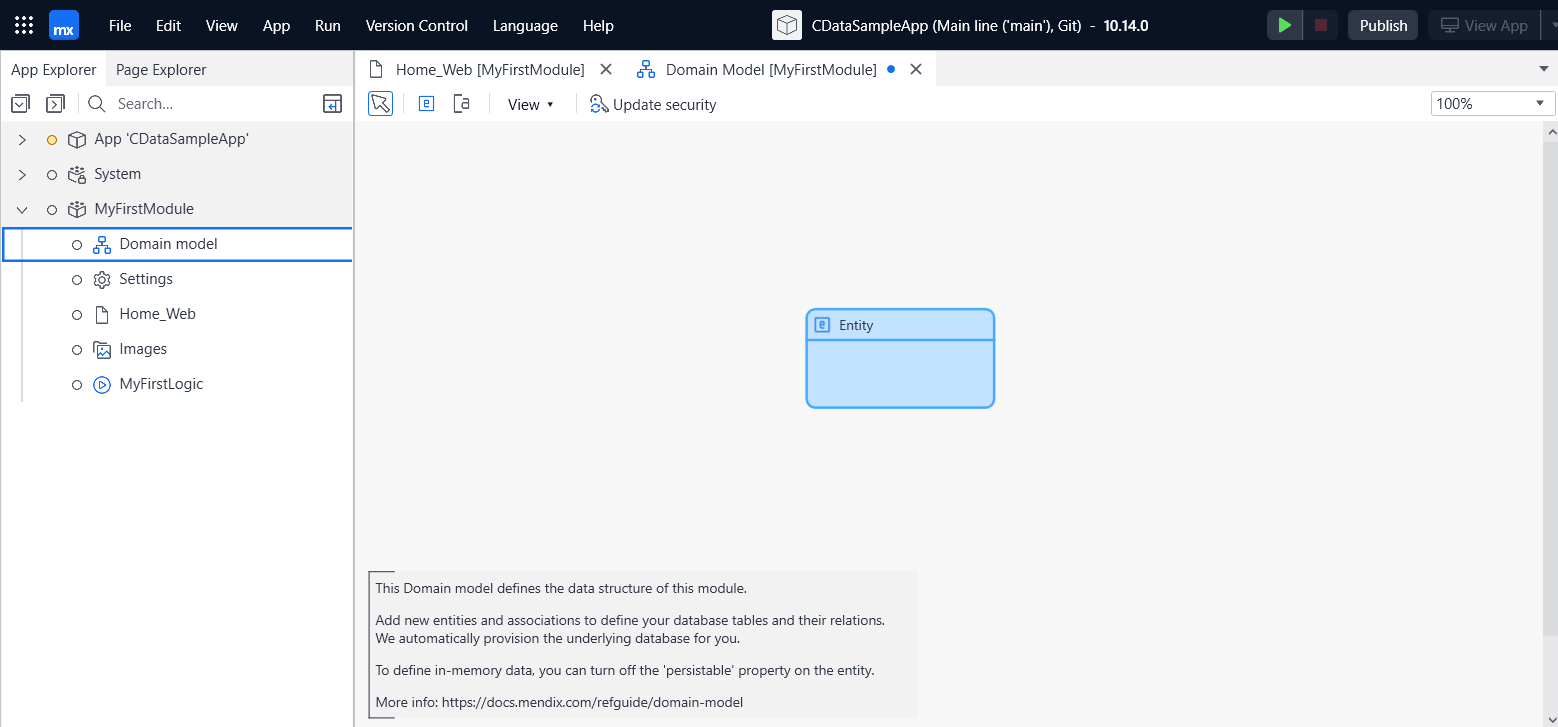
- Enter the entity name and field definitions.
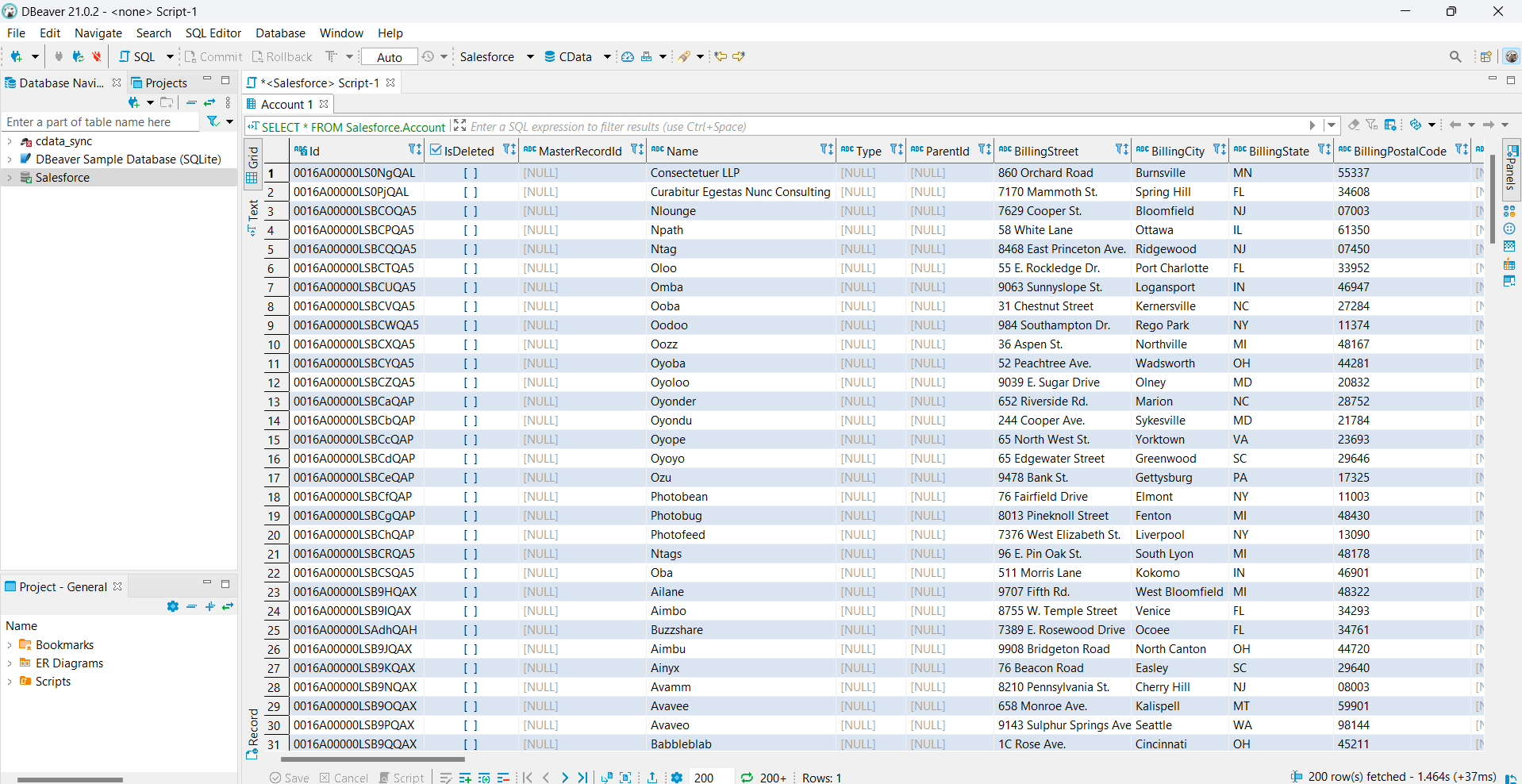
- You can easily configure the data by checking the table definition information through the CData JDBC driver using a tool such as DBeaver.
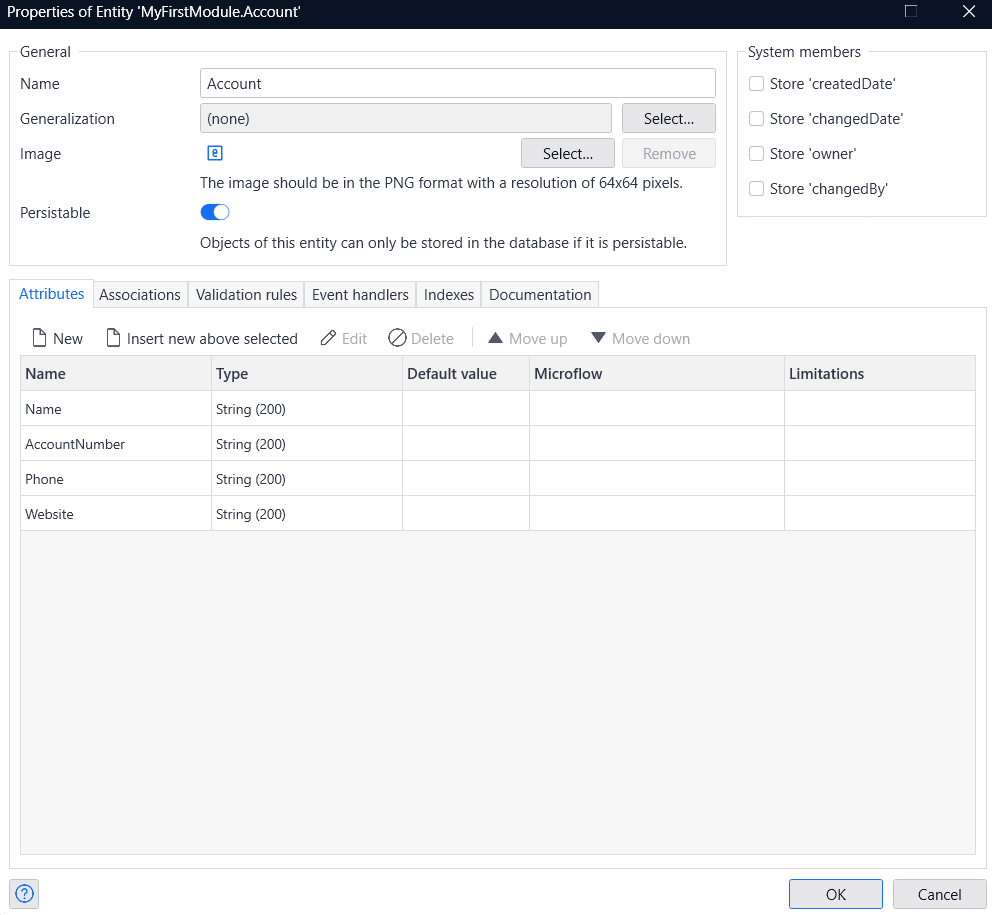
- Define the entities.
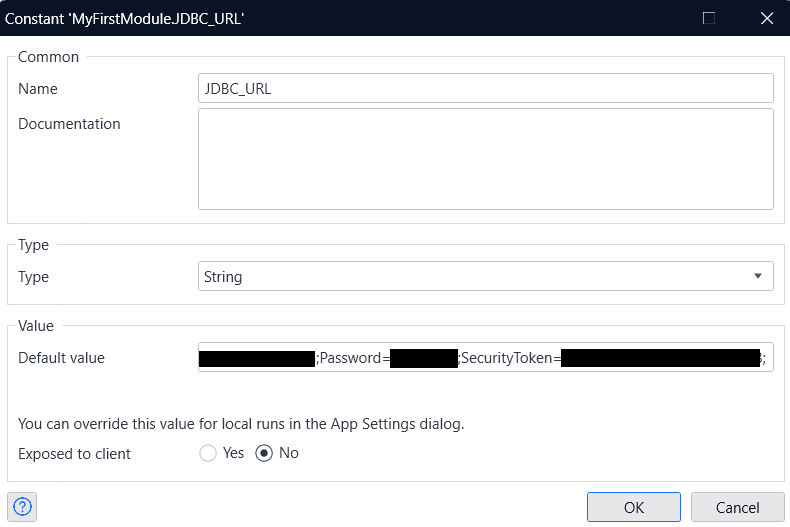
Create a constant for the JDBC URL
Next, create a JDBC URL constant to use with the Database Connector.
- Add 'Constant' to MyFirstModule.
- Add a name to the Constant in the Add Constant window.
Generate a JDBC URL for connecting to Amazon Athena, beginning with jdbc:amazonathena: followed by a series of semicolon-separated connection string properties.
Authenticating to Amazon Athena
To authorize Amazon Athena requests, provide the credentials for an administrator account or for an IAM user with custom permissions: Set AccessKey to the access key Id. Set SecretKey to the secret access key.
Note: Though you can connect as the AWS account administrator, it is recommended to use IAM user credentials to access AWS services.
Obtaining the Access Key
To obtain the credentials for an IAM user, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the IAM console.
- In the navigation pane, select Users.
- To create or manage the access keys for a user, select the user and then select the Security Credentials tab.
To obtain the credentials for your AWS root account, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the AWS Management console with the credentials for your root account.
- Select your account name or number and select My Security Credentials in the menu that is displayed.
- Click Continue to Security Credentials and expand the Access Keys section to manage or create root account access keys.
Authenticating from an EC2 Instance
If you are using the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 from an EC2 Instance and have an IAM Role assigned to the instance, you can use the IAM Role to authenticate. To do so, set UseEC2Roles to true and leave AccessKey and SecretKey empty. The CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 will automatically obtain your IAM Role credentials and authenticate with them.
Authenticating as an AWS Role
In many situations it may be preferable to use an IAM role for authentication instead of the direct security credentials of an AWS root user. An AWS role may be used instead by specifying the RoleARN. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to attempt to retrieve credentials for the specified role. If you are connecting to AWS (instead of already being connected such as on an EC2 instance), you must additionally specify the AccessKey and SecretKey of an IAM user to assume the role for. Roles may not be used when specifying the AccessKey and SecretKey of an AWS root user.
Authenticating with MFA
For users and roles that require Multi-factor Authentication, specify the MFASerialNumber and MFAToken connection properties. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to submit the MFA credentials in a request to retrieve temporary authentication credentials. Note that the duration of the temporary credentials may be controlled via the TemporaryTokenDuration (default 3600 seconds).
Connecting to Amazon Athena
In addition to the AccessKey and SecretKey properties, specify Database, S3StagingDirectory and Region. Set Region to the region where your Amazon Athena data is hosted. Set S3StagingDirectory to a folder in S3 where you would like to store the results of queries.
If Database is not set in the connection, the data provider connects to the default database set in Amazon Athena.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Amazon Athena JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.amazonathena.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
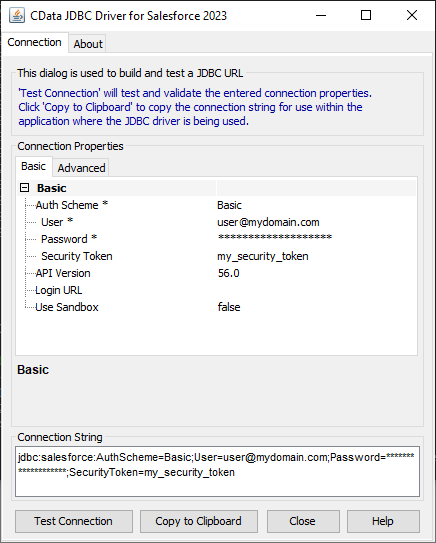
A typical JDBC URL is below:
jdbc:amazonathena:AWSAccessKey='a123';AWSSecretKey='s123';AWSRegion='IRELAND';Database='sampledb';S3StagingDirectory='s3://bucket/staging/';
- Specify the connection string copied from the previous step in the Default value section and click on OK.
Create a microflow to retrieve Amazon Athena data
Let's create a microflow that retrieves data from the Database Connector based on the entity we created.
- Click 'Add microflow' from MyFirstModule.
- Create a microflow with any name.
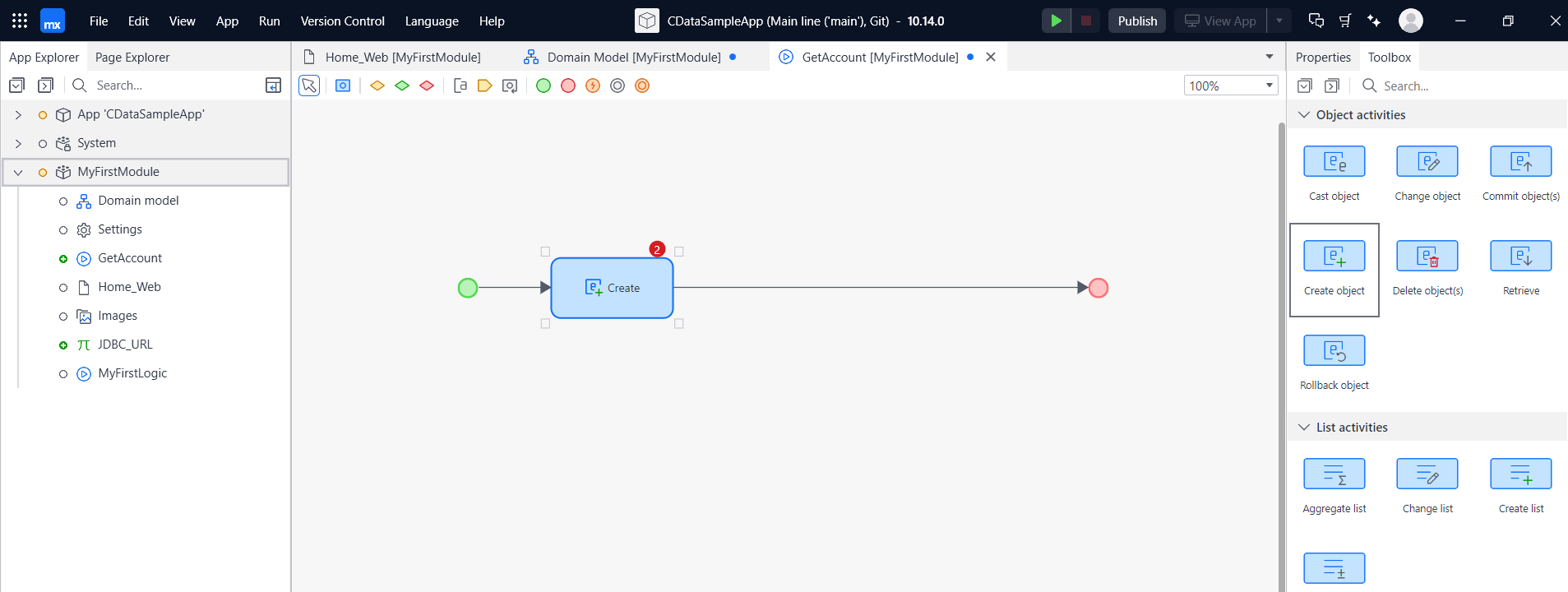
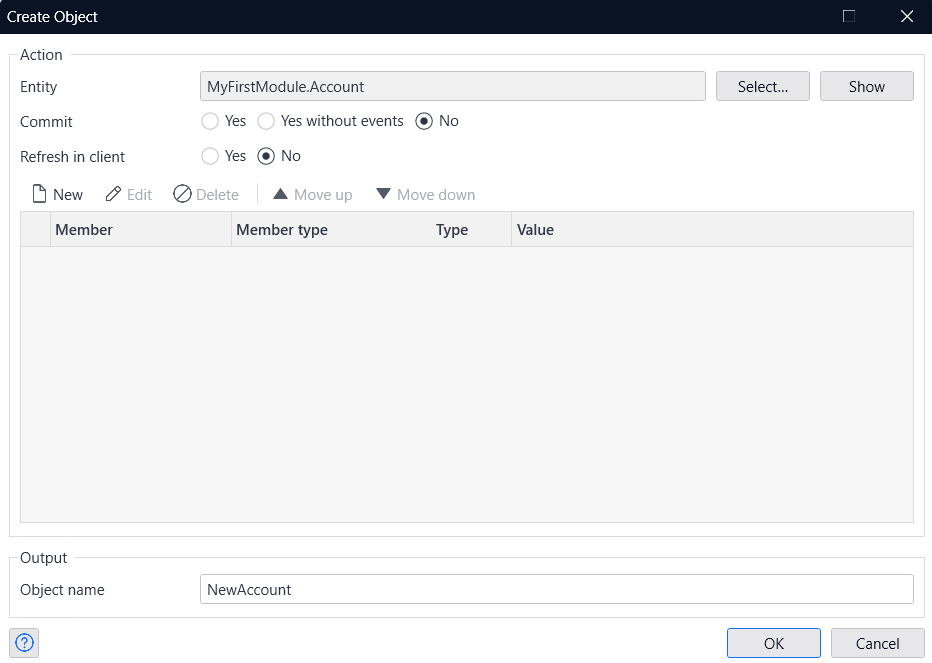
- First, create an object for the entity you defined earlier. Then, add the 'Create Object' action to the microflow.
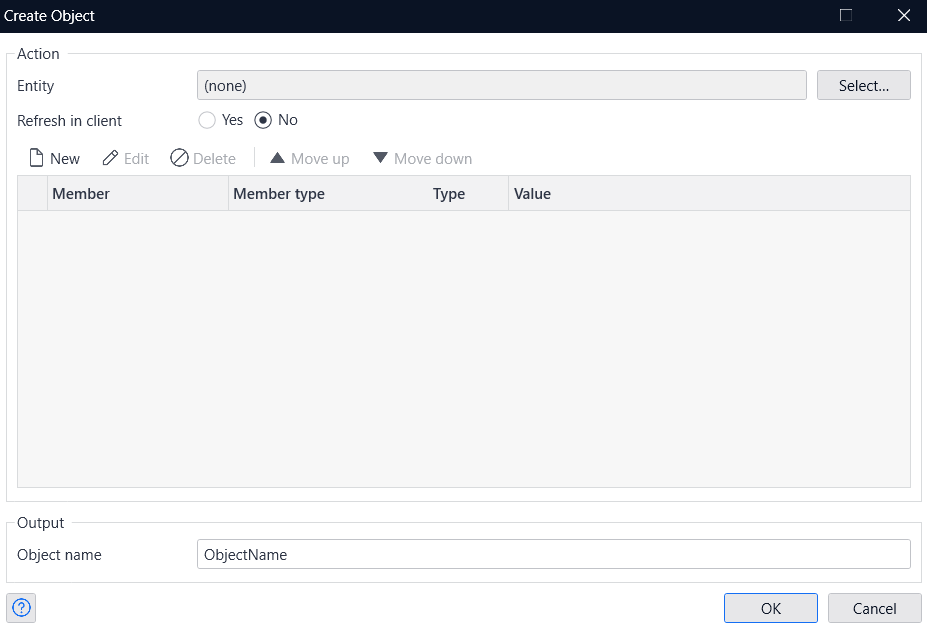
- Click on the 'Select' button for Entity in the Create Object window.
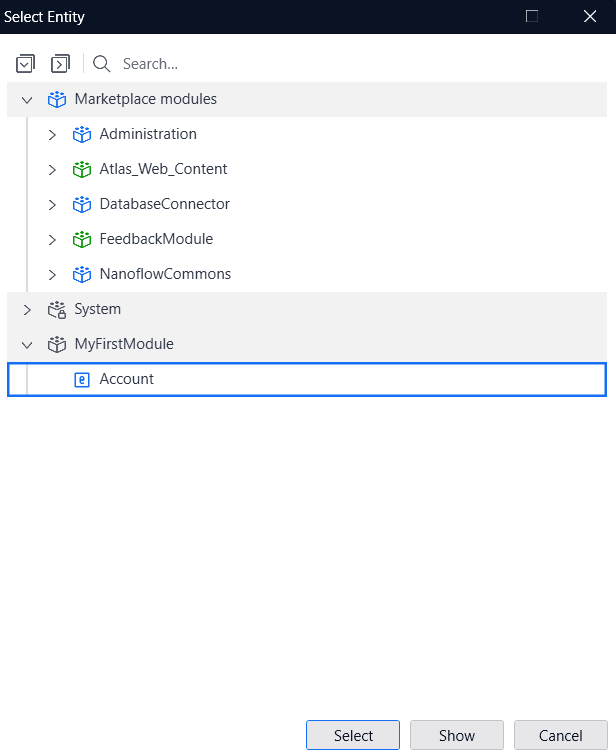
- Select a previously defined Entity.
- Enter an arbitrary Object name and click OK.
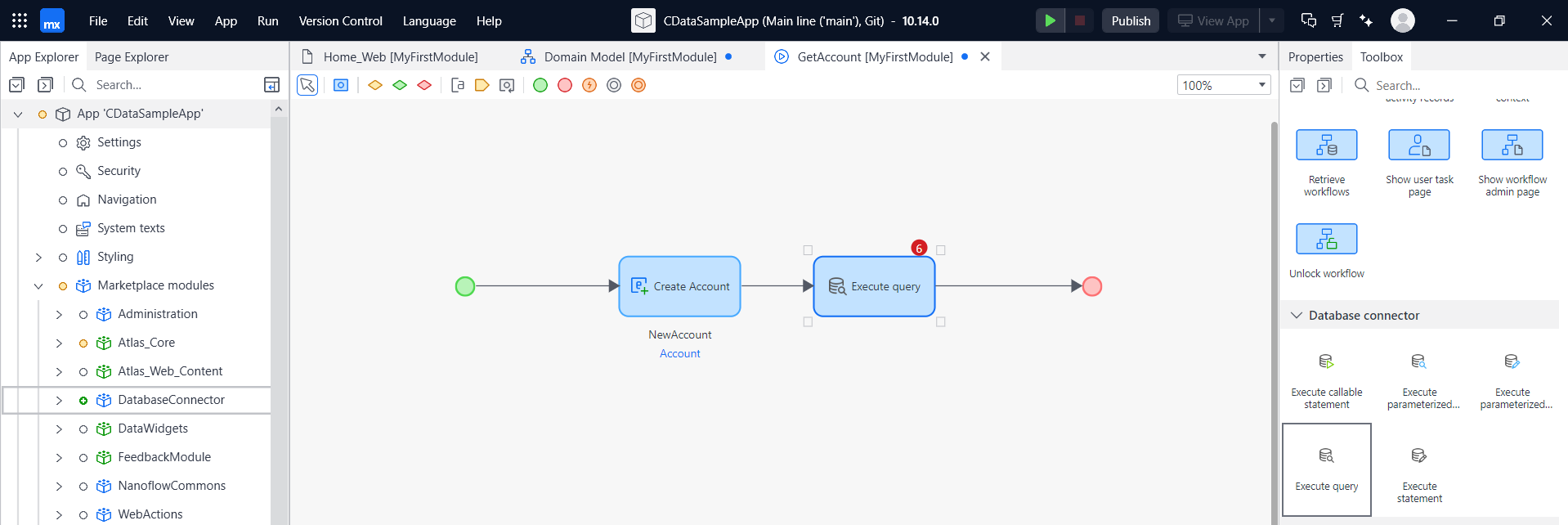
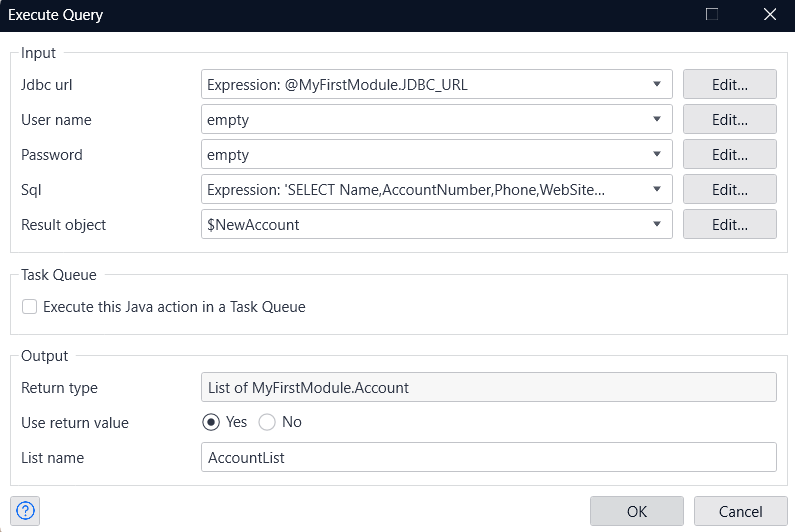
- Next, add an Execute Query action to the microflow to retrieve data from the Database Connector.
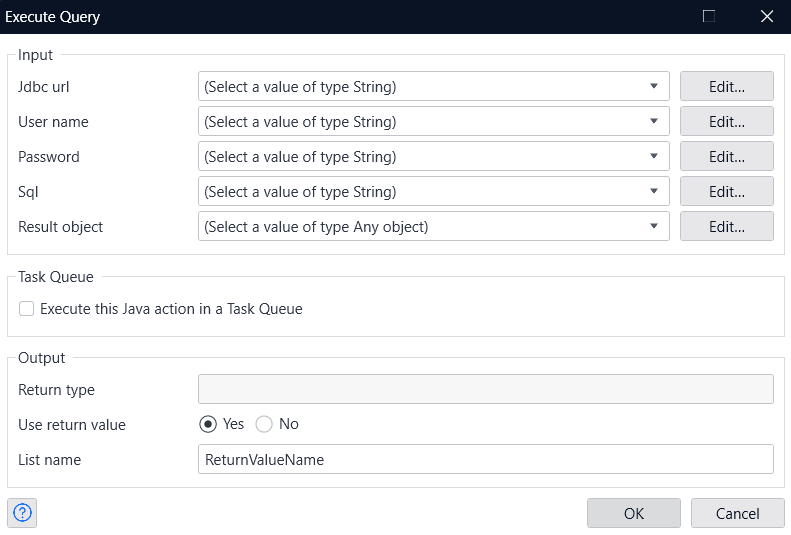
- Define each input in the Execute Query window.
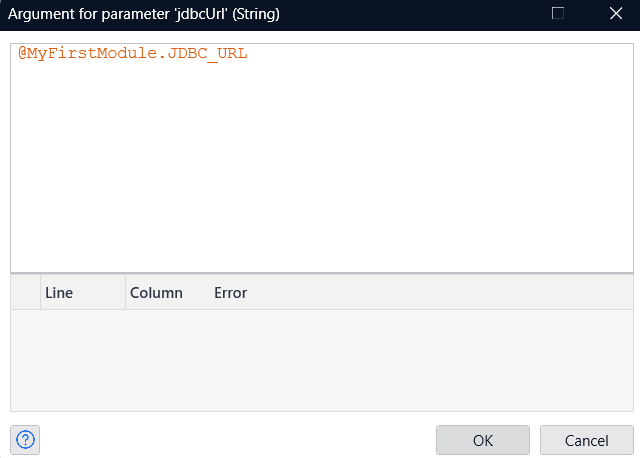
- In "jdbc url", specify the constant you defined beforehand.
- In SQL, write a query to retrieve data from Amazon Athena.
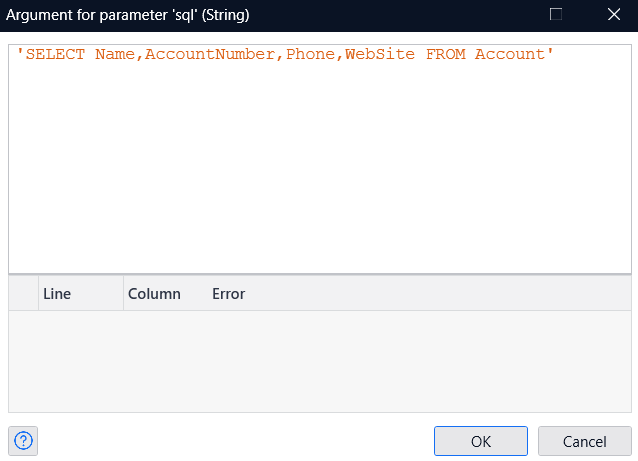
- You don't need a Username or Password this time, so set them to 'empty' and assign the object created in the previous flow as the Result object. Then, simply specify any name you prefer for the List in the List Name section.
- Finally, define the output of the microflow.
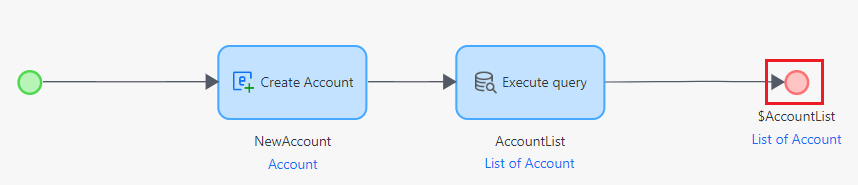
- Double-click the End Event to open it, select 'List' from the Type dropdown, and link it to the Entity you defined earlier. Then, set the output result of Execute Query as the Return value.
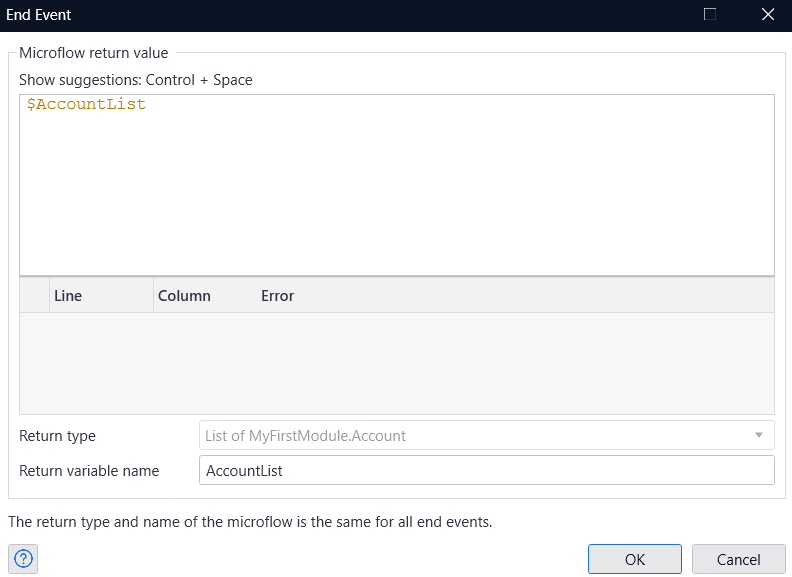
- This completes the microflow that retrieves data from Amazon Athena.
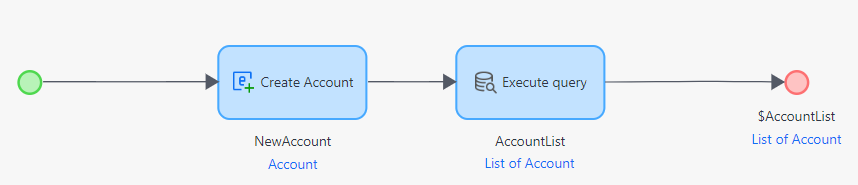
Create a list screen and link it to a microflow
Finally, let's create a screen that displays the results obtained from the microflow.
- Double-click 'Home_web' inside the Toolbox menu to open it.
- Drag and drop a Data grid template from the Data containers section into the list screen.
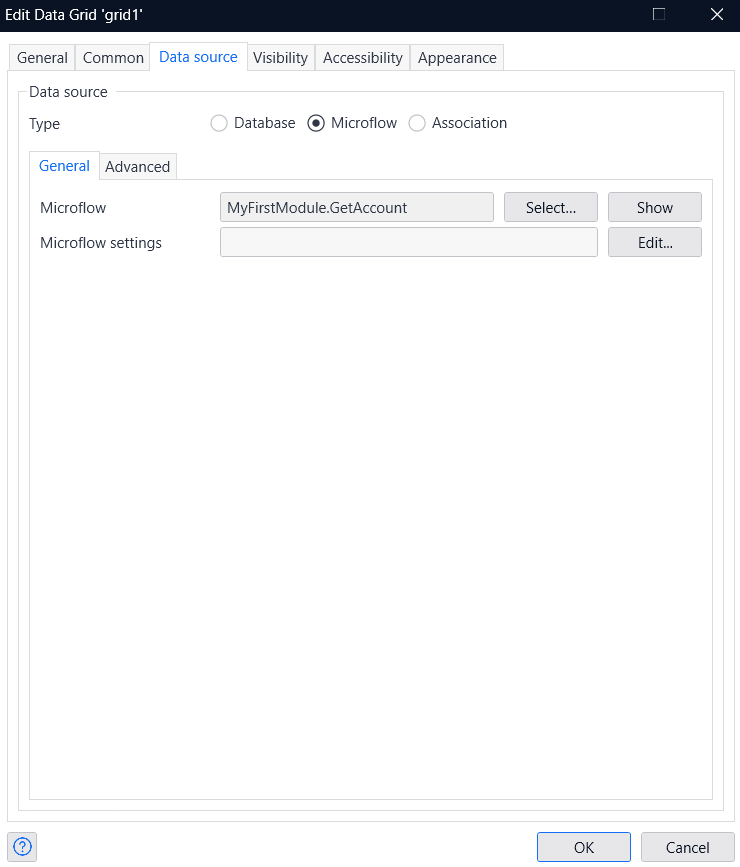
- Once you have placed the Data grid, double-click on it to display the Edit Data Grid settings screen.
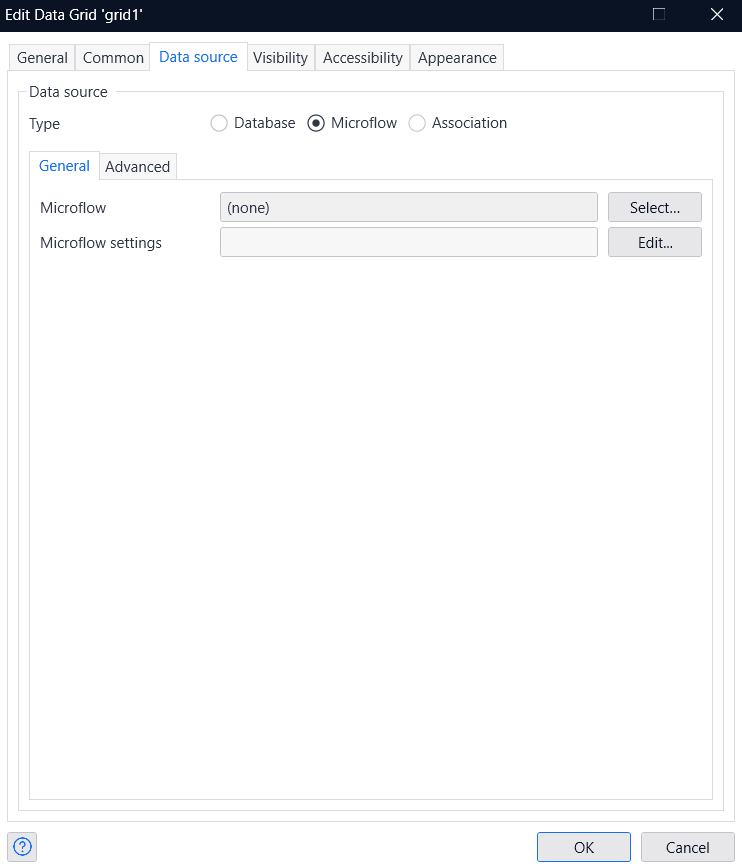
- Navigate to the Data source tab and link the data source type with the Microflow.
- Select the microflow you just created.
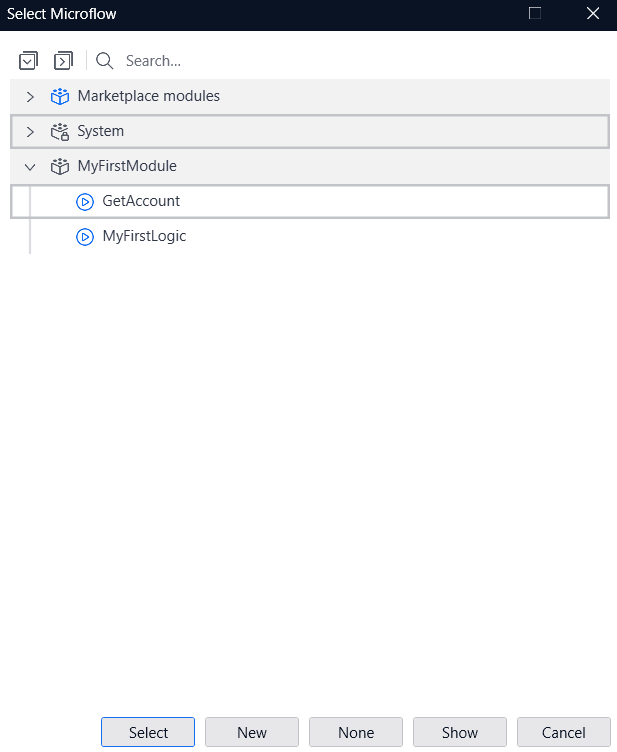
- Now click OK.
- When you click OK, you'll be prompted to auto-detect columns. Simply click 'Yes' to proceed.
- Next, you'll be prompted to generate controllers for various Data grids. Since we won't be configuring the logic for each one this time, click 'No.'

- This will create a simple data grid screen as shown below.
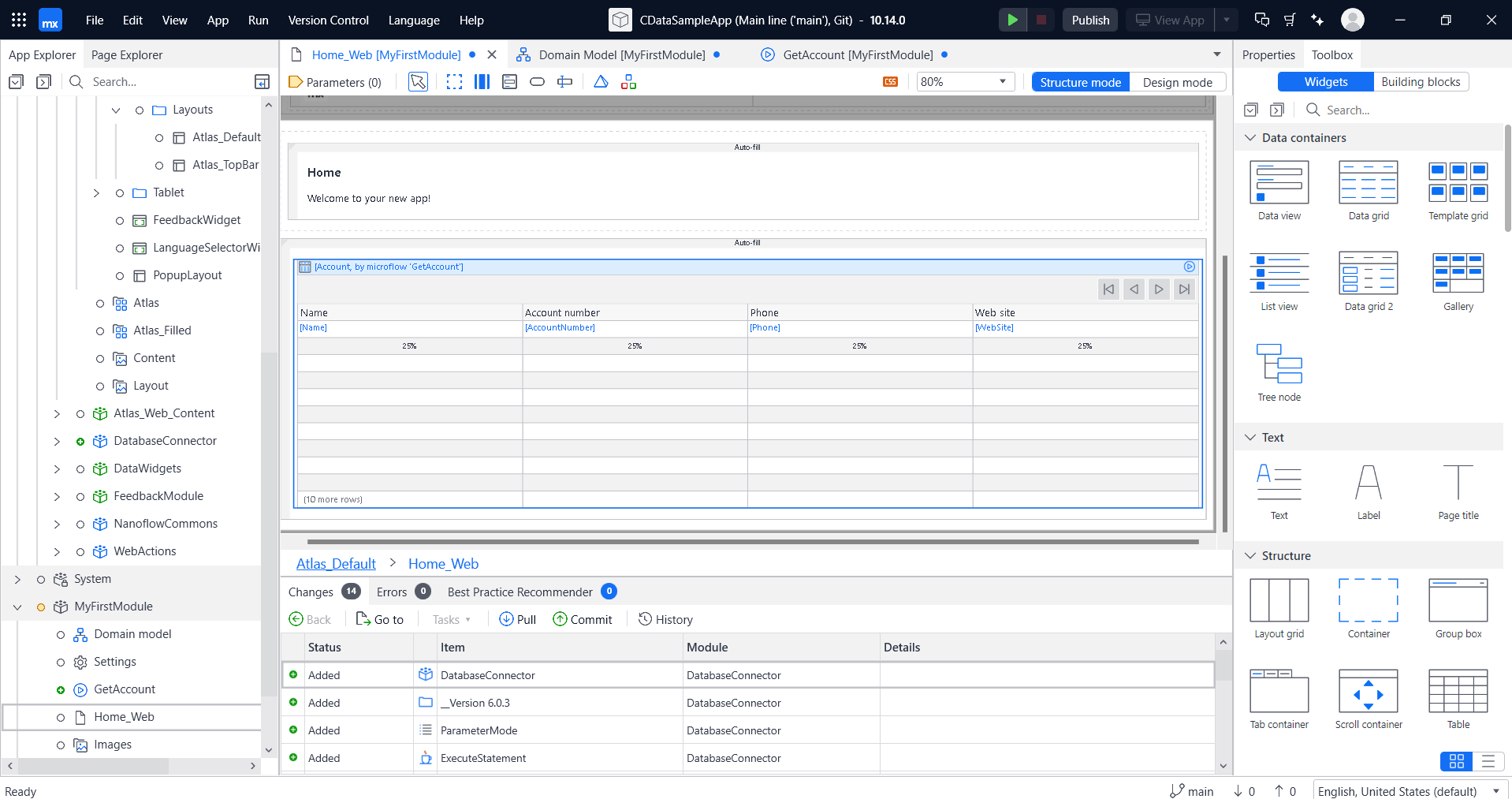
Try it out
Now let's check if it works properly.
- Click the 'Publish' button to prepare the app you created. Once that's done, click 'View App' to open the app.
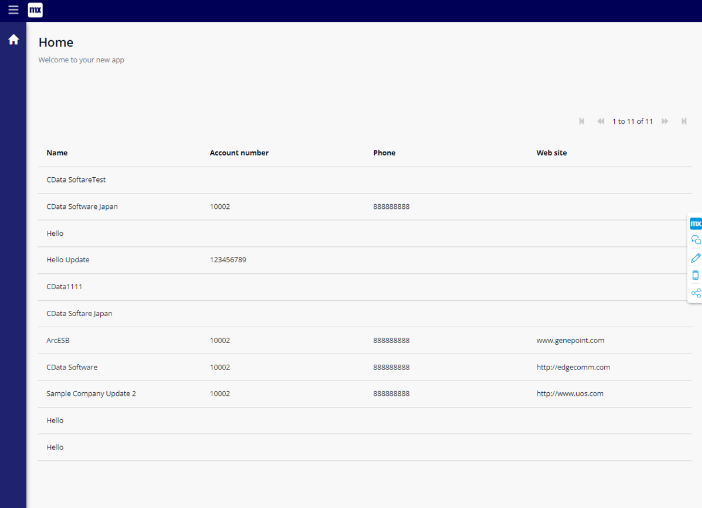
- If you see a list of Amazon Athena data like the one below, you're all set! You've successfully created a Amazon Athena-linked app with low code, without needing to worry about Amazon Athena's API.
Get Started Today
Download a free 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Amazon Athena with Mendix, and effortlessly create an app that connects to Amazon Athena data.
Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.


