Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Integrate Dynamics CRM Data in the Pentaho Report Designer
Publish reports based on Dynamics CRM data in the Pentaho BI tool.
The CData JDBC driver for Dynamics CRM data enables access to live data from dashboards and reports. This article shows how to connect to Dynamics CRM data as a JDBC data source and publish reports based on Dynamics CRM data in Pentaho.
About Dynamics CRM Data Integration
CData simplifies access and integration of live Microsoft Dynamics CRM data. Our customers leverage CData connectivity to:
- Read and write data in the Dynamics CRM 2011+ Services and Dynamics CRM Online.
- Extend the native features of Dynamics CRM with customizable caching and intelligent query aggregation and separation.
- Authenticate securely with Dynamics CRM in a variety of ways, including Azure Active Directory, Azure Managed Service Identity credentials, and Azure Service Principal using either a client secret or a certificate.
CData customers use our Dynamics CRM connectivity solutions for a variety of reasons, whether they're looking to replicate their data into a data warehouse (alongside other data sources) or analyze live Dynamics CRMa data from their preferred data tools inside the Microsoft ecosystem (Power BI, Excel, etc.) or with external tools (Tableau, Looker, etc.).
Getting Started
Connect and Create a Report
- Copy the JAR file of the driver, located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory, to the \Report-Designer\lib\jdbc\ folder in the Pentaho directory.
- Run the report-designer.bat file in the \Report-Designer\ folder to open the Report-Designer UI.
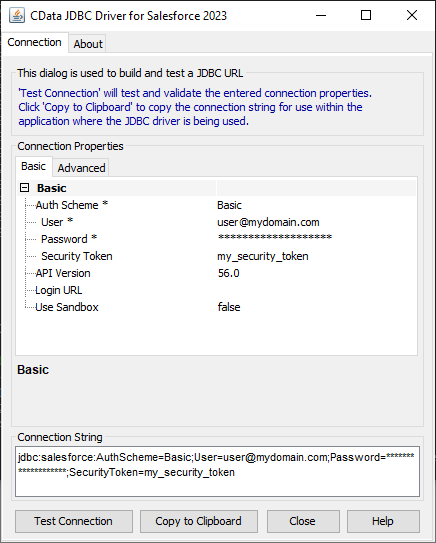
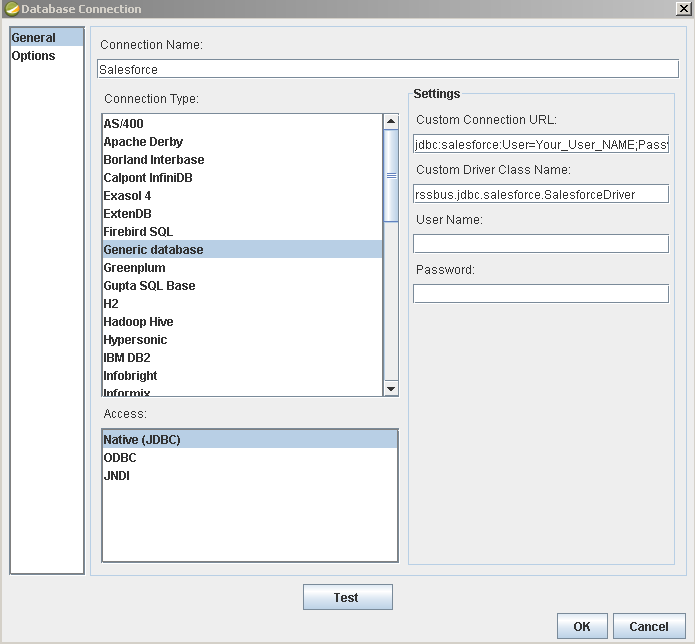
Create a new data source with the driver by clicking Data -> Add Data Source -> Advanced -> JDBC (Custom) and then creating a new Dynamics CRM connection. In the resulting dialog, configure the connection properties as shown below.
Custom Connection URL property: Enter the JDBC URL. This starts with jdbc:dynamicscrm: and is followed by a semicolon-separated list of connection properties.
The connection string options meet the authentication and connection requirements of different Dynamics CRM instances. To connect to your instance, set the User and Password properties, under the Authentication section, to valid Dynamics CRM user credentials and set the Url to a valid Dynamics CRM server organization root. Additionally, set the CRMVersion property to 'CRM2011+' or 'CRMOnline'. IFD configurations are supported as well; set InternetFacingDeployment to true.
Additionally, you can provide the security token service (STS) or AD FS endpoint in the STSURL property. This value can be retrieved with the GetSTSUrl stored procedure. Office 365 users can connect to the default STS URL by simply setting CRMVersion.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Dynamics CRM JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.dynamicscrm.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Below is a typical JDBC URL:
jdbc:dynamicscrm:User=myuseraccount;Password=mypassword;URL=https://myOrg.crm.dynamics.com/;CRM Version=CRM Online;
- Custom Driver Class Name: Enter cdata.jdbc.dynamicscrm.DynamicsCRMDriver.
- User Name: The username to authenticate with.
- Password: The password to authenticate with.
Add Dynamics CRM Data to a Report
You are now ready to create a report with Dynamics CRM data.
-
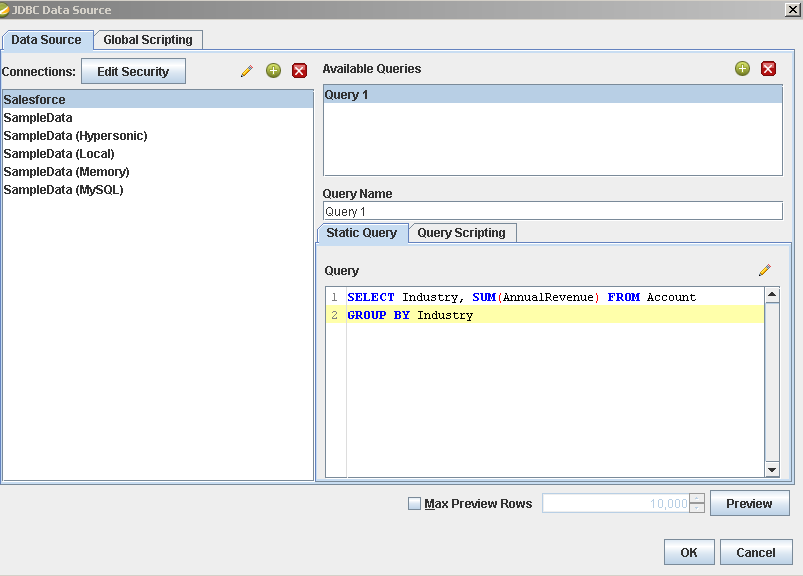
Add the Dynamics CRM source to your report: Click Data -> Add Data Source -> JDBC and select the data source.
Configure the query. This article uses the one below:
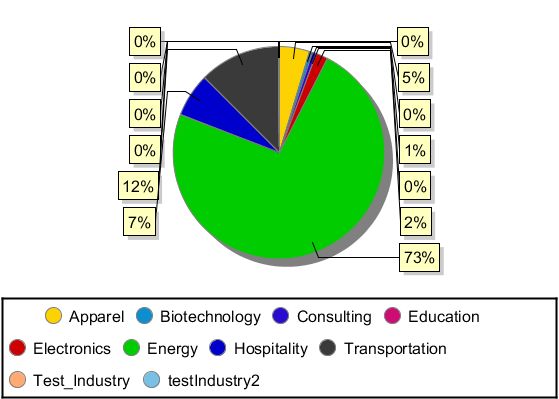
SELECT Contact.FirstName, SUM(Account.NumberOfEmployees) FROM Contact, Account GROUP BY Contact.FirstName
- Drag a chart onto your report and double-click it to edit the chart. Run the report to display the chart. You can use the results of this query to create a simple chart for the Account table.
- Finally, run the report to see the chart.