Model Context Protocol (MCP) finally gives AI models a way to access the business data needed to make them really useful at work. CData MCP Servers have the depth and performance to make sure AI has access to all of the answers.
Try them now for free →How to connect and process SingleStore data from Azure Databricks
Use CData, Azure, and Databricks to perform data engineering and data science on live SingleStore data.
Databricks is a cloud-based service that provides data processing capabilities through Apache Spark. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver, customers can use Databricks to perform data engineering and data science on live SingleStore data. This article walks through hosting the CData JDBC Driver in Azure, as well as connecting to and processing live SingleStore data in Databricks.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live SingleStore data. When you issue complex SQL queries to SingleStore, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to SingleStore and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze SingleStore data using native data types.
Install the CData JDBC Driver in Azure
To work with live SingleStore data in Databricks, install the driver through Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS). (Please note that the method of connecting through DBFS, which previous versions of this article described, has been deprecated, but has not published an end-of-life.)
- Upload the JDBC JAR file to a blob container of your choice (i.e. "jdbcjars" container of the "databrickslibraries" storage account).
- Fetch the Account Key from the storage account by expanding "Security + networking" and clicking on "Access Keys". Show and copy whichever of the two keys you wish to use.
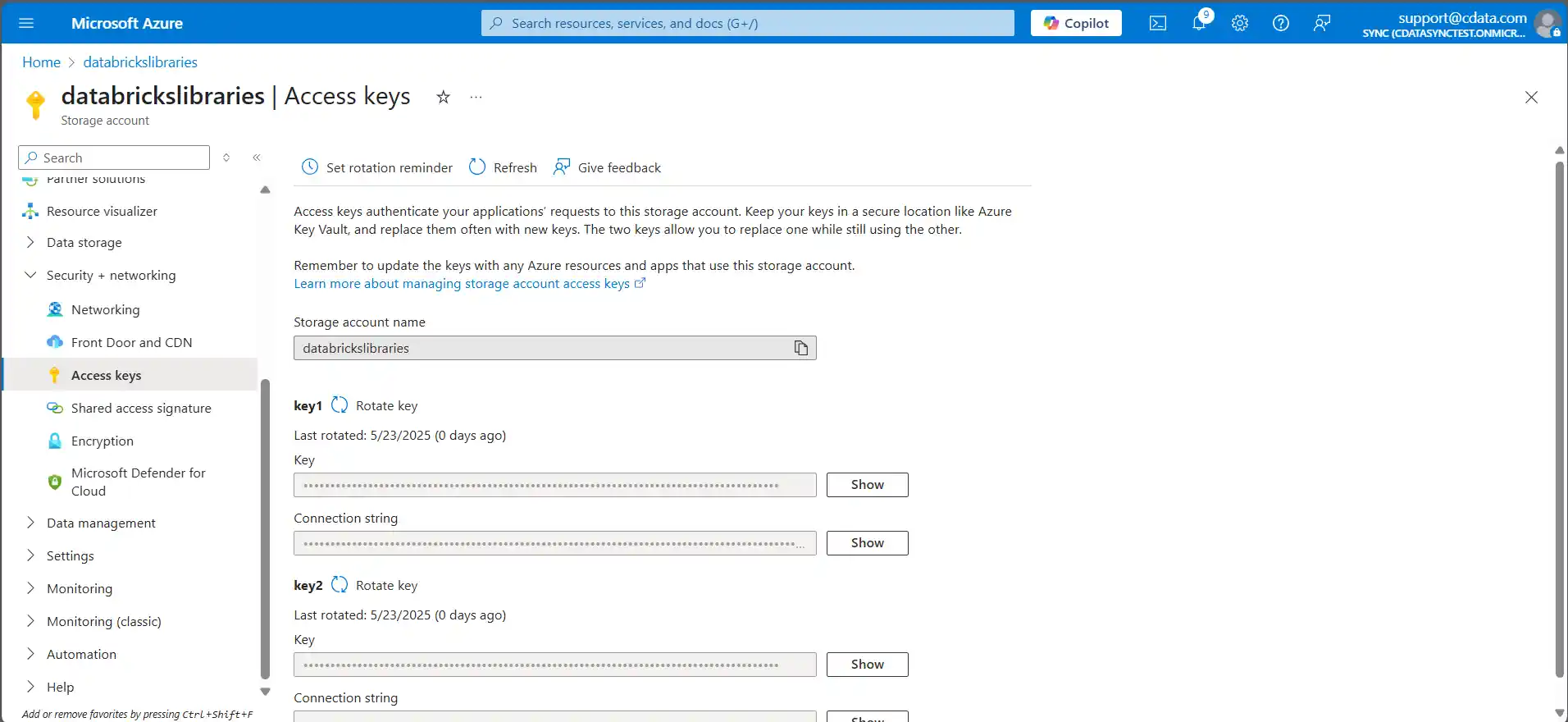
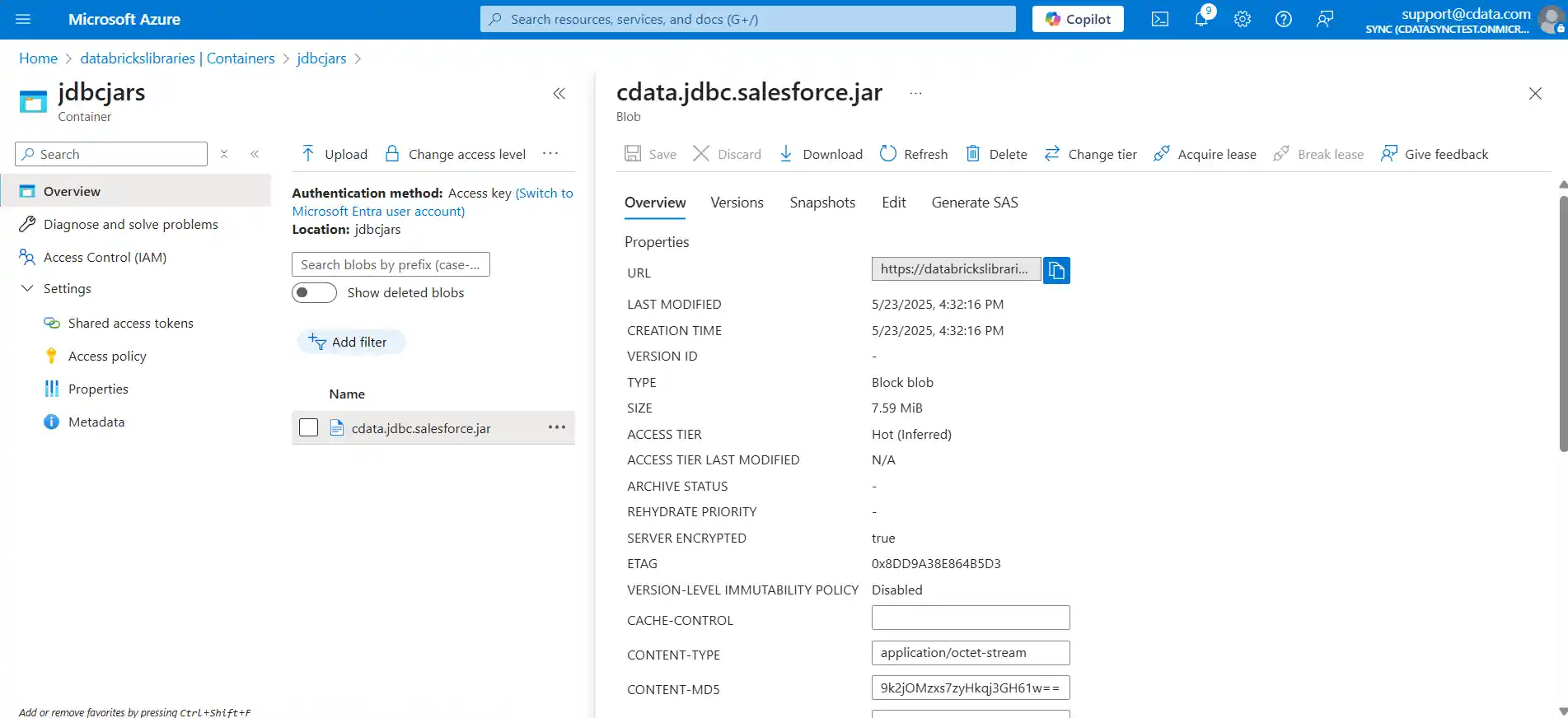
- Get the JDBC JAR file's URL by navigating to Containers, opening the specific container storing the JAR, and selecting the entry for the JDBC JAR file. This should open the file's details, where there should be a convenient button to copy the URL button to clipboard. This value will look similar to the below, though the "blob" component may vary depending on storage account type:
https://databrickslibraries.blob.core.windows.net/jdbcjars/cdata.jdbc.salesforce.jar
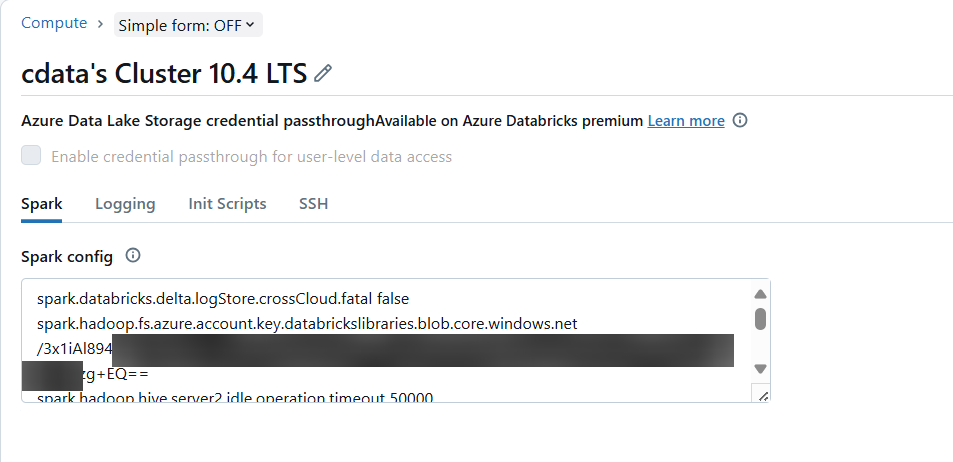
- In the Configuration tab of your Databricks cluster, click on the Edit button and expand "Advanced options". From there, add the following Spark option (derived from the JAR URL's domain name) with your copied Account key as its value and click Confirm:
spark.hadoop.fs.azure.account.key.databrickslibraries.blob.core.windows.net
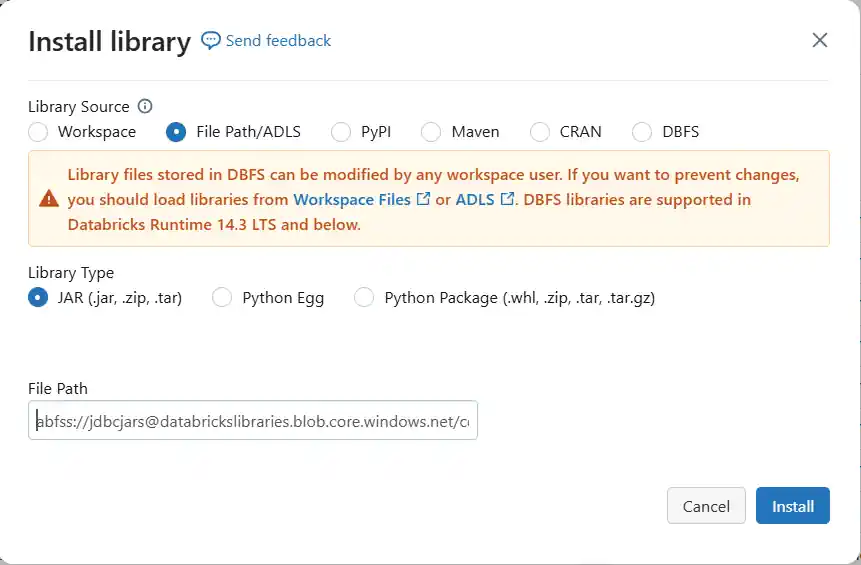
- In the Libraries tab of your Databricks cluster, click on "Install new", and select the ADLS option. Specify the ABFSS URL for the driver JAR (also derived from the JAR URL's domain name), and click Install. The ABFSS URL should resemble the below:
abfss://[email protected]/cdata.jdbc.salesforce.jar
Connect to SingleStore from Databricks
With the JAR file installed, we are ready to work with live SingleStore data in Databricks. Start by creating a new notebook in your workspace. Name the workbook, make sure Python is selected as the language (which should be by default), click on Connect and under General Compute select the cluster where you installed the JDBC driver (should be selected by default).
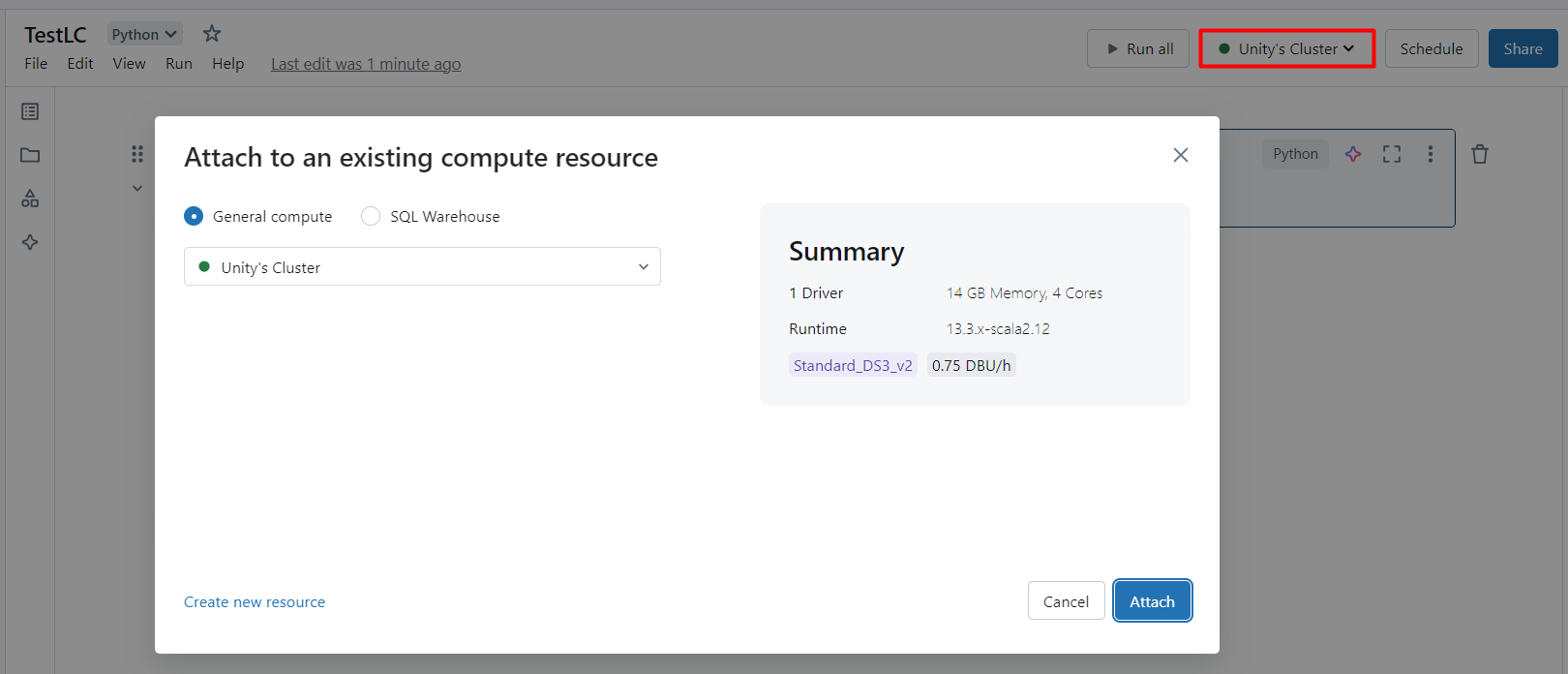
Configure the Connection to SingleStore
Connect to SingleStore by referencing the class for the JDBC Driver and constructing a connection string to use in the JDBC URL. Additionally, you will need to set the RTK property in the JDBC URL (unless you are using a Beta driver). You can view the licensing file included in the installation for information on how to set this property.
driver = "cdata.jdbc.singlestore.SingleStoreDriver" url = "jdbc:singlestore:RTK=5246...;User=myUser;Password=myPassword;Database=NorthWind;Server=myServer;Port=3306;"
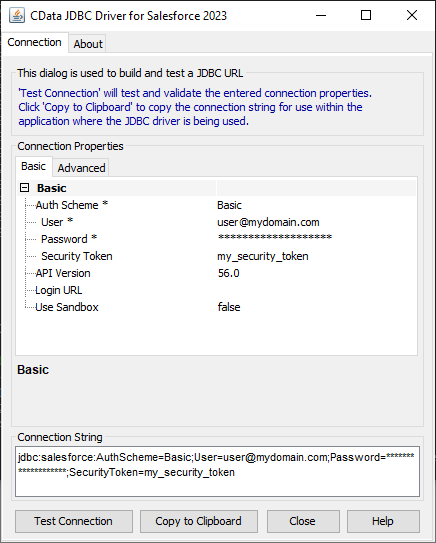
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the SingleStore JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the JAR file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.singlestore.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
The following connection properties are required in order to connect to data.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Database (Optional): The default database to connect to when connecting to the SingleStore Server. If this is not set, tables from all databases will be returned.
Connect Using Standard Authentication
To authenticate using standard authentication, set the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
Connect Using Integrated Security
As an alternative to providing the standard username and password, you can set IntegratedSecurity to True to authenticate trusted users to the server via Windows Authentication.
Connect Using SSL Authentication
You can leverage SSL authentication to connect to SingleStore data via a secure session. Configure the following connection properties to connect to data:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate. Used in the case of 2-way SSL, where truststore and keystore are kept on both the client and server machines.
- SSLClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSLClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSLClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSLServerCert: The certificate to be accepted from the server.
Connect Using SSH Authentication
Using SSH, you can securely login to a remote machine. To access SingleStore data via SSH, configure the following connection properties:
- SSHClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate.
- SSHClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSHClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSHClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSHPassword: The password that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
- SSHPort: The port used for SSH operations.
- SSHServer: The SSH authentication server you are trying to authenticate against.
- SSHServerFingerPrint: The SSH Server fingerprint used for verification of the host you are connecting to.
- SSHUser: Set this to the username that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
Load SingleStore Data
Once the connection is configured, you can load SingleStore data as a dataframe using the CData JDBC Driver and the connection information.
remote_table = spark.read.format ( "jdbc" ) \ .option ( "driver" , driver) \ .option ( "url" , url) \ .option ( "dbtable" , "Orders") \ .load ()
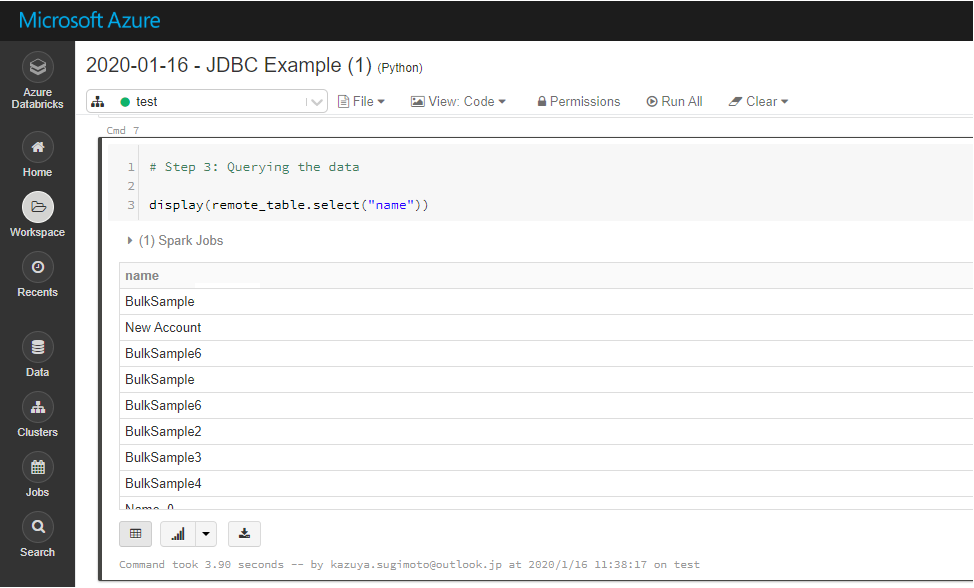
Display SingleStore Data
Check the loaded SingleStore data by calling the display function.
display (remote_table.select ("ShipName"))
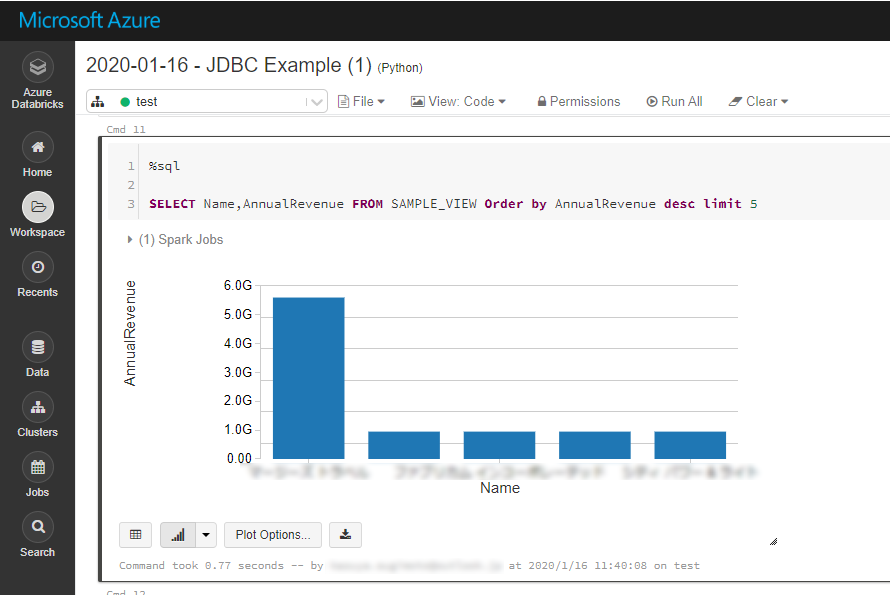
Analyze SingleStore Data in Azure Databricks
If you want to process data with Databricks SparkSQL, register the loaded data as a Temp View.
remote_table.createOrReplaceTempView ( "SAMPLE_VIEW" )
The SparkSQL below retrieves the SingleStore data for analysis.
result = spark.sql("SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM SAMPLE_VIEW WHERE ShipCountry = 'USA'")
The data from SingleStore is only available in the target notebook. If you want to use it with other users, save it as a table.
remote_table.write.format ( "parquet" ) .saveAsTable ( "SAMPLE_TABLE" )
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for SingleStore and start working with your live SingleStore data in Azure Databricks. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.


