Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Automated Continuous Azure Blob Storage Replication to SQL Server
Use CData Sync for automated, continuous, customizable Azure Blob Storage replication to SQL Server.
Always-on applications rely on automatic failover capabilities and real-time data access. CData Sync integrates live Azure Blob Storage data into your SQL Server instance, allowing you to consolidate all of your data into a single location for archiving, reporting, analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence and more.
Configure SQL Server as a Replication Destination
Using CData Sync, you can replicate Azure Blob Storage data to SQL Server. To add a replication destination, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click Add Connection.
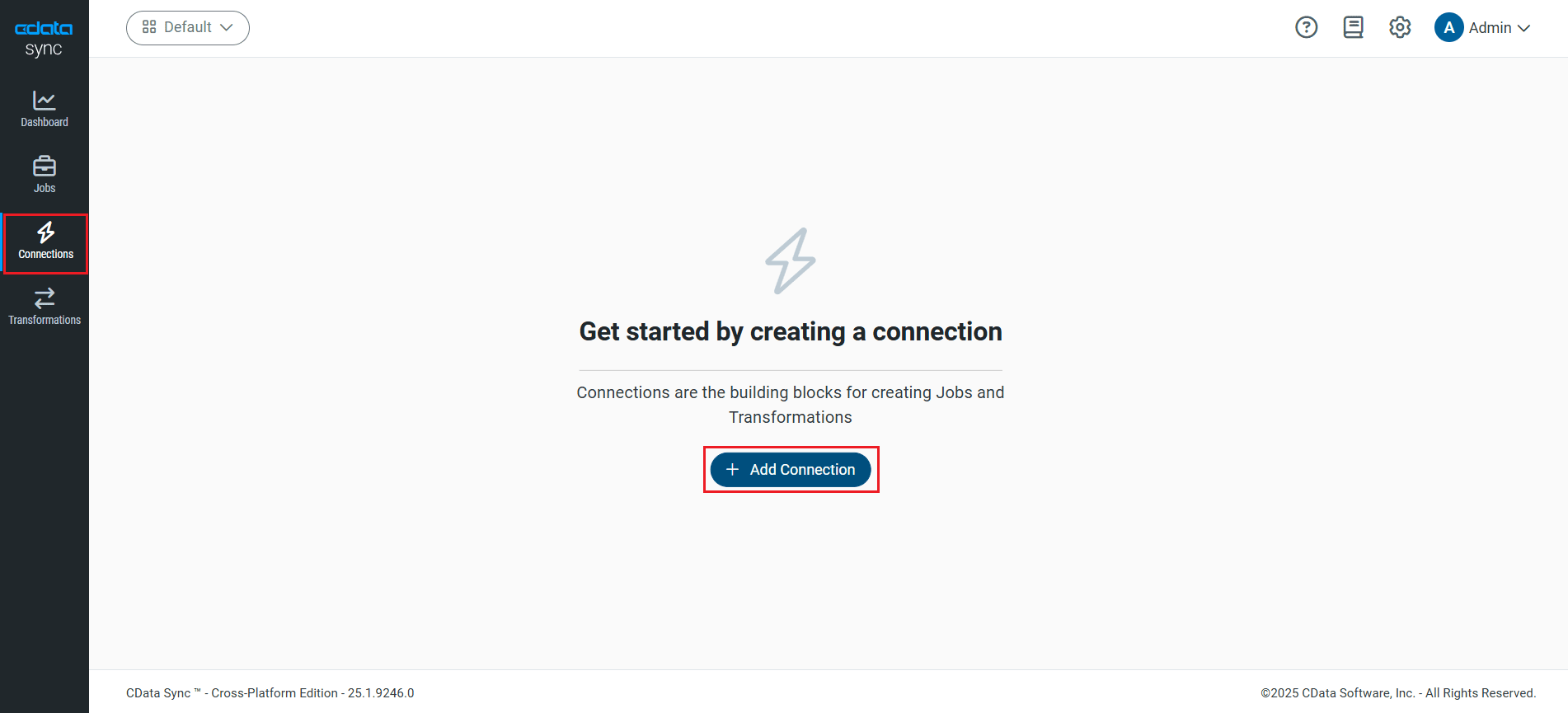
- Select the Destinations tab and locate the SQL Server connector.
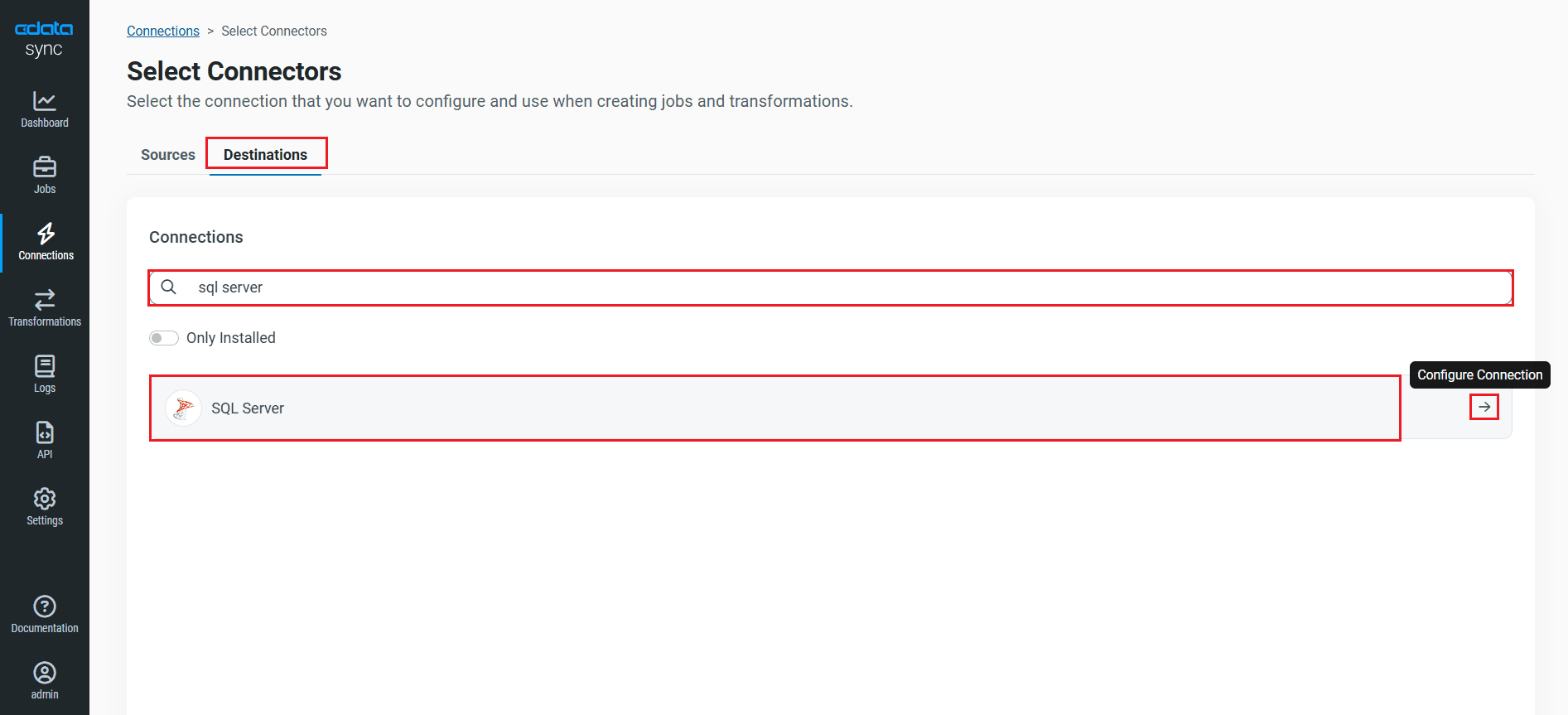
- Click the Configure Connection icon at the end of that row to open the New Connection page. If the Configure Connection icon is not available, click the Download Connector icon to install the SQL Server connector. For more information about installing new connectors, see Connections in the Help documentation.
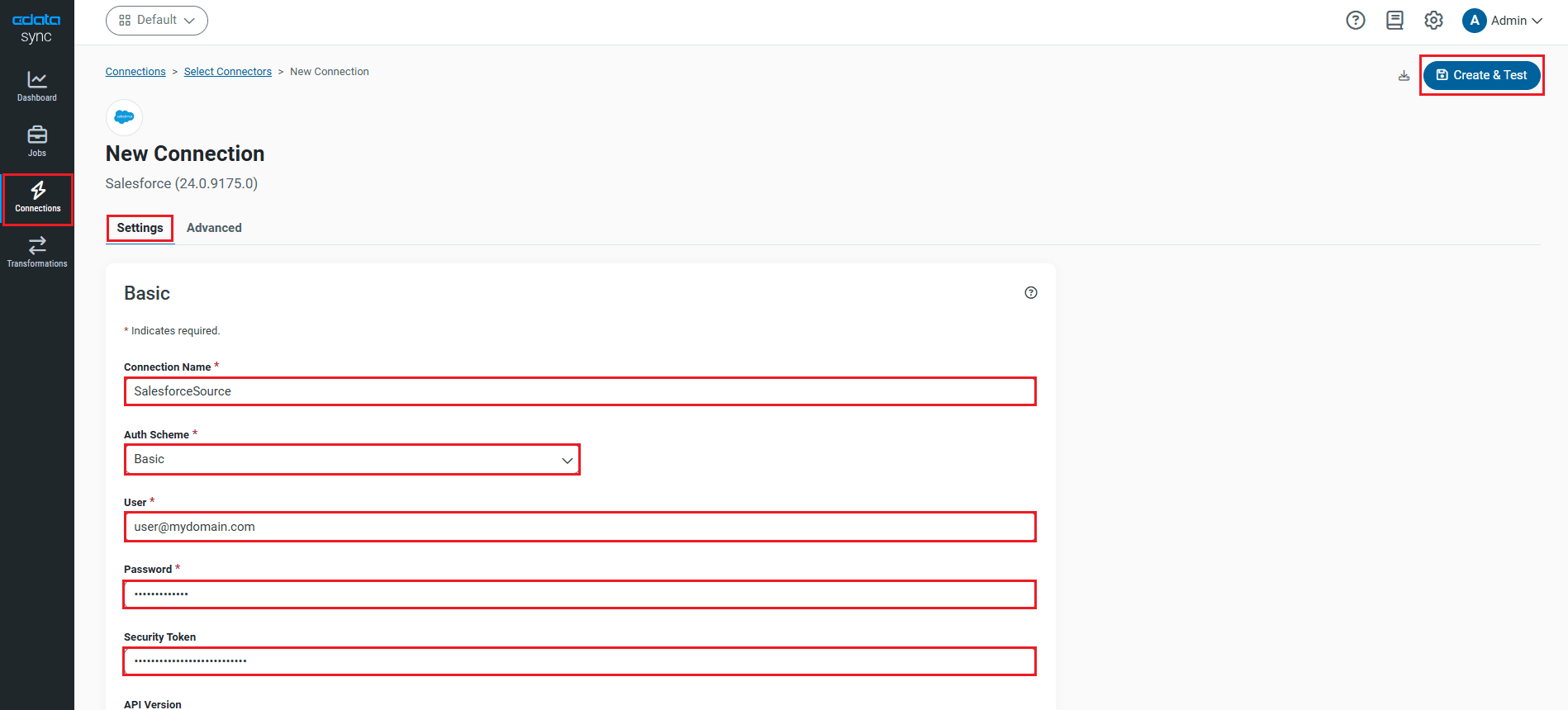
- To connect to SQL Server, set the following connection properties:
- Connection Name: Enter a connection name of your choice for the SQL Server connection.
- Server: Enter the name or network address of the computer running SQL Server.
- Port: Enter the port used to connect to the server hosting the SQL Server database.
- Database: Enter the name of the SQL Server database.
- User: Enter the username provided for authentication with SQL Server, if using forms authentication.
- Password: Enter the password provided for authentication with SQL Server, if using forms authentication.
Java Edition
The Java version requires the Microsoft SQL Server JDBC driver, which can be downloaded from the Microsoft Download Center. Copy the JDBC driver to the lib folder of your Java Web server to make a connection.
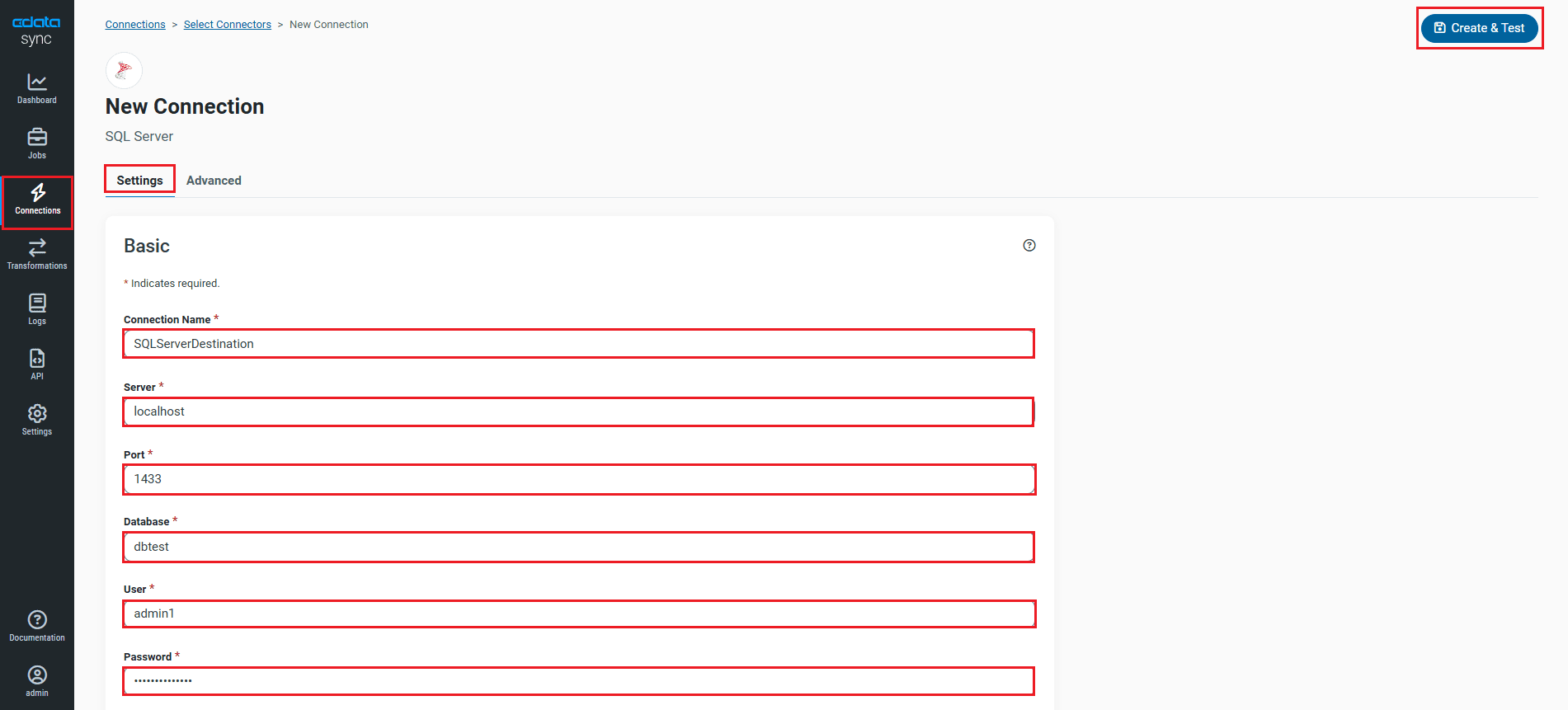
- Once connected, click Create & Test to create, test and save the connection.
You are now connected to SQL Server and can use it as both a source and a destination.
NOTE: You can use the Label feature to add a label for a source or a destination.
In this article, we will demonstrate how to load Azure Blob Storage data into SQL Server and utilize it as a destination.
Configure the Azure Blob Storage Connection
You can configure a connection to Azure Blob Storage from the Connections tab. To add a connection to your Azure Blob Storage account, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click Add Connection.
- Select a source (Azure Blob Storage).
- Configure the connection properties.
To connect with Azure Blog Storage, set the following connection properties:
- Connection Name - Enter a connection name of your choice.
- File Format - Select the file format that you want to use. Sync supports the CSV, PARQUET, and AVRO file formats.
- Azure Storage Account - Enter the name of your Azure storage account.
- URI - Enter the path of the file system and folder that contains your files. For example, azureblob://MyContainer/MyBlob
CData Sync supports authenticating to Microsoft OneLake in several ways. For Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), please see the instructions below.
Entra ID (formerly Azure AD)
To connect with an Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) user account, select "Entra ID" (formerly Azure AD) for Auth Scheme. CData Sync provides an embedded OAuth application with which to connect so no additional properties are required.
For other authentication methods (see below), refer to the Help documentation.
Other Supported Authentication Methods
- Azure Service Principal
- Azure Service Principal Certificate
- Azure Managed Service Identity
- Azure Access Key (default)
- Azure Storage SAS
- Click Connect to Azure Blob Storage to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
- Click Save & Test to save the changes.
Configure Replication Queries
CData Sync enables you to control replication with a point-and-click interface and with SQL queries. For each replication you wish to configure, navigate to the Jobs tab and click Add Job. Select the Source and Destination for your replication.
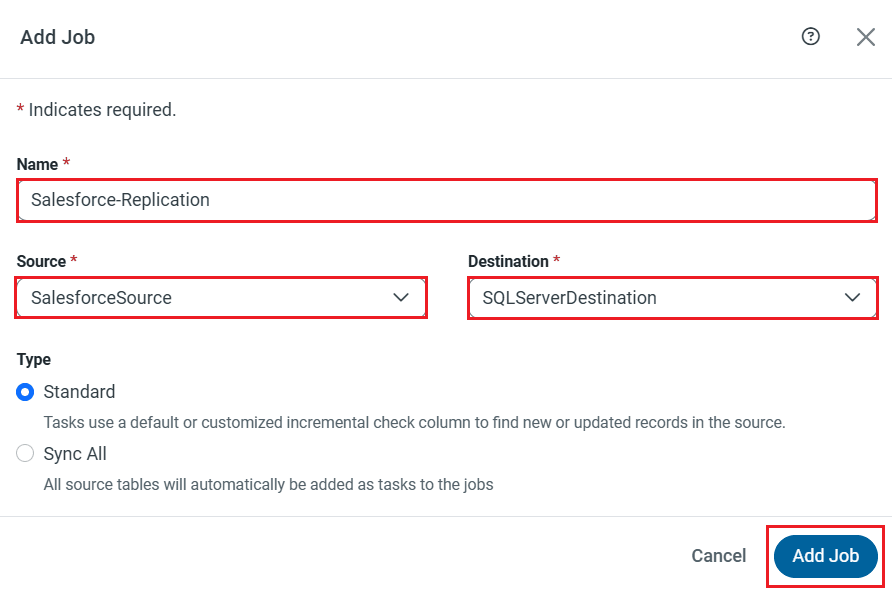
Replicate Entire Tables
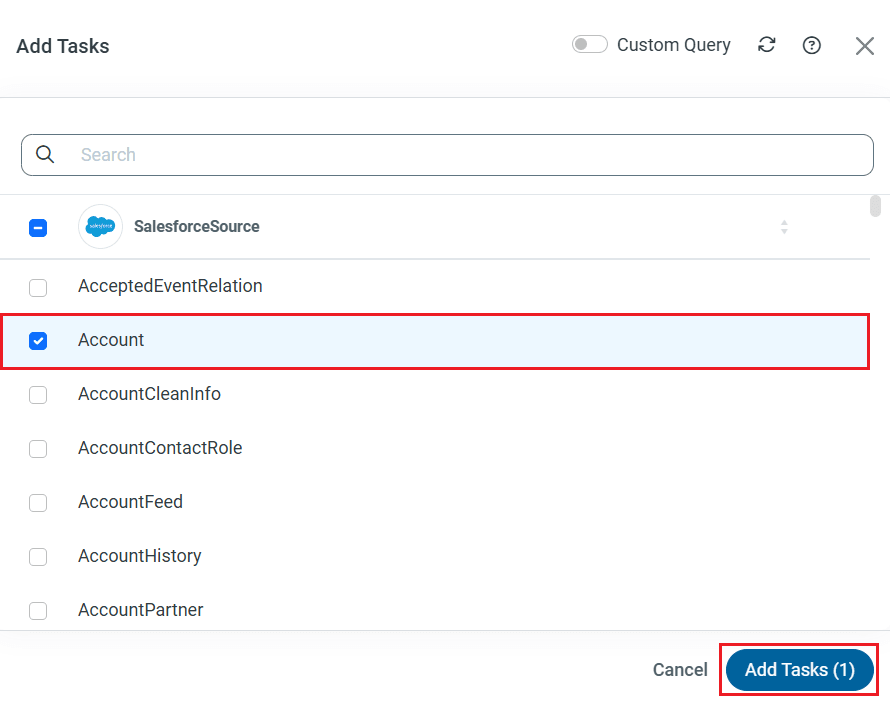
To replicate an entire table, navigate to the Task tab in the Job, click Add Tasks, choose the table(s) from the list of Azure Blob Storage tables you wish to replicate into SQL Server, and click Add Tasks again.
Customize Your Replication
You can use the Columns and Query tabs of a task to customize your replication. The Columns tab allows you to specify which columns to replicate, rename the columns at the destination, and even perform operations on the source data before replicating. The Query tab allows you to add filters, grouping, and sorting to the replication with the help of SQL queries.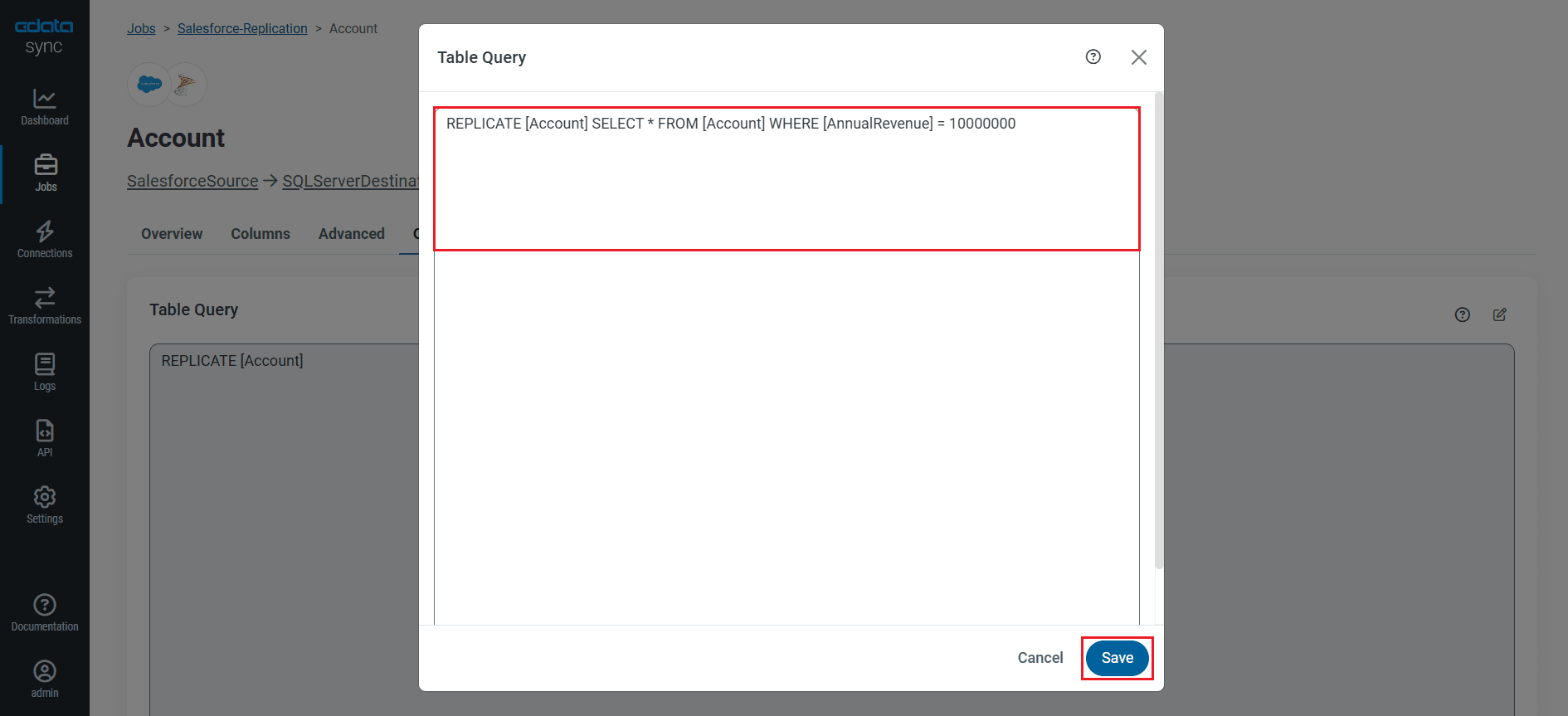
Schedule Your Replication
Select the Overview tab in the Job, and click Configure under Schedule. You can schedule a job to run automatically by configuring it to run at specified intervals, ranging from once every 10 minutes to once every month.
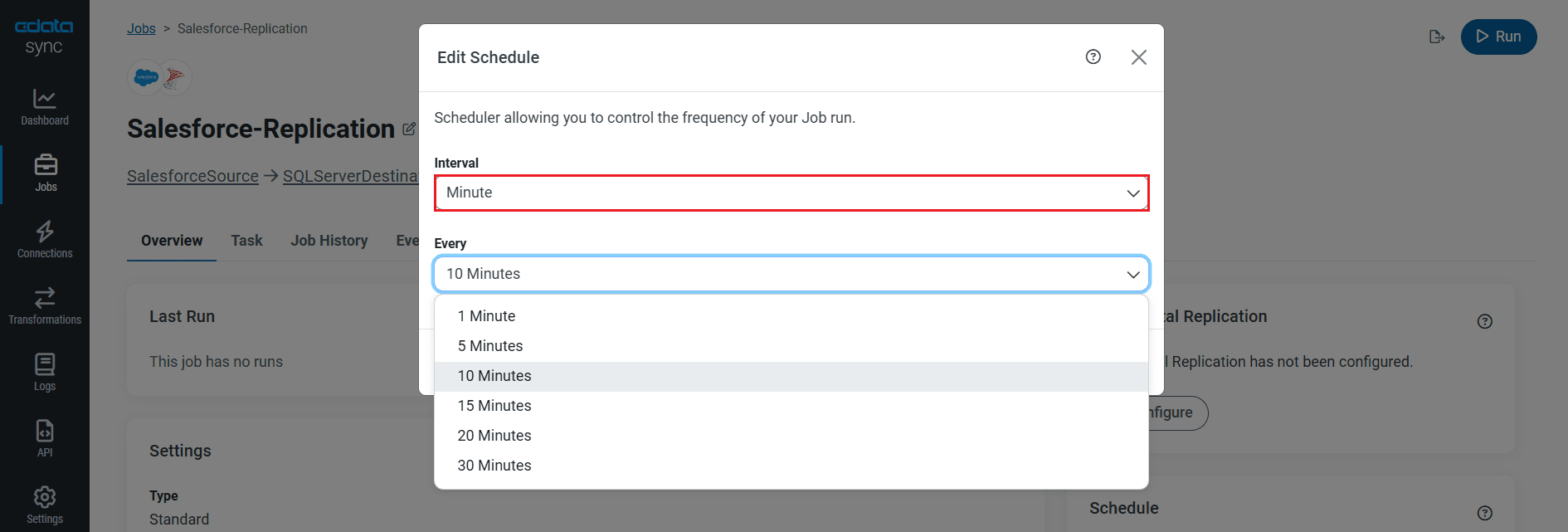
Once you have configured the replication job, click Save Changes. You can configure any number of jobs to manage the replication of your Azure Blob Storage data to SQL Server.
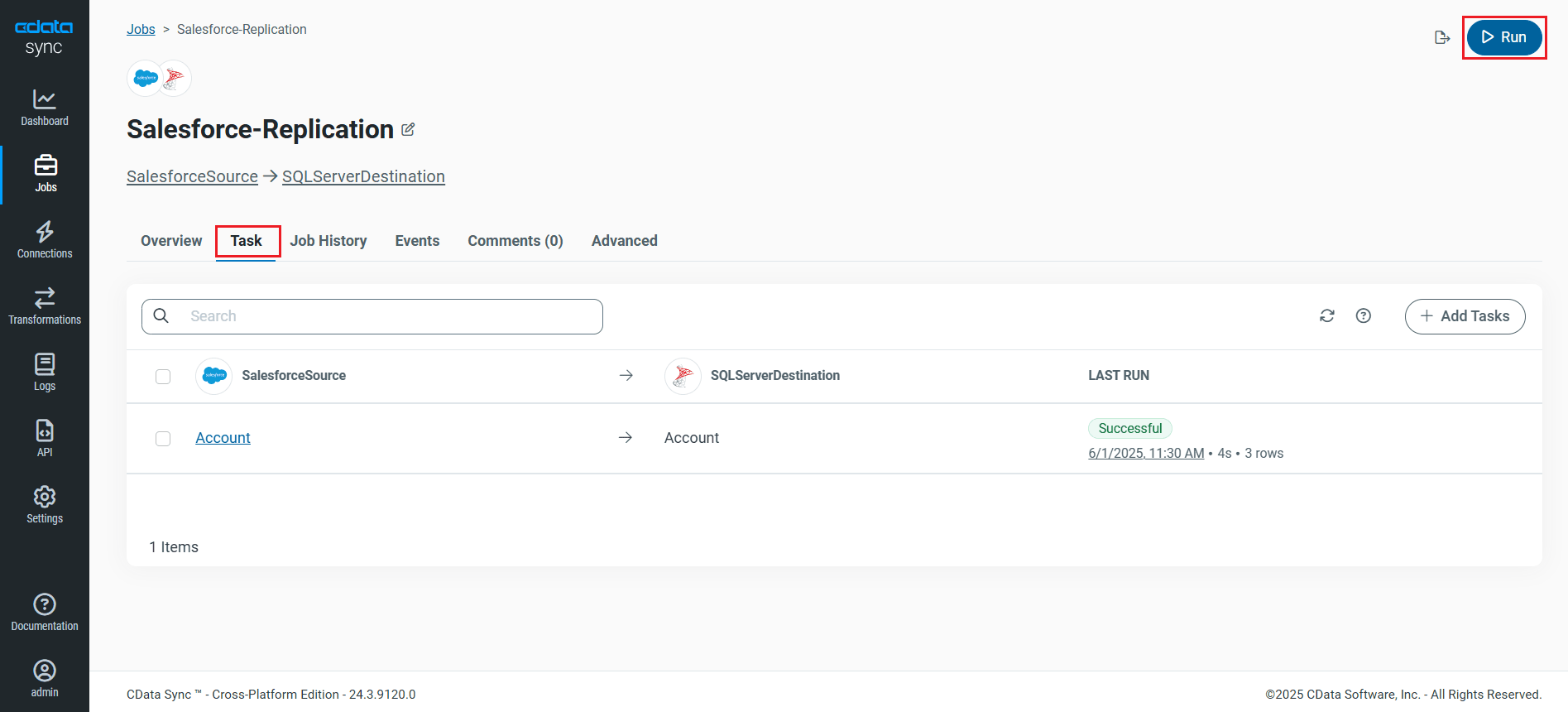
Run the Replication Job
Once all the required configurations are made for the job, select the Azure Blob Storage table you wish to replicate and click Run. After the replication completes successfully, a notification appears, showing the time taken to run the job and the number of rows replicated.
Free Trial & More Information
Now that you have seen how to replicate Azure Blob Storage data into SQL Server, visit our CData Sync page to explore more about CData Sync and download a free 30-day trial. Start consolidating your enterprise data today!
As always, our world-class Support Team is ready to answer any questions you may have.


