Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Connect and Query Live Microsoft Dataverse Data in Databricks with CData Connect Cloud
Use CData Connect Cloud to integrate live Microsoft Dataverse data into Databricks and enable direct, live querying and analysis without replication.
Databricks is a leading AI cloud-native platform that unifies data engineering, machine learning, and analytics at scale. Its powerful data lakehouse architecture combines the performance of data warehouses with the flexibility of data lakes. Integrating Databricks with CData Connect Cloud gives organizations live, real-time access to Microsoft Dataverse data without the need for complex ETL pipelines or data duplication—streamlining operations and reducing time-to-insights.
In this article, we'll walk through how to configure a secure, live connection from Databricks to Microsoft Dataverse using CData Connect Cloud. Once configured, you'll be able to access Microsoft Dataverse data directly from Databricks notebooks using standard SQL—enabling unified, real-time analytics across your data ecosystem.
About Microsoft Dataverse Data Integration
CData provides the easiest way to access and integrate live data from Microsoft Dataverse (formerly the Common Data Service). Customers use CData connectivity to:
- Access both Dataverse Entities and Dataverse system tables to work with exactly the data they need.
- Authenticate securely with Microsoft Dataverse in a variety of ways, including Azure Active Directory, Azure Managed Service Identity credentials, and Azure Service Principal using either a client secret or a certificate.
- Use SQL stored procedures to manage Microsoft Dataverse entities - listing, creating, and removing associations between entities.
CData customers use our Dataverse connectivity solutions for a variety of reasons, whether they're looking to replicate their data into a data warehouse (alongside other data sources)or analyze live Dataverse data from their preferred data tools inside the Microsoft ecosystem (Power BI, Excel, etc.) or with external tools (Tableau, Looker, etc.).
Getting Started
Overview
Here is an overview of the simple steps:
- Step 1 — Connect and Configure: In CData Connect Cloud, create a connection to your Microsoft Dataverse source, configure user permissions, and generate a Personal Access Token (PAT).
- Step 2 — Query from Databricks: Install the CData JDBC driver in Databricks, configure your notebook with the connection details, and run SQL queries to access live Microsoft Dataverse data.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have the following:
- An active Microsoft Dataverse account.
- A CData Connect Cloud account. You can log in or sign up for a free trial here.
- A Databricks account. Sign up or log in here.
Step 1: Connect and Configure a Microsoft Dataverse Connection in CData Connect Cloud
1.1 Add a Connection to Microsoft Dataverse
CData Connect Cloud uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to available data sources.
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Sources on the left, and then click Add Connection in the top-right.
- Select "Microsoft Dataverse" from the Add Connection panel.
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Microsoft Dataverse.
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. Below are the minimum connection properties required to connect.
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH. You can use InitiateOAuth to avoid repeating the OAuth exchange and manually setting the OAuthAccessToken.
- OrganizationUrl: Set this to the organization URL you are connecting to, such as https://myorganization.crm.dynamics.com.
- Tenant (optional): Set this if you wish to authenticate to a different tenant than your default. This is required to work with an organization not on your default Tenant.
When you connect the Common Data Service OAuth endpoint opens in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions. The OAuth process completes automatically.
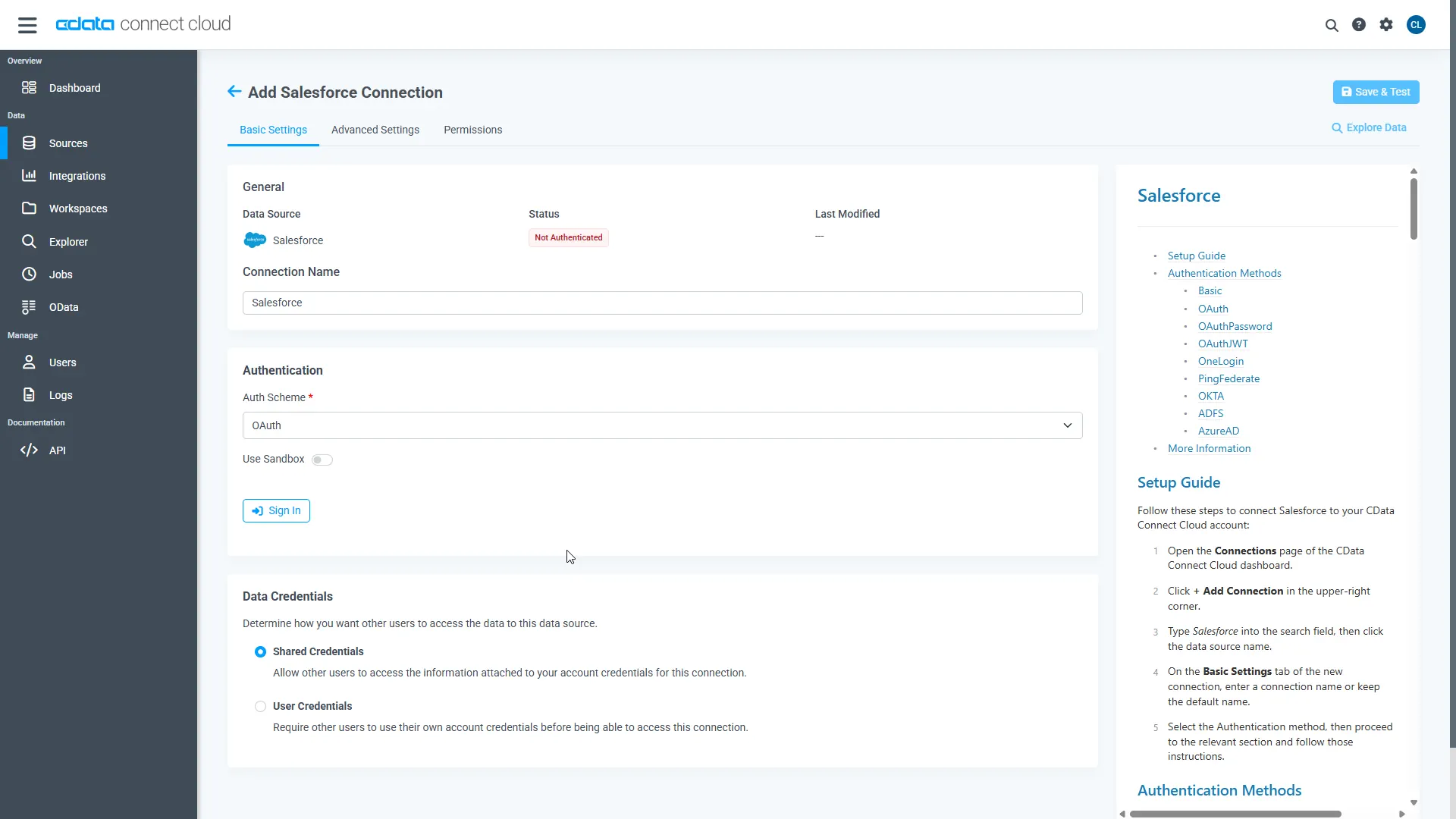
- Click Save & Test in the top-right.
-
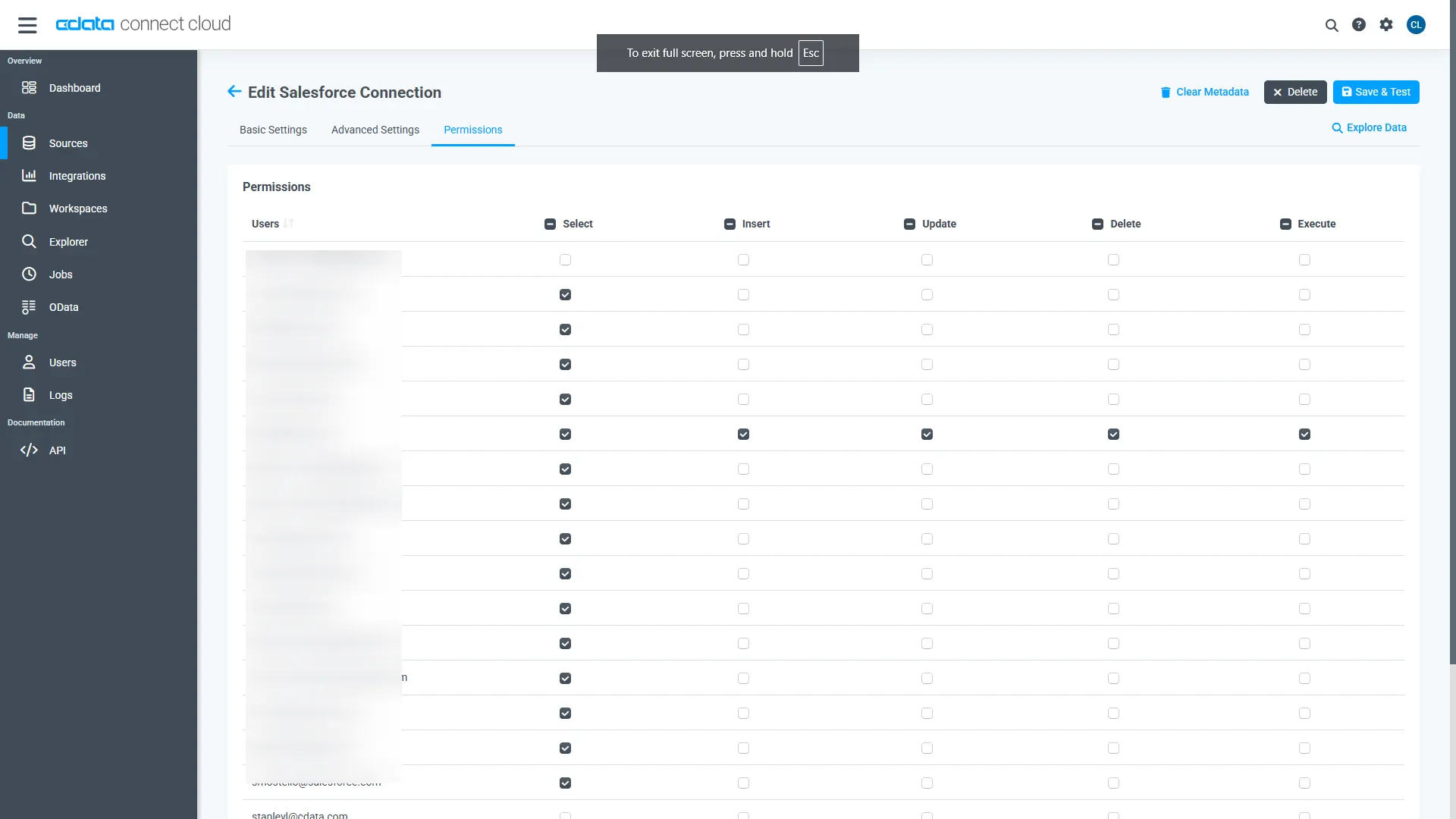
Navigate to the Permissions tab on the Microsoft Dataverse Connection page
and update the user-based permissions based on your preferences.

1.2 Generate a Personal Access Token (PAT)
When connecting to Connect Cloud through the REST API, the OData API, or the Virtual SQL Server, a Personal Access Token (PAT) is used to authenticate the connection to Connect Cloud. PAT functions as an alternative to your login credentials for secure, token-based authentication. It is a best practice to create a separate PAT for each service to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on the Gear icon () at the top right of the Connect Cloud app to open the settings page.
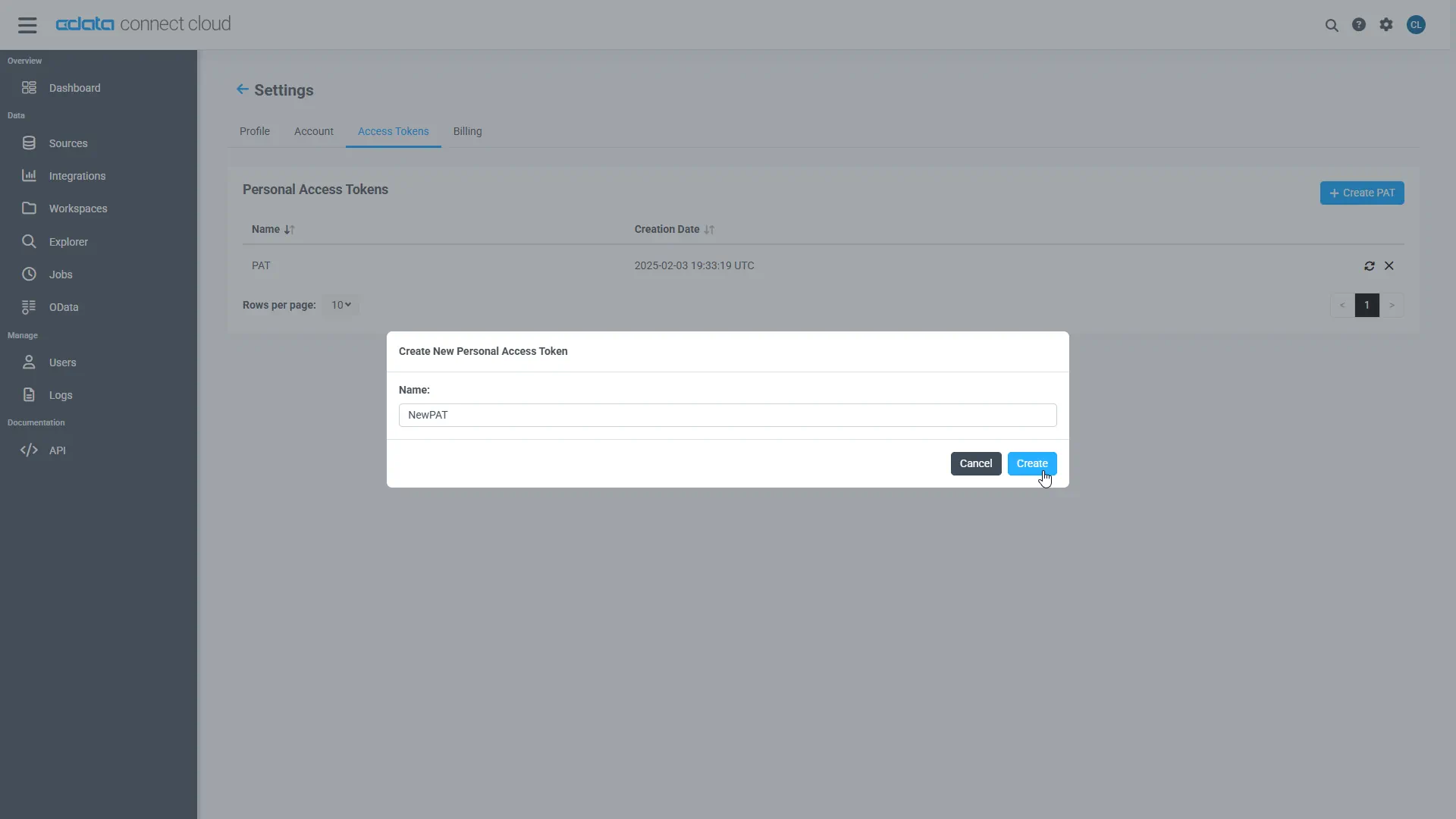
- On the Settings page, go to the Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
-
Give the PAT a name and click Create.
- Note: The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
Step 2: Connect and Query Microsoft Dataverse Data in Databricks
Follow these steps to establish a connection from Databricks to Microsoft Dataverse. You'll install the CData JDBC Driver for Connect Cloud, add the JAR file to your cluster, configure your notebooks, and run SQL queries to access live Microsoft Dataverse data data.
2.1 Install the CData JDBC Driver for Connect Cloud
- In CData Connect Cloud, click the Integrations page on the left. Search for JDBC or Databricks, click Download, and select the installer for your operating system.
-
Once downloaded, run the installer and follow the instructions:
- For Windows: Run the setup file and follow the installation wizard.
- For Mac/Linux: Unpack the archive and move the folder to /opt or /Applications. Make sure you have execute permissions.
-
After installation, locate the JAR file in the installation directory:
- Windows:
C:\Program Files\CData\CData JDBC Driver for Connect Cloud\lib\cdata.jdbc.connect.jar
- Mac/Linux:
/Applications/CData/CData JDBC Driver for Connect Cloud/lib/cdata.jdbc.connect.jar
- Windows:
2.2 Install the JAR File on Databricks
-
Log in to Databricks. In the navigation pane, click Compute on the left. Start or create a compute cluster.
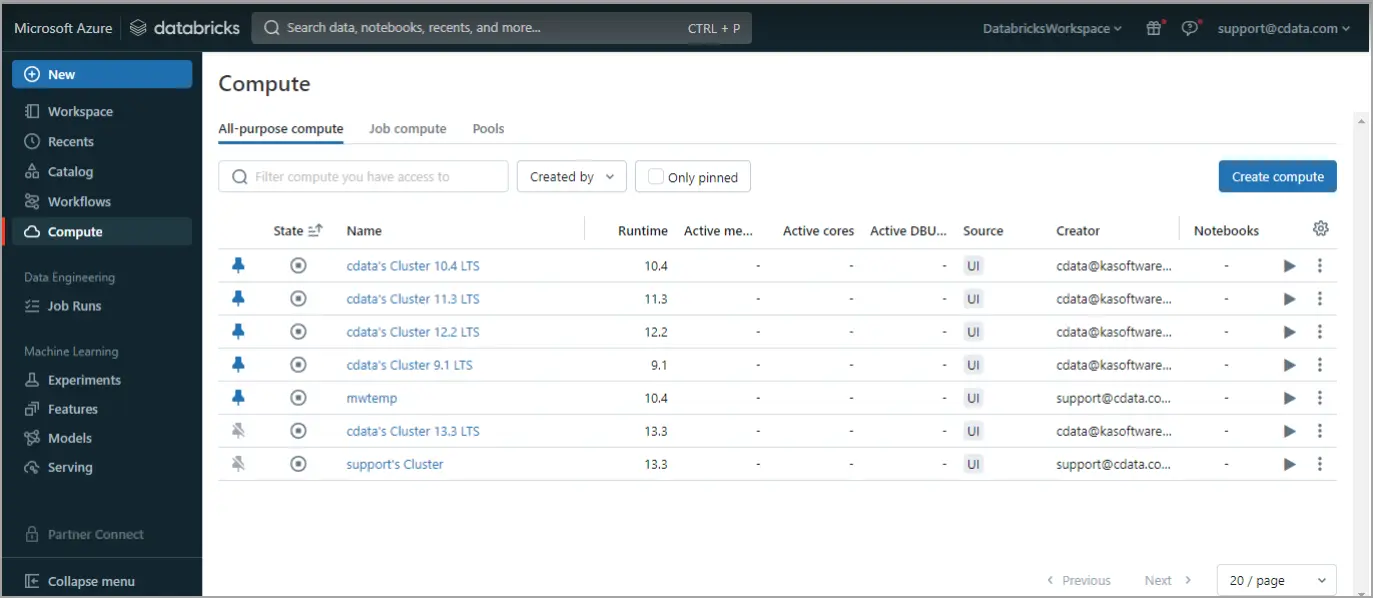
-
Click on the running cluster, go to the Libraries tab, and click Install New at the top right.
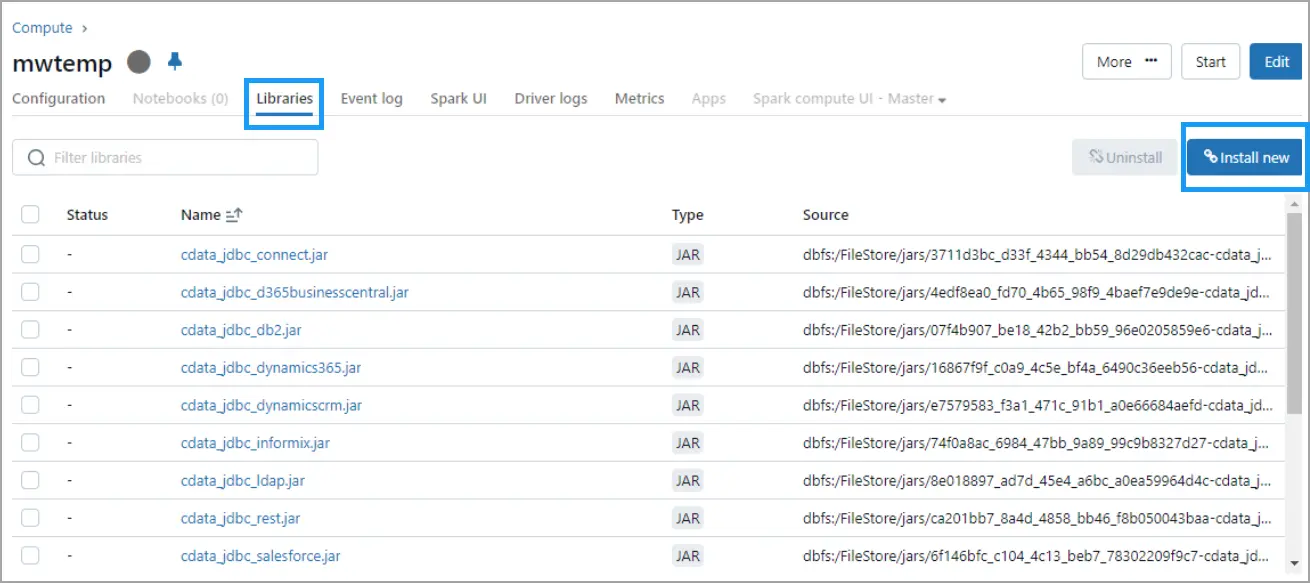
-
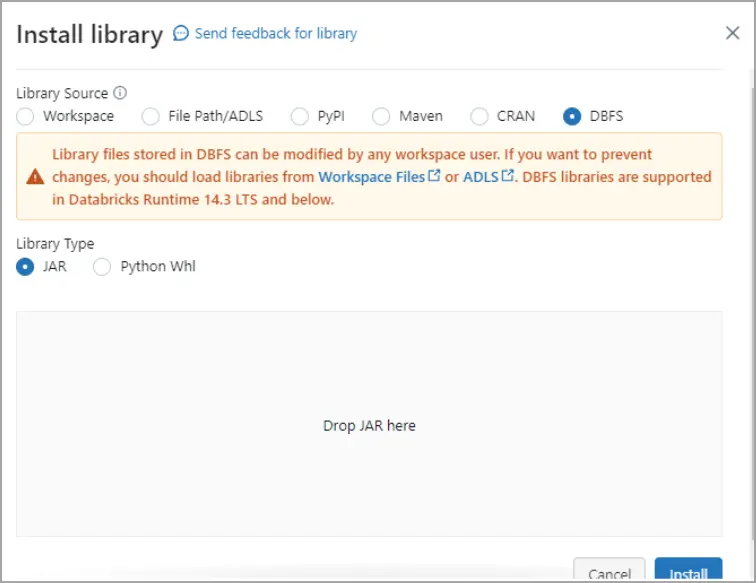
In the Install Library dialog, select DBFS, and drag and drop the
cdata.jdbc.connect.jar file. Click Install.
2.3 Query Microsoft Dataverse Data in a Databricks Notebook
Notebook Script 1 — Define JDBC Connection:
- Paste the following script into the notebook cell:
driver = "cdata.jdbc.connect.ConnectDriver" url = "jdbc:connect:AuthScheme=Basic;User=your_username;Password=your_pat;URL=https://cloud.cdata.com/api/;DefaultCatalog=Your_Connection_Name;"
- Replace:
- your_username - With your CData Connect Cloud username
- your_pat - With your CData Connect Cloud Personal Access Token (PAT)
- Your_Connection_Name - With the name of your Connect Cloud data source, from the Sources page
- Run the script.
Notebook Script 2 — Load DataFrame from Microsoft Dataverse data:
- Add a new cell for this second script. From the menu on the right side of your notebook, click Add cell below.
- Paste the following script into the new cell:
remote_table = spark.read.format("jdbc") \
.option("driver", "cdata.jdbc.connect.ConnectDriver") \
.option("url", "jdbc:connect:AuthScheme=Basic;User=your_username;Password=your_pat;URL=https://cloud.cdata.com/api/;DefaultCatalog=Your_Connection_Name;") \
.option("dbtable", "YOUR_SCHEMA.YOUR_TABLE") \
.load()
- Replace:
- your_username - With your CData Connect Cloud username
- your_pat - With your CData Connect Cloud Personal Access Token (PAT)
- Your_Connection_Name - With the name of your Connect Cloud data source, from the Sources page
- YOUR_SCHEMA.YOUR_TABLE - With your schema and table, for example, CDS.Accounts
- Run the script.
Notebook Script 3 — Preview Columns:
- Similarly, add a new cell for this third script.
- Paste the following script into the new cell:
display(remote_table.select("ColumnName1", "ColumnName2"))
- Replace ColumnName1 and ColumnName2 with the actual columns from your Microsoft Dataverse structure (e.g. AccountId, Name, etc.).
- Run the script.
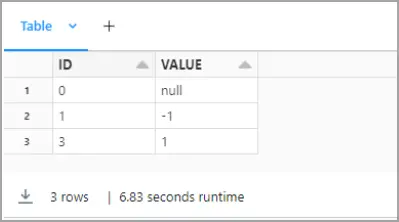
You can now explore, join, and analyze live Microsoft Dataverse data directly within Databricks notebooks—without needing to know the complexities of the back-end API and without replicating Microsoft Dataverse data.
Try CData Connect Cloud Free for 14 Days
Ready to simplify real-time access to Microsoft Dataverse data? Start your free 14-day trial of CData Connect Cloud today and experience seamless, live connectivity from Databricks to Microsoft Dataverse.
Low code, zero infrastructure, zero replication — just seamless, secure access to your most critical data and insights.


