Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Integrate Real-Time Access to MongoDB in SAPUI5 MVC Apps
Use the built-in ODataModel class in SAPUI5 to create Web apps that reflect changes to MongoDB data in real time.
In this article we show how to use the CData API Server to write SAPUI5 apps that leverage the capabilities of the MongoDB API, without writing to a back-end database. The API Server is a lightweight Web application that runs on your server and produces OData feeds of MongoDB data. OData is the standard for real-time data access over the Web and has built-in support in SAPUI5 and OpenUI5.
About MongoDB Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from MongoDB has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access data from MongoDB 2.6 and above, ensuring broad usability across various MongoDB versions.
- Easily manage unstructured data thanks to flexible NoSQL (learn more here: Leading-Edge Drivers for NoSQL Integration).
- Leverage feature advantages over other NoSQL drivers and realize functional benefits when working with MongoDB data (learn more here: A Feature Comparison of Drivers for NoSQL).
MongoDB's flexibility means that it can be used as a transactional, operational, or analytical database. That means CData customers use our solutions to integrate their business data with MongoDB or integrate their MongoDB data with their data warehouse (or both). Customers also leverage our live connectivity options to analyze and report on MongoDB directly from their preferred tools, like Power BI and Tableau.
For more details on MongoDB use case and how CData enhances your MongoDB experience, check out our blog post: The Top 10 Real-World MongoDB Use Cases You Should Know in 2024.
Getting Started
Set Up the API Server
If you have not already done so, download the CData API Server. Once you have installed the API Server, follow the steps below to begin producing secure MongoDB OData services:
Connect to MongoDB
To work with MongoDB data from SAPUI5, we start by creating and configuring a MongoDB connection. Follow the steps below to configure the API Server to connect to MongoDB data:
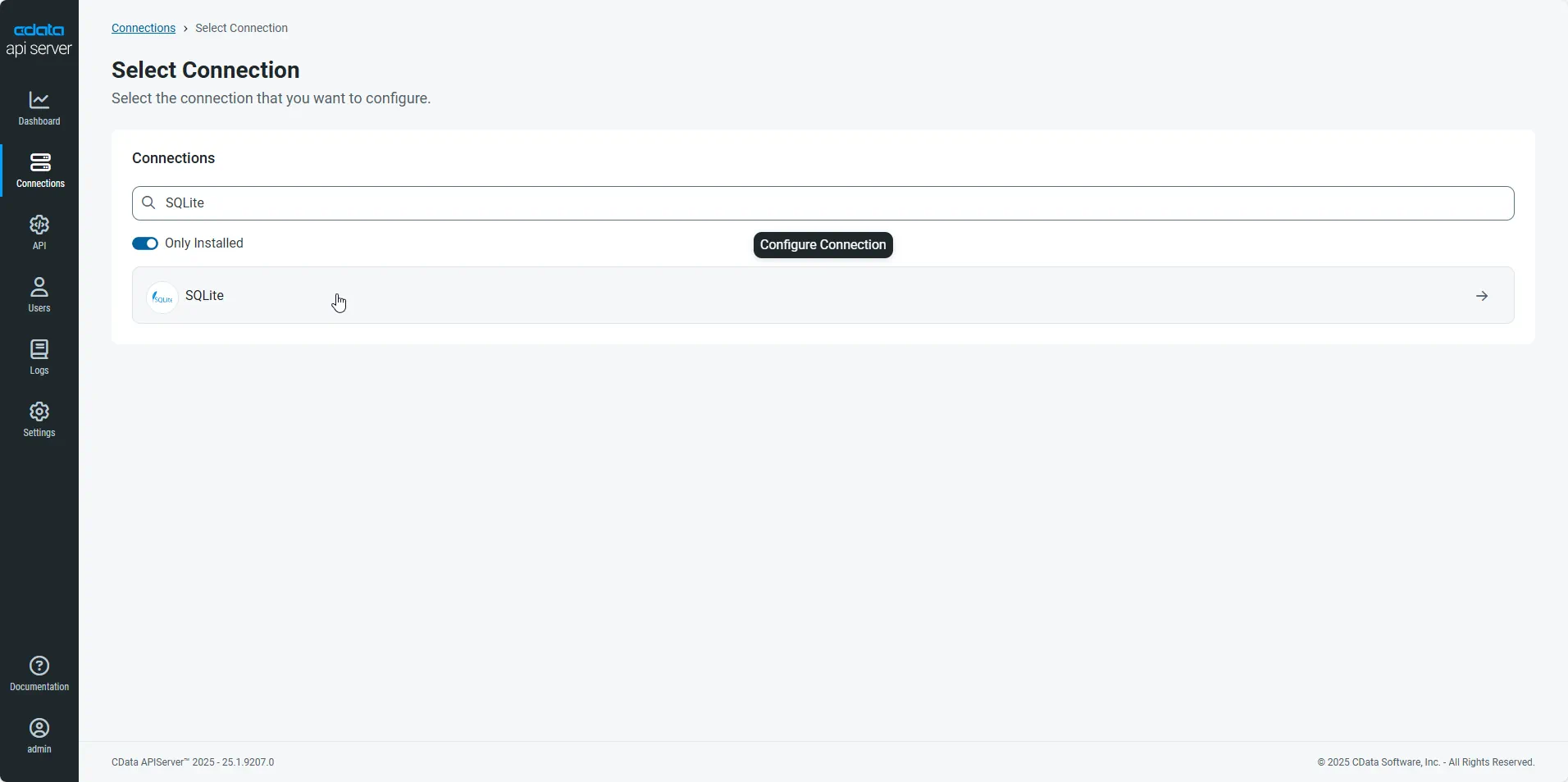
- First, navigate to the Connections page.
-
Click Add Connection and then search for and select the MongoDB connection.
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to MongoDB.
Set the Server, Database, User, and Password connection properties to connect to MongoDB. To access MongoDB collections as tables you can use automatic schema discovery or write your own schema definitions. Schemas are defined in .rsd files, which have a simple format. You can also execute free-form queries that are not tied to the schema.
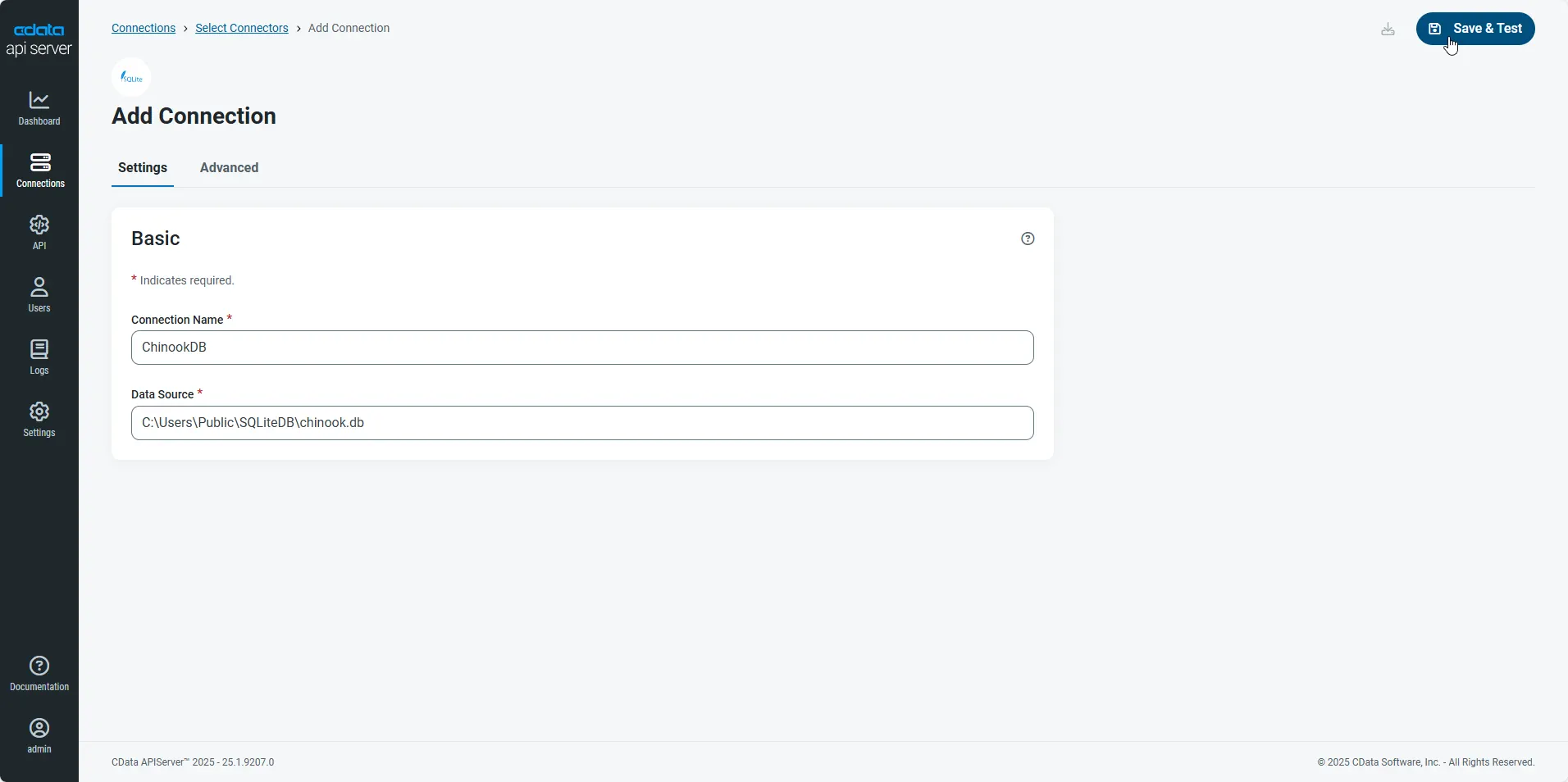
- After configuring the connection, click Save & Test to confirm a successful connection.
Configure API Server Users
Next, create a user to access your MongoDB data through the API Server. You can add and configure users on the Users page. Follow the steps below to configure and create a user:
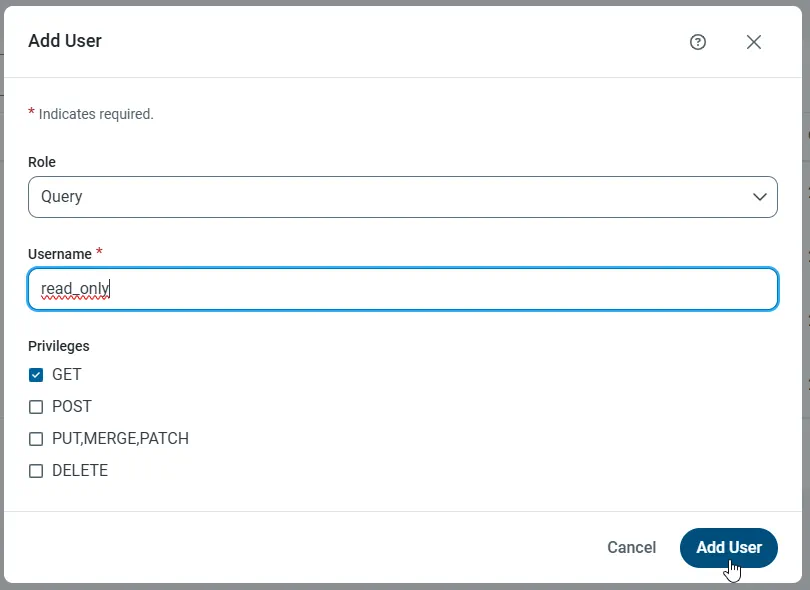
- On the Users page, click Add User to open the Add User dialog.
-
Next, set the Role, Username, and Privileges properties and then click Add User.
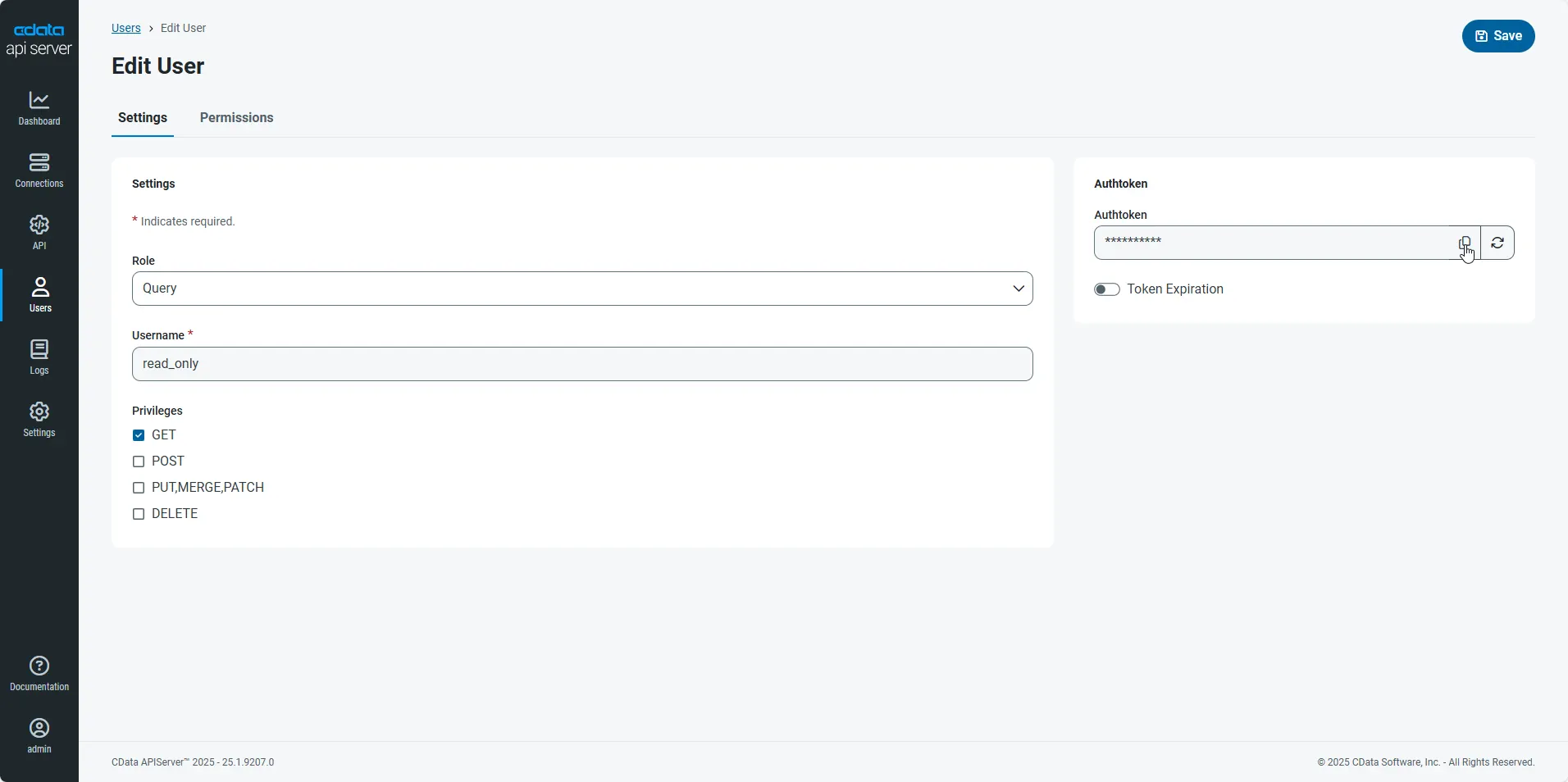
-
An Authtoken is then generated for the user. You can find the Authtoken and other information for each user on the Users page:
Creating API Endpoints for MongoDB
Having created a user, you are ready to create API endpoints for the MongoDB tables:
-
First, navigate to the API page and then click
Add Table
.
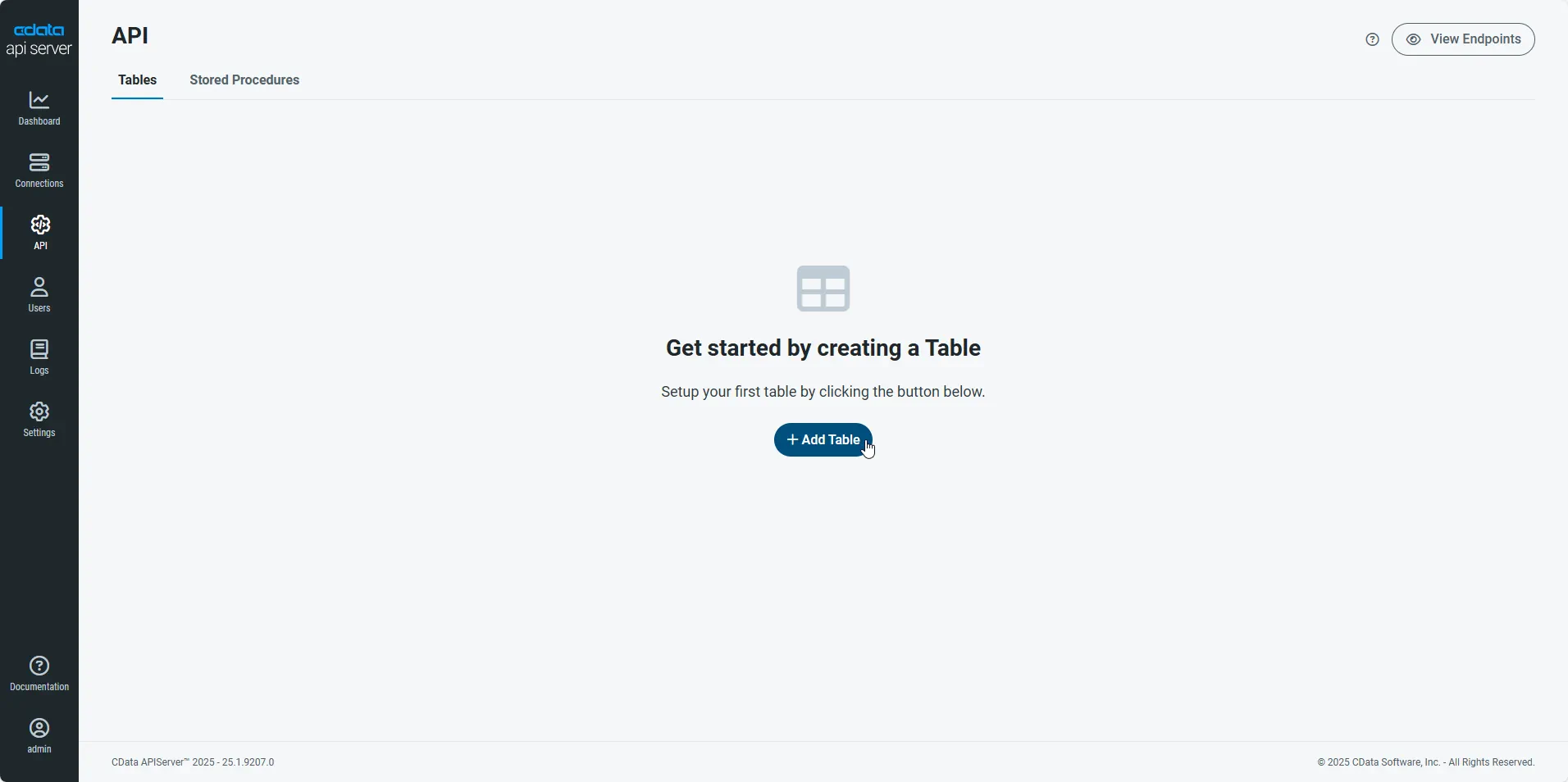
-
Select the connection you wish to access and click Next.
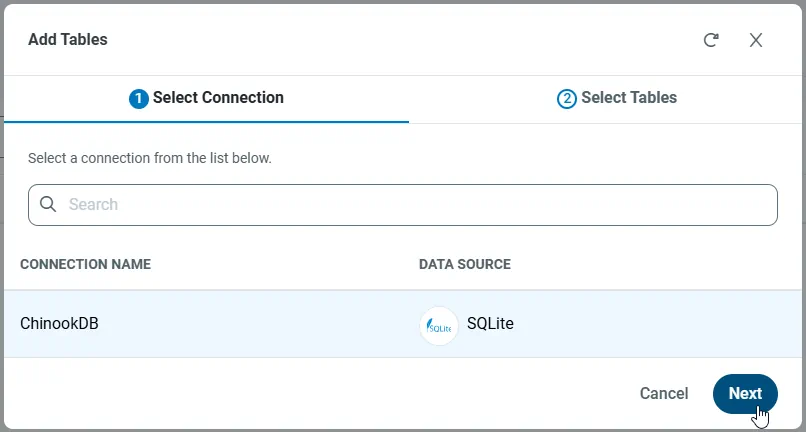
-
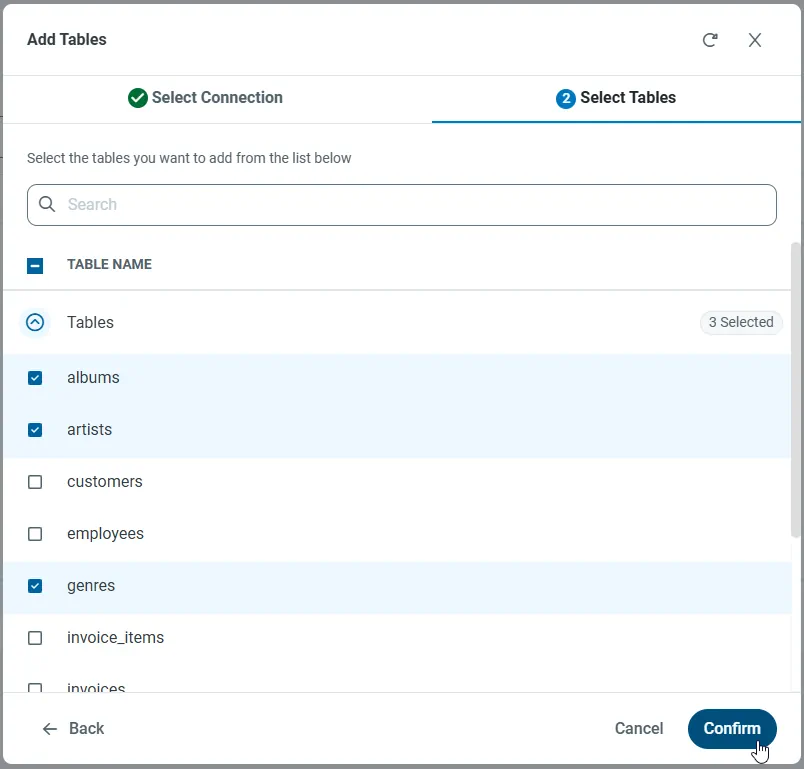
With the connection selected, create endpoints by selecting each table and then clicking Confirm.
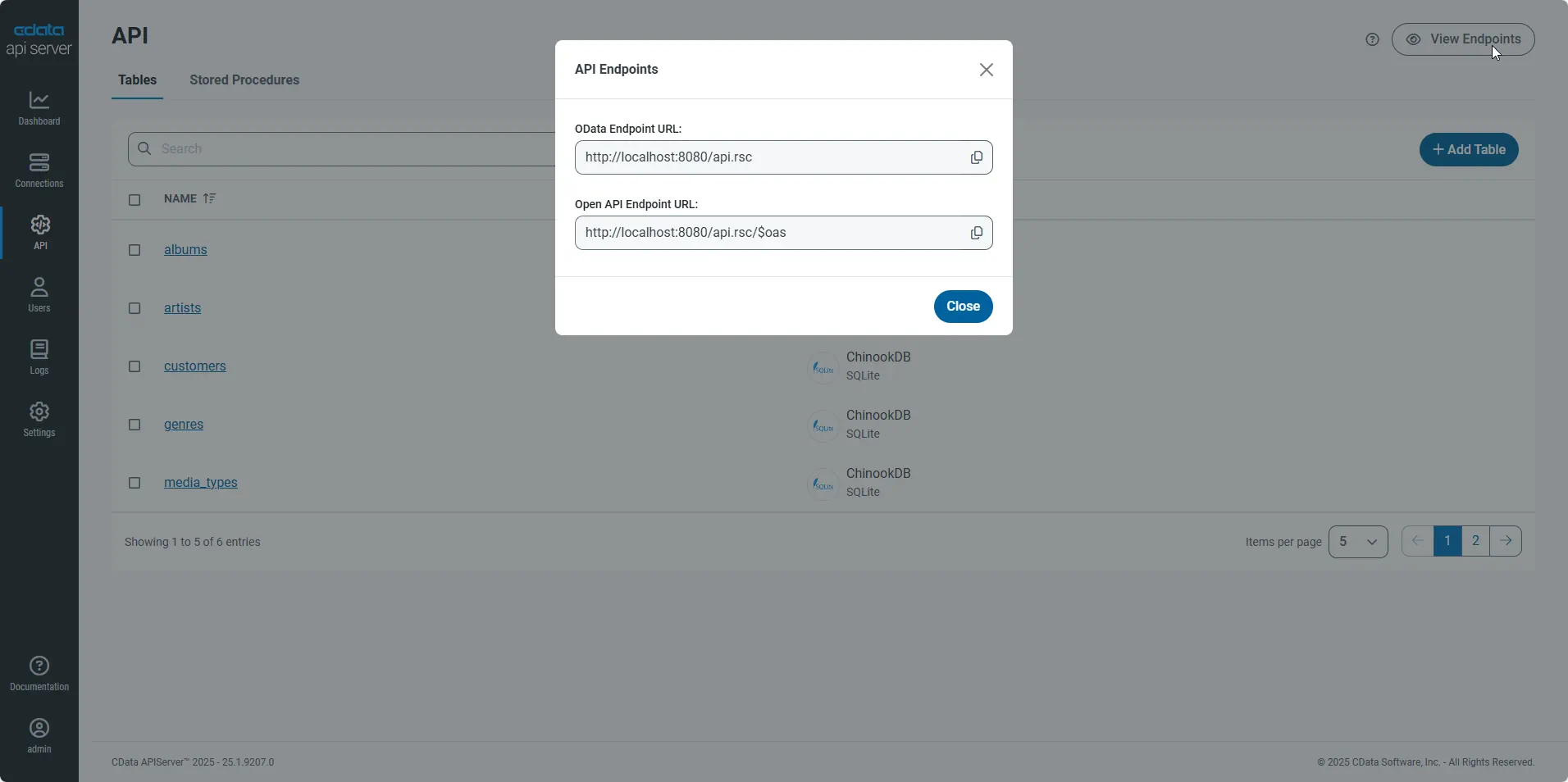
Gather the OData Url
Having configured a connection to MongoDB data, created a user, and added resources to the API Server, you now have an easily accessible REST API based on the OData protocol for those resources. From the API page in API Server, you can view and copy the API Endpoints for the API:
Create the View
In this article the user views and interacts with MongoDB data through an SAPUI5 table control. Table columns will be automatically detected from the metadata retrieved from the API Server's API endpoint. We define the following table in a separate View.view.xml file:
<mvc:View
controllerName="sap.ui.table.sample.OData2.Controller"
xmlns="sap.ui.table"
xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc"
xmlns:u="sap.ui.unified"
xmlns:c="sap.ui.core"
xmlns:m="sap.m">
<m:Page
showHeader="false"
enableScrolling="false"
class="sapUiContentPadding">
<m:content>
<Table
id="table"
selectionMode="MultiToggle"
visibleRowCount="10"
enableSelectAll="false"
rows="{/restaurants}"
threshold="15"
enableBusyIndicator="true"
columns="{
path: 'meta>/dataServices/schema/[${namespace}===\'CData\']/entityType/[${name}===\'restaurants\']/property',
factory: '.columnFactory'
}">
<toolbar>
<m:Toolbar>
<m:Title text="MongoDB restaurants"></m:Title>
</m:Toolbar>
</toolbar>
<noData>
<m:BusyIndicator class="sapUiMediumMargin"/>
</noData>
</Table>
</m:content>
</m:Page>
</mvc:View>
Create the Model and Controller
In SAPUI5, you do not need to write any OData queries; an ODataModel instance handles the application's data access commands. The API Server then translates the queries into MongoDB API calls.
The controller processes user input and represents information to the user through a view. Define the controller in a new file, Controller.controller.js. Instantiate the model in the onInit function -- you will need to replace the placeholder values for the URL to the API Server, a user allowed to access the OData endpoint of the API Server, and the authtoken for the user.
sap.ui.define([
"sap/ui/core/mvc/Controller",
"sap/ui/model/odata/v2/ODataModel",
"sap/ui/model/json/JSONModel",
"sap/ui/table/Column",
"sap/m/Text",
], function(Controller, ODataModel, JSONModel, Column, Text ) {
"use strict";
return Controller.extend("sap.ui.table.sample.OData2.Controller", {
onInit : function () {
var oView = this.getView();
var oDataModel = new ODataModel("http://myserver/api.rsc/",{user: "MyUser", password: "MyAuthToken"});
oDataModel.getMetaModel().loaded().then(function(){
oView.setModel(oDataModel.getMetaModel(), "meta");
});
oView.setModel(oDataModel);
var oTable = oView.byId("table");
var oBinding = oTable.getBinding("rows");
var oBusyIndicator = oTable.getNoData();
oBinding.attachDataRequested(function(){
oTable.setNoData(oBusyIndicator);
});
oBinding.attachDataReceived(function(){
oTable.setNoData(null); //use default again ("no data" in case no data is available)
});
},
onExit : function () {
},
columnFactory : function(sId, oContext) {
var oModel = this.getView().getModel();
var sName = oContext.getProperty("name");
var sType = oContext.getProperty("type");
var iLen = oContext.getProperty("maxLength");
iLen = iLen ? parseInt(iLen, 10) : 10;
return new Column(sId, {
sortProperty: sName,
filterProperty: sName,
width: (iLen > 9 ? (iLen > 50 ? 15 : 10) : 5) + "rem",
label: new sap.m.Label({text: "{/#restaurants/" + sName + "/@name}"}),
hAlign: sType && sType.indexOf("Decimal") >= 0 ? "End" : "Begin",
template: new Text({text: {path: sName}})
});
}
});
});
Describe Application Logic
Create a component that contains the resources of your application. Define the following in Component.js:
sap.ui.define([
'sap/ui/core/UIComponent'
], function(UIComponent) {
"use strict";
return UIComponent.extend("sap.ui.table.sample.OData2.Component", {
metadata : {
rootView : "sap.ui.table.sample.OData2.View",
dependencies : {
libs : [
"sap.ui.table",
"sap.ui.unified",
"sap.m"
]
},
config : {
sample : {
stretch : true,
files : [
"View.view.xml",
"Controller.controller.js"
]
}
}
}
});
});
Bootstrap OpenUI5 and Launch
To complete the MVC application, simply add the bootstrap and initialization code. Add these directly to index.html:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="ie=edge">
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>MongoDB restaurants</title>
<script id="sap-ui-bootstrap"
src="https://openui5.hana.ondemand.com/resources/sap-ui-core.js"
data-sap-ui-libs="sap.m"
data-sap-ui-theme="sap_bluecrystal"
data-sap-ui-xx-bindingSyntax="complex"
data-sap-ui-preload="async"
data-sap-ui-compatVersion="edge"
data-sap-ui-resourceroots='{"sap.ui.table.sample.OData2": "./", "sap.ui.demo.mock": "mockdata"}'>
</script>
<!-- application launch configuration -->
<script>
sap.ui.getCore().attachInit(function() {
new sap.m.App ({
pages: [
new sap.m.Page({
title: "MongoDB restaurants",
enableScrolling : false,
content: [ new sap.ui.core.ComponentContainer({
height : "100%", name : "sap.ui.table.sample.OData2"
})]
})
]
}).placeAt("content");
});
</script>
</head>
<!-- UI Content -->
<body class="sapUiBody" id="content" role="application">
</body>
</html>
The resulting SAPUI5 table control reflects any changes to a table in the remote MongoDB data. You can now browse and search current MongoDB data.



