Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →Stream PingOne Data into Apache Kafka Topics
Access and stream PingOne data in Apache Kafka using the CData JDBC Driver and the Kafka Connect JDBC connector.
Apache Kafka is an open-source stream processing platform that is primarily used for building real-time data pipelines and event-driven applications. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for PingOne, Kafka can work with live PingOne data. This article describes how to connect, access and stream PingOne data into Apache Kafka Topics and to start Confluent Control Center to help users secure, manage, and monitor the PingOne data received using Kafka infrastructure in the Confluent Platform.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live PingOne data. When you issue complex SQL queries to PingOne, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to PingOne and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze PingOne data using native data types.
Prerequisites
Before connecting the CData JDBC Driver for streaming PingOne data in Apache Kafka Topics, install and configure the following in the client Linux-based system.
- Confluent Platform for Apache Kafka
- Confluent Hub CLI Installation
- Self-Managed Kafka JDBC Source Connector for Confluent Platform
Define a New JDBC Connection to PingOne data
- Download CData JDBC Driver for PingOne on a Linux-based system
- Follow the given instructions to create a new directory extract all the driver contents into it:
- Create a new directory named PingOne
mkdir PingOne
- Move the downloaded driver file (.zip) into this new directory
mv PingOneJDBCDriver.zip PingOne/
- Unzip the CData PingOneJDBCDriver contents into this new directory
unzip PingOneJDBCDriver.zip
- Create a new directory named PingOne
- Open the PingOne directory and navigate to the lib folder
ls cd lib/
- Copy the contents of the lib folder of the CData JDBC Driver for PingOne into the lib folder of Kafka Connect JDBC. Check the Kafka Connect JDBC folder contents to confirm that the cdata.jdbc.pingone.jar file is successfully copied into the lib folder
cp -r /path/to/CData JDBC Driver for PingOne/lib/* /usr/share/confluent-hub-components/confluentinc-kafka-connect-jdbc/lib/ cd /usr/share/confluent-hub-components/confluentinc-kafka-connect-jdbc/lib/
- Install the CData PingOne JDBC driver license using the given command, followed by your Name and Email ID
java -jar cdata.jdbc.pingone.jar -l
- Enter the product key or "TRIAL" (In the scenarios of license expiry, please contact our CData Support team)
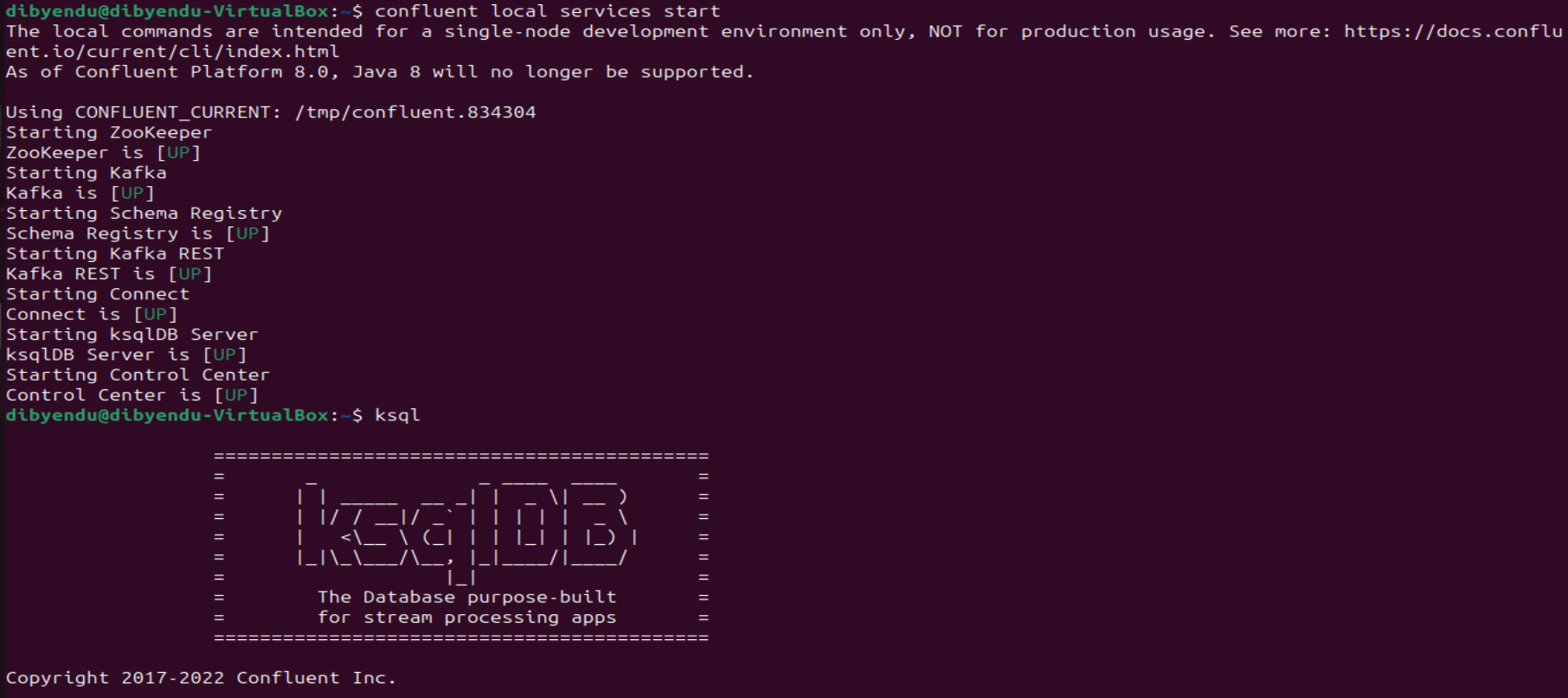
- Start the Confluent local services using the command:
confluent local services start
This starts all the Confluent Services like Zookeeper, Kafka, Schema Registry, Kafka REST, Kafka CONNECT, ksqlDB and Control Center. You are now ready to use the CData JDBC driver for PingOne to stream messages using Kafka Connect Driver into Kafka Topics on ksqlDB.
- Create the Kafka topics manually using a POST HTTP API Request:
curl --location 'server_address:8083/connectors' --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data '{ "name": "jdbc_source_cdata_pingone_01", "config": { "connector.class": "io.confluent.connect.jdbc.JdbcSourceConnector", "connection.url": "jdbc:pingone:AuthScheme=OAuth;WorkerAppEnvironmentId=eebc33a8-xxxx-4f3a-yyyy-d3e5262fd49e;Region=NA;OAuthClientId=client_id;OAuthClientSecret=client_secret;; InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH", "topic.prefix": "pingone-01-", "mode": "bulk" } }'Let us understand the fields used in the HTTP POST body (shown above):
- connector.class: Specifies the Java class of the Kafka Connect connector to be used.
- connection.url: The JDBC connection URL to connect with PingOne data.
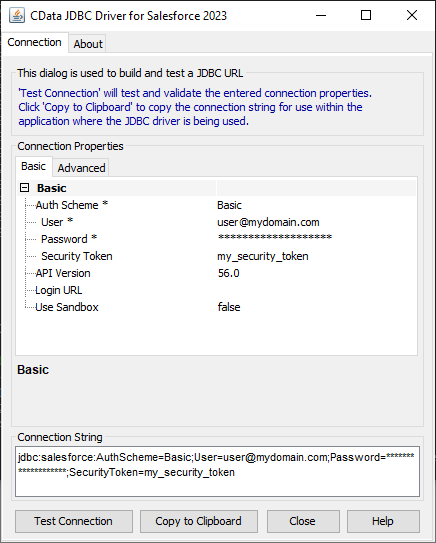
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the CData JDBC Driver for PingOne. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.pingone.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
To connect to PingOne, configure these properties:
- Region: The region where the data for your PingOne organization is being hosted.
- AuthScheme: The type of authentication to use when connecting to PingOne.
- Either WorkerAppEnvironmentId (required when using the default PingOne domain) or AuthorizationServerURL, configured as described below.
Configuring WorkerAppEnvironmentId
WorkerAppEnvironmentId is the ID of the PingOne environment in which your Worker application resides. This parameter is used only when the environment is using the default PingOne domain (auth.pingone). It is configured after you have created the custom OAuth application you will use to authenticate to PingOne, as described in Creating a Custom OAuth Application in the Help documentation.
First, find the value for this property:
- From the home page of your PingOne organization, move to the navigation sidebar and click Environments.
- Find the environment in which you have created your custom OAuth/Worker application (usually Administrators), and click Manage Environment. The environment's home page displays.
- In the environment's home page navigation sidebar, click Applications.
- Find your OAuth or Worker application details in the list.
-
Copy the value in the Environment ID field.
It should look similar to:
WorkerAppEnvironmentId='11e96fc7-aa4d-4a60-8196-9acf91424eca'
Now set WorkerAppEnvironmentId to the value of the Environment ID field.
Configuring AuthorizationServerURL
AuthorizationServerURL is the base URL of the PingOne authorization server for the environment where your application is located. This property is only used when you have set up a custom domain for the environment, as described in the PingOne platform API documentation. See Custom Domains.
Authenticating to PingOne with OAuth
PingOne supports both OAuth and OAuthClient authentication. In addition to performing the configuration steps described above, there are two more steps to complete to support OAuth or OAuthCliet authentication:
- Create and configure a custom OAuth application, as described in Creating a Custom OAuth Application in the Help documentation.
- To ensure that the driver can access the entities in Data Model, confirm that you have configured the correct roles for the admin user/worker application you will be using, as described in Administrator Roles in the Help documentation.
- Set the appropriate properties for the authscheme and authflow of your choice, as described in the following subsections.
OAuth (Authorization Code grant)
Set AuthScheme to OAuth.
Desktop Applications
Get and Refresh the OAuth Access Token
After setting the following, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: GETANDREFRESH. To avoid the need to repeat the OAuth exchange and manually setting the OAuthAccessToken each time you connect, use InitiateOAuth.
- OAuthClientId: The Client ID you obtained when you created your custom OAuth application.
- OAuthClientSecret: The Client Secret you obtained when you created your custom OAuth application.
- CallbackURL: The redirect URI you defined when you registered your custom OAuth application. For example: https://localhost:3333
When you connect, the driver opens PingOne's OAuth endpoint in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions to the application. The driver then completes the OAuth process:
- The driver obtains an access token from PingOne and uses it to request data.
- The OAuth values are saved in the location specified in OAuthSettingsLocation, to be persisted across connections.
The driver refreshes the access token automatically when it expires.
For other OAuth methods, including Web Applications, Headless Machines, or Client Credentials Grant, refer to the Help documentation.
- topic.prefix: A prefix that will be added to the Kafka topics created by the connector. It's set to "pingone-01-".
- mode: Specifies the mode in which the connector operates. In this case, it's set to "bulk", which suggests that the connector is configured to perform bulk data transfer.
This request adds all the tables/contents from PingOne as Kafka Topics.
Note: The IP Address (server) to POST the request (shown above) is the Linux Network IP Address.
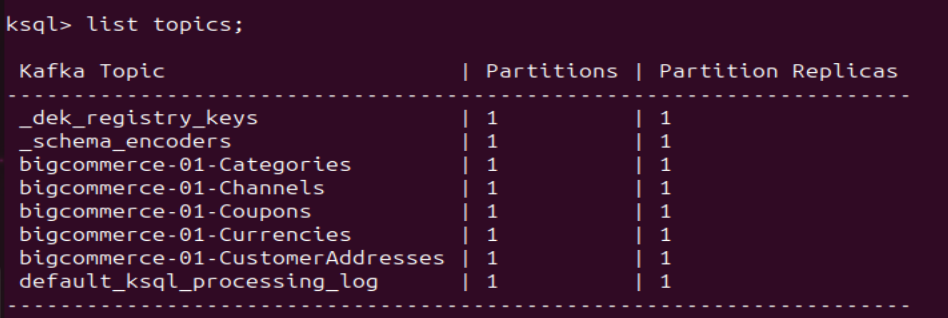
- Run ksqlDB and list the topics. Use the commands:
ksql list topics;
- To view the data inside the topics, type the SQL Statement:
PRINT topic FROM BEGINNING;
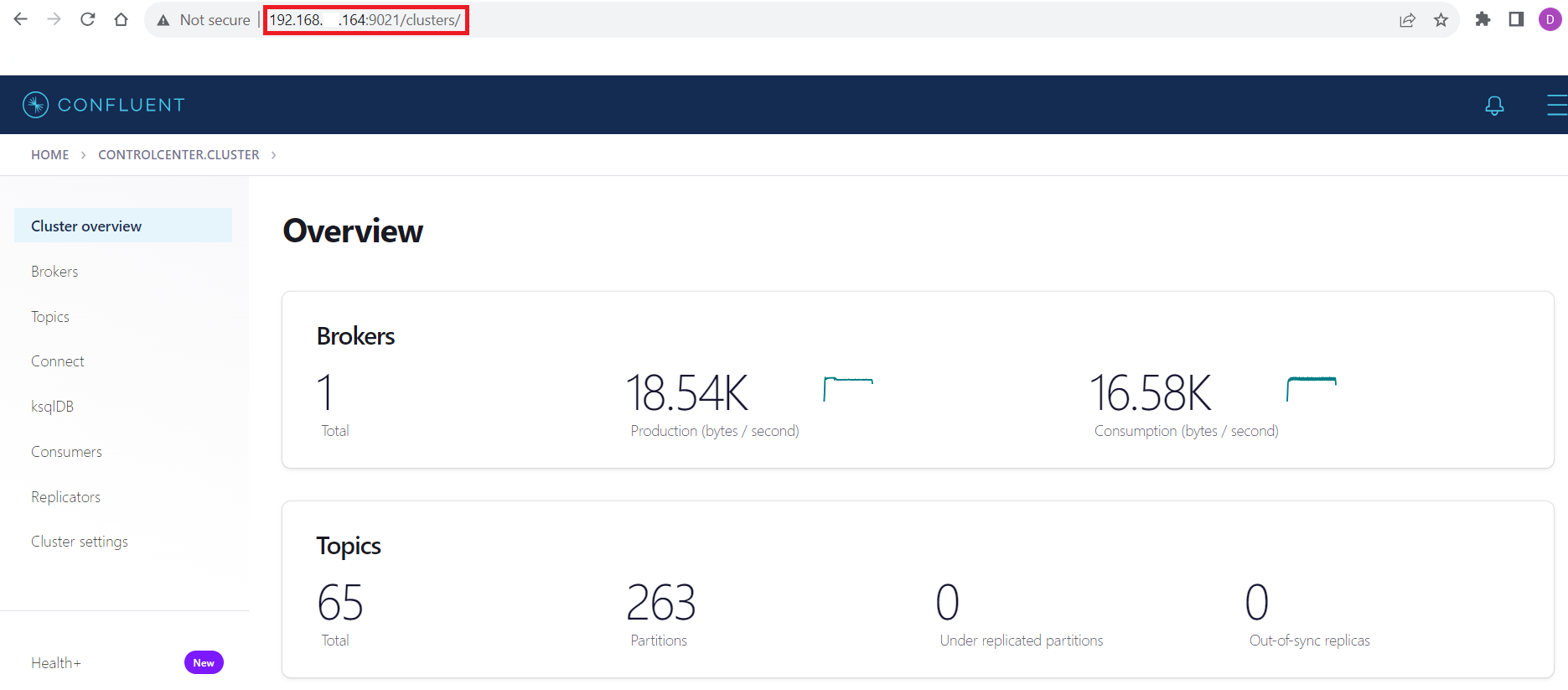
Connecting with the Confluent Control Center
To access the Confluent Control Center user interface, ensure to run the "confluent local services" as described in the above section and type http://<server address>:9021/clusters/ on your local browser.
Get Started Today
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for PingOne and start streaming PingOne data into Apache Kafka. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.


