Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Migrating data from HubDB to Databricks using CData SSIS Components.
Easily push HubDB data to Databricks using the CData SSIS Tasks for HubDB and Databricks.
Databricks is a unified data analytics platform that allows organizations to easily process, analyze, and visualize large amounts of data. It combines data engineering, data science, and machine learning capabilities in a single platform, making it easier for teams to collaborate and derive insights from their data.
The CData SSIS Components enhance SQL Server Integration Services by enabling users to easily import and export data from various sources and destinations.
In this article, we explore the data type mapping considerations when exporting to Databricks and walk through how to migrate HubDB data to Databricks using the CData SSIS Components for HubDB and Databricks.
Data Type Mapping
| Databricks Schema | CData Schema |
|---|---|
|
int, integer, int32 |
int |
|
smallint, short, int16 |
smallint |
|
double, float, real |
float |
|
date |
date |
|
datetime, timestamp |
datetime |
|
time, timespan |
time |
|
string, varchar |
If length > 4000: nvarchar(max), Otherwise: nvarchar(length) |
|
long, int64, bigint |
bigint |
|
boolean, bool |
tinyint |
|
decimal, numeric |
decimal |
|
uuid |
nvarchar(length) |
|
binary, varbinary, longvarbinary |
binary(1000) or varbinary(max) after SQL Server 2000 |
Special Considerations
- String/VARCHAR: String columns from Databricks can map to different data types depending on the length of the column. If the column length exceeds 4000, then the column is mapped to nvarchar (max). Otherwise, the column is mapped to nvarchar (length).
- DECIMAL Databricks supports DECIMAL types up to 38 digits of precision, but any source column beyond that can cause load errors.
Prerequisites
- Visual Studio 2022
- SQL Server Integration Services Projects extension for Visual Studio 2022
- CData SSIS Components for Databricks
- CData SSIS Components for HubDB
Create the project and add components
-
Open Visual Studio and create a new Integration Services Project.
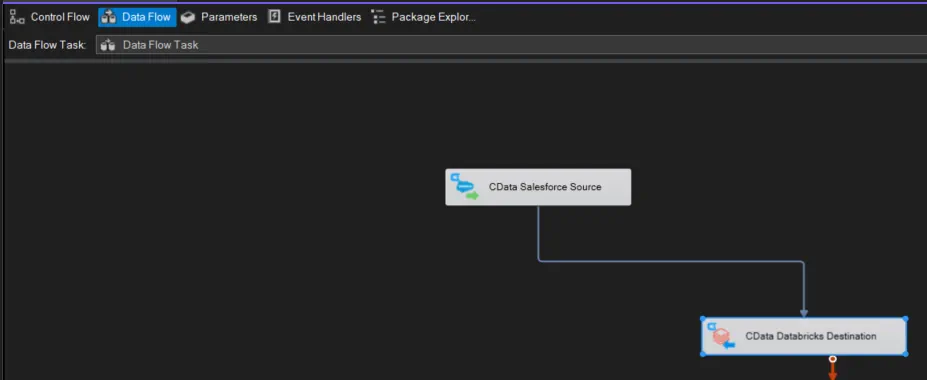
- Add a new Data Flow Task to the Control Flow screen and open the Data Flow Task.
-
Add a CData HubDB Source control and a CData Databricks Destination control to the data flow task.
Configure the HubDB source
Follow the steps below to specify properties required to connect to HubDB.
-
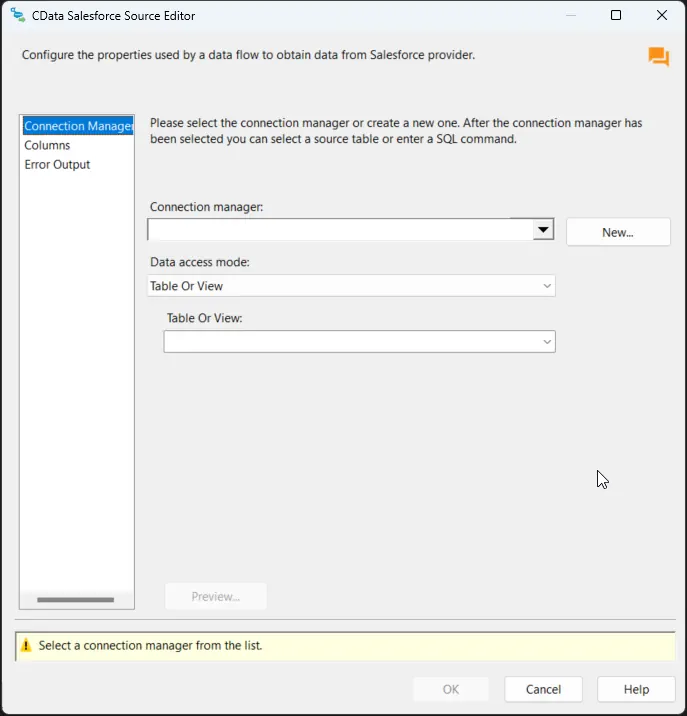
Double-click the CData HubDB Source to open the source component editor and add a new connection.
-
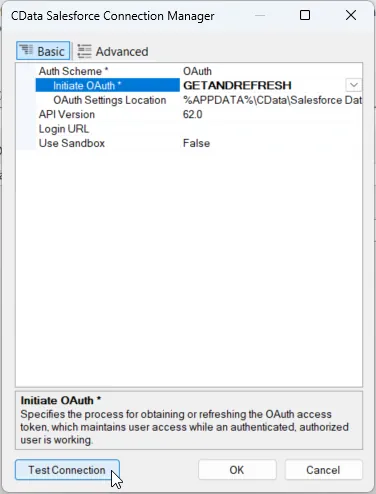
In the CData HubDB Connection Manager, configure the connection properties, then test and save the connection.
There are two authentication methods available for connecting to HubDB data source: OAuth Authentication with a public HubSpot application and authentication with a Private application token.
Using a Custom OAuth App
AuthScheme must be set to "OAuth" in all OAuth flows. Be sure to review the Help documentation for the required connection properties for you specific authentication needs (desktop applications, web applications, and headless machines).
Follow the steps below to register an application and obtain the OAuth client credentials:
- Log into your HubSpot app developer account.
- Note that it must be an app developer account. Standard HubSpot accounts cannot create public apps.
- On the developer account home page, click the Apps tab.
- Click Create app.
- On the App info tab, enter and optionally modify values that are displayed to users when they connect. These values include the public application name, application logo, and a description of the application.
- On the Auth tab, supply a callback URL in the "Redirect URLs" box.
- If you're creating a desktop application, set this to a locally accessible URL like http://localhost:33333.
- If you are creating a Web application, set this to a trusted URL where you want users to be redirected to when they authorize your application.
- Click Create App. HubSpot then generates the application, along with its associated credentials.
- On the Auth tab, note the Client ID and Client secret. You will use these later to configure the driver.
Under Scopes, select any scopes you need for your application's intended functionality.
A minimum of the following scopes is required to access tables:
- hubdb
- oauth
- crm.objects.owners.read
- Click Save changes.
- Install the application into a production portal with access to the features that are required by the integration.
- Under "Install URL (OAuth)", click Copy full URL to copy the installation URL for your application.
- Navigate to the copied link in your browser. Select a standard account in which to install the application.
- Click Connect app. You can close the resulting tab.
Using a Private App
To connect using a HubSpot private application token, set the AuthScheme property to "PrivateApp."
You can generate a private application token by following the steps below:
- In your HubDB account, click the settings icon (the gear) in the main navigation bar.
- In the left sidebar menu, navigate to Integrations > Private Apps.
- Click Create private app.
- On the Basic Info tab, configure the details of your application (name, logo, and description).
- On the Scopes tab, select Read or Write for each scope you want your private application to be able to access.
- A minimum of hubdb and crm.objects.owners.read is required to access tables.
- After you are done configuring your application, click Create app in the top right.
- Review the info about your application's access token, click Continue creating, and then Show token.
- Click Copy to copy the private application token.
To connect, set PrivateAppToken to the private application token you retrieved.
- Log into your HubSpot app developer account.
-
After saving the connection, select "Table or view" and select the table or view to export into Databricks, then close the CData HubDB Source Editor.
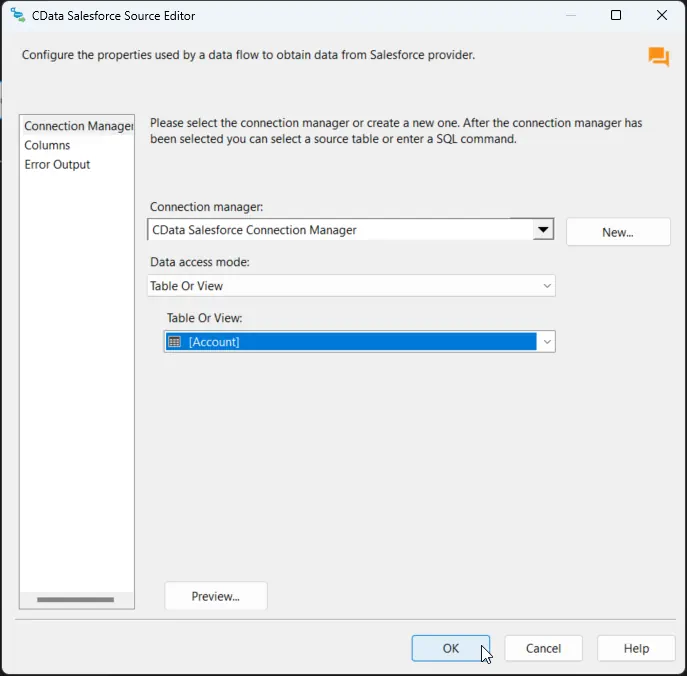
Configure the Databricks destination
With the HubDB Source configured, we can configure the Databricks connection and map the columns.
-
Double-click the CData Databricks Destination to open the destination component editor and add a new connection.
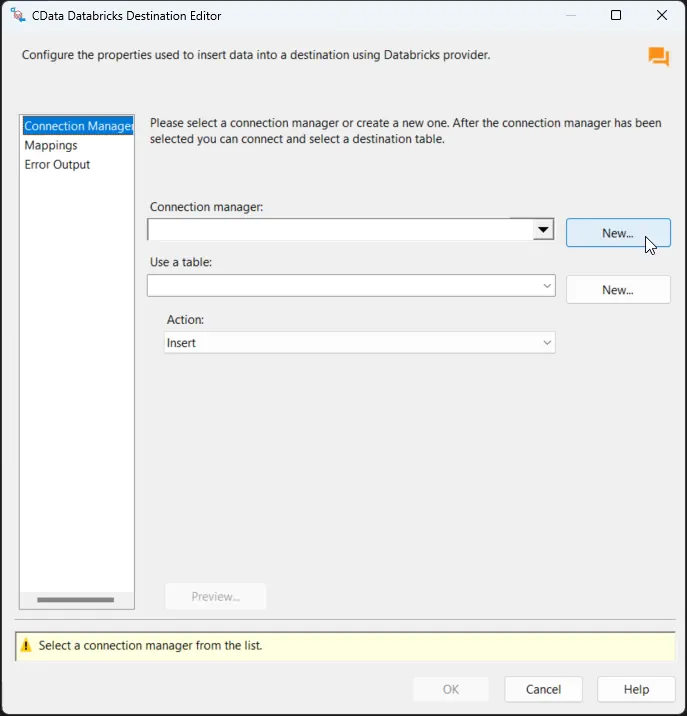
-
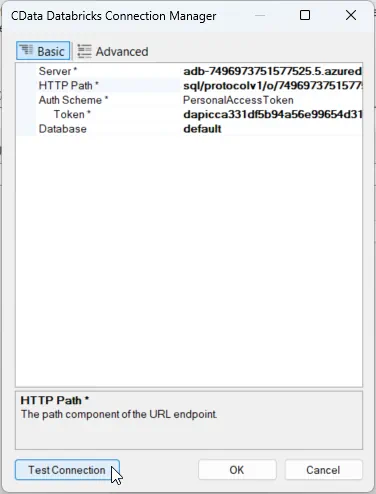
In the CData Databricks Connection Manager, configure the connection properties, then test and save the connection. To connect to a Databricks cluster, set the properties as described below.
Note: The needed values can be found in your Databricks instance by navigating to Clusters, selecting the desired cluster, and selecting the JDBC/ODBC tab under Advanced Options.
- Server: Set to the Server Hostname of your Databricks cluster.
- HTTPPath: Set to the HTTP Path of your Databricks cluster.
- Token: Set to your personal access token (this value can be obtained by navigating to the User Settings page of your Databricks instance and selecting the Access Tokens tab).
Other helpful connection properties
- QueryPassthrough: When this is set to True, queries are passed through directly to Databricks.
- ConvertDateTimetoGMT: When this is set to True, the components will convert date-time values to GMT, instead of the local time of the machine.
- UseUploadApi: Setting this property to true will improve performance if there is a large amount of data in a Bulk INSERT operation.
- UseCloudFetch: This option specifies whether to use CloudFetch to improve query efficiency when the table contains over one million entries.
-
After saving the connection, select a table in the Use a Table menu and in the Action menu, select Insert.
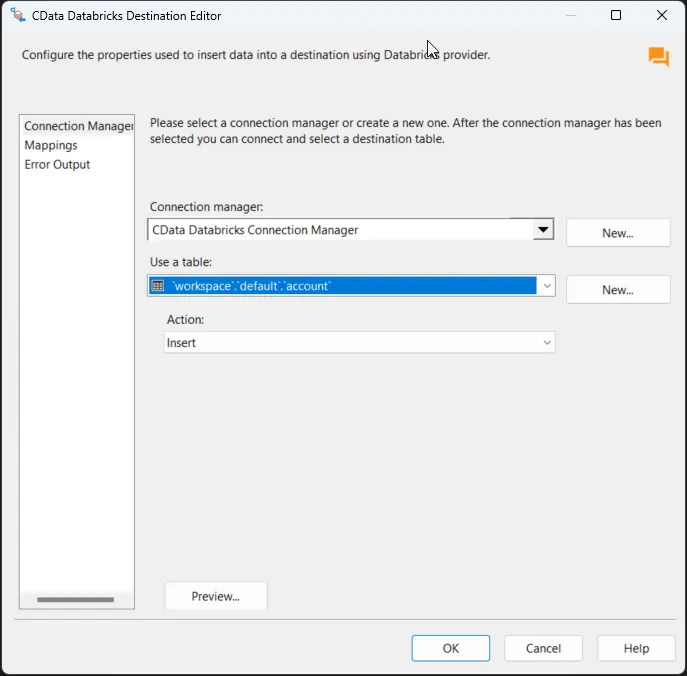
-
On the Column Mappings tab, configure the mappings from the input columns to the destination columns.
Run the project
You can now run the project. After the SSIS Task has finished executing, data from your SQL table will be exported to the chosen table.


